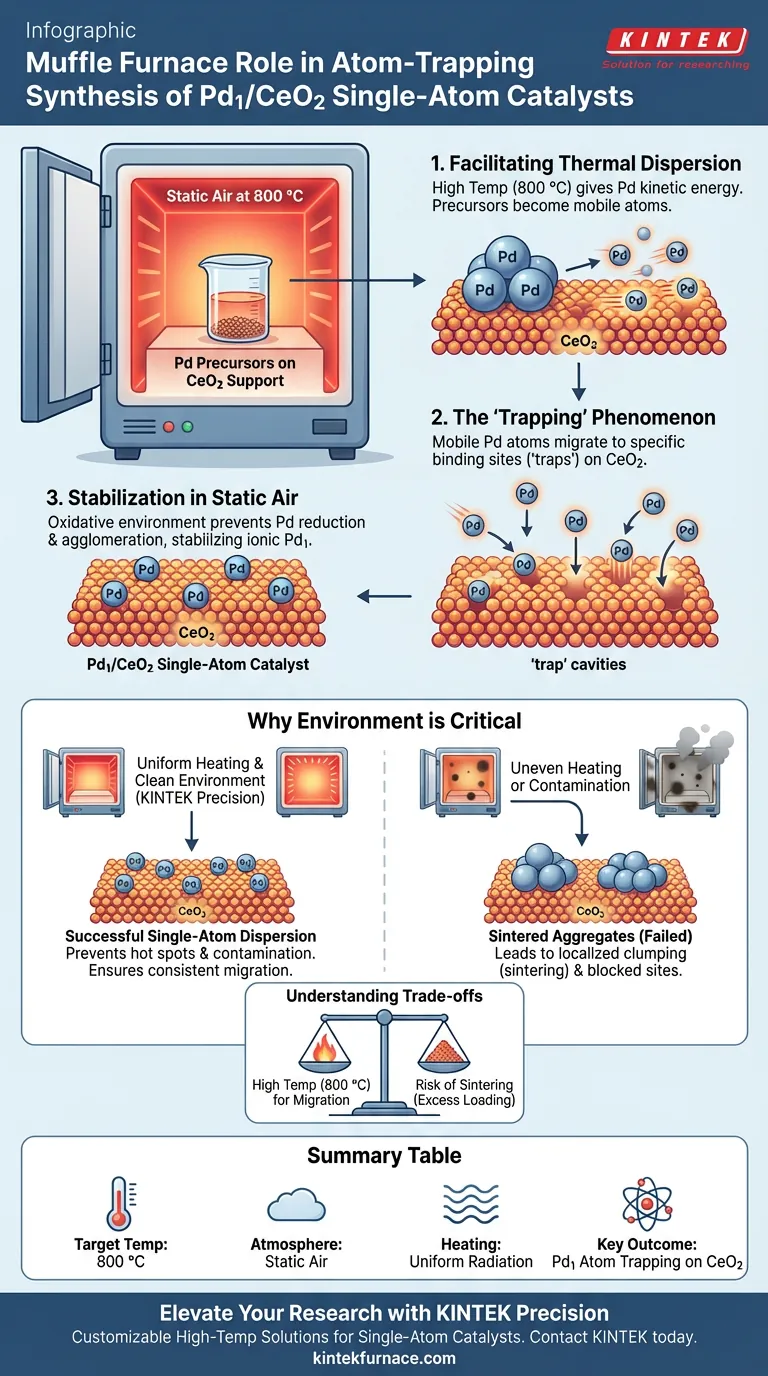
The muffle furnace serves as the high-temperature facilitator for atomic migration and stabilization. In the specific context of synthesizing Pd1/CeO2 single-atom catalysts via atom trapping, the furnace maintains a controlled environment of static air at 800 °C. This precise thermal treatment drives the dispersion of palladium precursors, forcing them to migrate across the support until they are captured by specific binding sites on the cerium oxide surface.
By providing a uniform, high-temperature oxidative environment, the muffle furnace mobilizes metal atoms to prevent them from clustering. This allows the ceria support to "trap" individual palladium atoms in stable configurations, achieving the desired single-atom dispersion.

The Mechanics of Atom Trapping via Thermal Treatment
Facilitating Thermal Dispersion
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this process is to induce thermal dispersion.
At the elevated temperature of 800 °C, the palladium precursors on the catalyst surface gain significant kinetic energy. This energy allows the metal species to become mobile, effectively moving across the surface of the support material rather than remaining static.
The "Trapping" Phenomenon
As the palladium atoms migrate due to the thermal energy provided by the furnace, they encounter specific sites on the cerium oxide (CeO2) support.
These sites act as "traps," utilizing strong chemical interactions to bind the mobile palladium atoms. The furnace maintains the temperature necessary to ensure the atoms migrate until they find these traps, rather than agglomerating into larger metal nanoparticles.
Stabilization in Static Air
The muffle furnace maintains a static air atmosphere throughout the calcination process.
This oxidative environment is crucial for stabilizing the palladium in its ionic form within the lattice or surface defects of the ceria. It prevents the reduction of the metal to a state where it might easily clump together, ensuring the final product remains a true single-atom catalyst.
Why the Muffle Furnace Environment is Critical
Uniform Heating for Consistency
For atom trapping to work effectively, the thermal energy must be applied uniformly across the entire sample.
The muffle furnace isolates the sample from direct combustion sources, heating the chamber walls to radiate heat evenly. This ensures that the migration and trapping process occurs simultaneously and identically throughout the material batch, preventing localized hot spots that could lead to sintering (clumping).
Contamination Control
The muffle furnace isolates the catalyst material from fuel byproducts and external contaminants.
Because single-atom catalysts rely on the precise interaction between the metal atom and the support, any external impurities could block the trapping sites. The clean, electrically heated environment of the muffle furnace preserves the chemical integrity of the ceria surface sites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Sintering
While the furnace promotes atom trapping, the high temperature of 800 °C is a double-edged sword.
If the loading of palladium exceeds the number of available "trap" sites on the ceria, the excess atoms will have nowhere to go. Under the intense heat of the furnace, these untrapped atoms will aggregate into larger clusters, failing to achieve the single-atom structure.
Energy and Material Stability
Operating at 800 °C requires significant energy input and demands high thermal stability from the support material.
While cerium oxide is robust, other potential support materials might degrade or undergo unwanted phase changes at these temperatures. The muffle furnace's high heat is strictly necessary for the atom-trapping mechanism, but it limits the choice of support materials to those that can withstand such calcination without collapsing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your synthesis protocol for Pd1/CeO2 catalysts, consider these factors:
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Atom Dispersion: Ensure your furnace is calibrated strictly to 800 °C; deviations below this may not provide enough energy for migration, while higher temperatures risk sintering.
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: Use a muffle furnace with programmable ramp rates to control how quickly the sample reaches 800 °C, ensuring the precursor decomposition creates a uniform distribution before trapping begins.
The muffle furnace is not just a heater; it is the tool that balances the thermodynamic competition between metal aggregation and atomic stabilization.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Atom Trapping Process |
|---|---|
| Target Temperature | 800 °C (Induces kinetic energy for thermal dispersion) |
| Atmosphere | Static Air (Oxidative environment for ionic stabilization) |
| Heating Method | Uniform Radiation (Ensures consistent migration across support) |
| Key Outcome | Atomic Migration vs. Agglomeration (Trapping Pd on CeO2 sites) |
| Support Material | Cerium Oxide (Must withstand high-temp calcination) |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect 800 °C environment for Pd1/CeO2 atom trapping requires absolute thermal uniformity and contamination control. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—specifically designed to meet the rigorous demands of single-atom catalyst synthesis.
Our equipment is backed by expert R&D and is fully customizable to suit your unique lab requirements. Ensure your metal atoms are trapped, not sintered.
Contact KINTEK today for a custom furnace solution
Visual Guide
References
- Lina Zhang, Haifeng Xiong. Generating active metal/oxide reverse interfaces through coordinated migration of single atoms. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45483-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does the air atmosphere play in a high-temperature muffle furnace? Master Ceramic Sintering Stability
- How does the design of a muffle furnace ensure uniform and safe heating? Discover Precision and Safety in Heat Treatment
- What are the typical technical specifications of a muffle furnace? Key Specs for Precise Heating
- What specialized processes utilize box furnaces? Discover Versatile Heat Treatment Solutions
- Why is the temperature control of a muffle furnace critical for ZnO nanomaterials? Achieve Optimal ZnO Calcination
- Why use vacuum muffle furnaces for nitrogen-doped biochar? Essential Atmosphere Control for Photocatalysis
- How do muffle furnaces contribute to drug testing in pharmaceuticals? Ensure Purity and Compliance with Precision
- Why is a muffle furnace used for the desizing treatment of basalt or S-glass fibers? Precision Thermal Cleaning Guide



















