At their core, box furnaces are specialized for processes that demand uniform temperature and controlled environments to fundamentally transform materials. They are critical in applications ranging from powder metallurgy for sintering metals and advanced ceramics to highly precise semiconductor fabrication processes like oxidation diffusion and metallization annealing.
The true value of a box furnace lies not in just its ability to get hot, but in its capacity to serve as a highly controllable environment for a wide range of batch processes, making it a versatile workhorse for both foundational metallurgy and high-tech manufacturing.

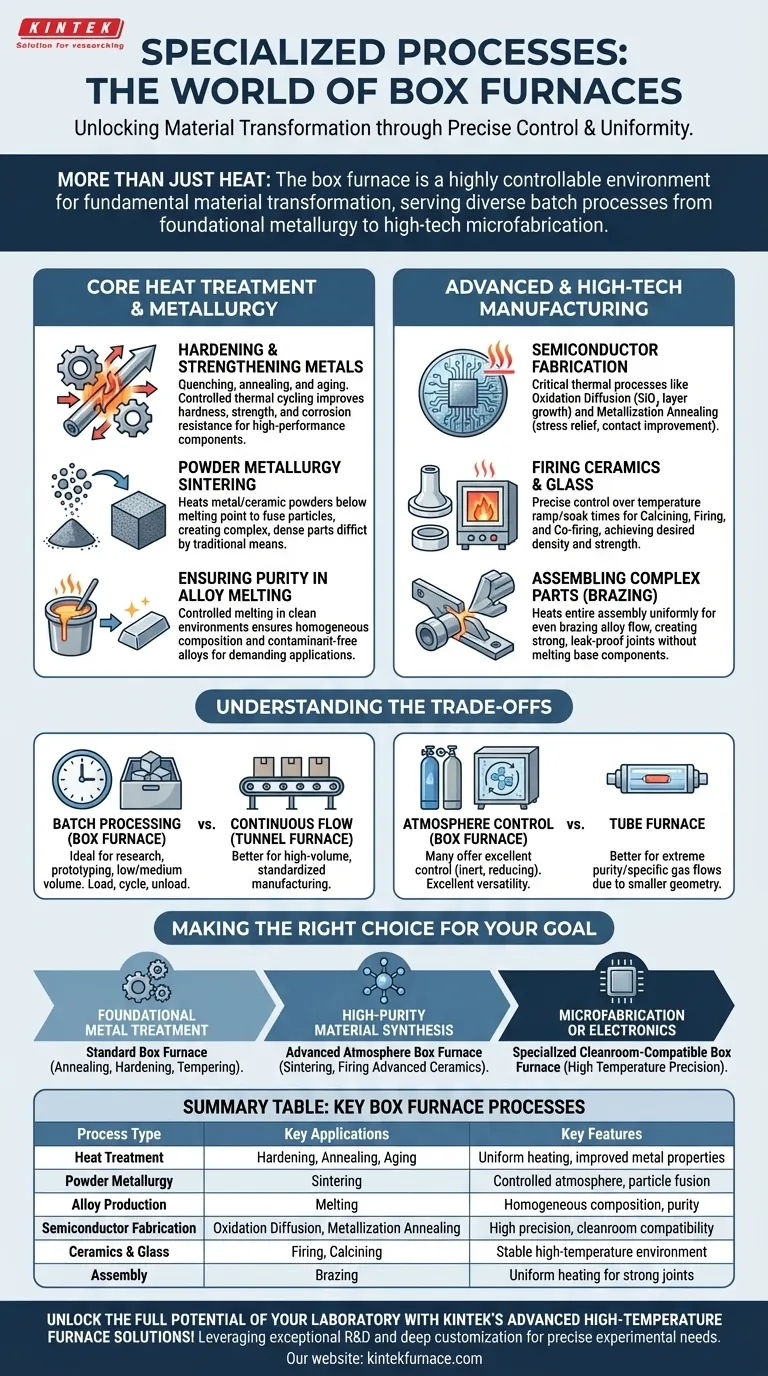
Core Heat Treatment and Metallurgical Applications
The most common applications for box furnaces involve improving the properties of metals and alloys. Their design provides the uniform, stable heat required for predictable and repeatable results.
Hardening and Strengthening Metals
Processes like quenching, annealing, and aging treatments are fundamental to metallurgy. A box furnace heats a metal part to a specific temperature and holds it there, allowing its internal crystal structure to change.
This controlled thermal cycling improves properties like hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance, turning a standard metal into a high-performance component.
Creating New Materials with Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is a process where fine metal or ceramic powders are heated below their melting point until their particles fuse together, forming a solid, dense object.
Box furnaces provide the precise temperature and atmospheric control needed for this process, enabling the creation of complex parts and materials that would be difficult or impossible to make through traditional melting and casting.
Ensuring Purity in Alloy Melting
When creating specialized alloys, achieving a uniform and pure composition is paramount. A box furnace allows for the controlled melting of constituent metals in a clean environment.
This ensures that the final alloy is homogenous and free from contaminants, which is critical for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical, and other demanding industries.
Advanced and High-Tech Manufacturing Processes
Beyond traditional metallurgy, the precision of modern box furnaces makes them essential tools in the manufacturing of sophisticated electronic and ceramic components.
Fabricating Semiconductor Components
In semiconductor manufacturing, box furnaces are used for critical thermal processes. Oxidation diffusion involves heating silicon wafers to 800-1200°C to grow a high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO₂) insulating layer.
They are also used for metallization annealing, a lower-temperature process that relieves stress in sputtered metal films and improves electrical contacts on the microchip.
Firing Ceramics and Glass
The production of advanced ceramics and specialized glass relies on processes like calcining, firing, and co-firing. These applications require precise control over temperature ramp rates and soak times.
A box furnace provides the stable, high-temperature environment necessary to achieve the desired density, strength, and dielectric properties in these non-metallic materials.
Assembling Complex Parts
Brazing is a process that joins two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint. A box furnace can heat an entire assembly uniformly, ensuring the brazing alloy flows evenly.
This method is ideal for creating strong, leak-proof joints in complex assemblies without melting the base components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, the box furnace is not the universal solution for all thermal processing. Understanding its inherent design trade-offs is key to using it effectively.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
The primary characteristic of a box furnace is its suitability for batch processing. You load parts, run a thermal cycle, and unload them. This is ideal for research, prototyping, and low-to-medium volume production.
This stands in contrast to tunnel or conveyor furnaces, which are designed for a continuous flow of parts and are better suited for high-volume, standardized manufacturing.
Atmosphere Control
While many box furnaces offer excellent atmosphere control (e.g., inert gas or reducing environments), highly sensitive processes may require a more specialized system.
For processes demanding extreme purity or specific gas flows, a tube furnace might be a better choice, as its smaller, contained geometry can make precise atmosphere management easier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process depends entirely on your end goal. The versatility of a box furnace means it can serve many functions, but specialization often yields the best results.
- If your primary focus is foundational metal treatment: A standard box furnace is the ideal workhorse for annealing, hardening, and tempering common metals and alloys.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis: Seek a box furnace with advanced atmosphere controls for processes like sintering powders or firing advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is microfabrication or electronics: You will require a specialized, cleanroom-compatible box furnace with exceptional temperature precision for semiconductor processes.
Ultimately, understanding that the furnace is a tool to create a specific material transformation is the key to leveraging its full potential.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Hardening, Annealing, Aging | Uniform heating, improved metal properties |
| Powder Metallurgy | Sintering | Controlled atmosphere, particle fusion |
| Alloy Production | Melting | Homogeneous composition, purity |
| Semiconductor Fabrication | Oxidation Diffusion, Metallization Annealing | High precision, cleanroom compatibility |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing, Calcining | Stable high-temperature environment |
| Assembly | Brazing | Uniform heating for strong joints |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specialized processes and drive innovation in your work!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- What happens to convective and radiative heat transfer effects at high furnace gas temperatures? Radiation Dominates for Superior Heating



















