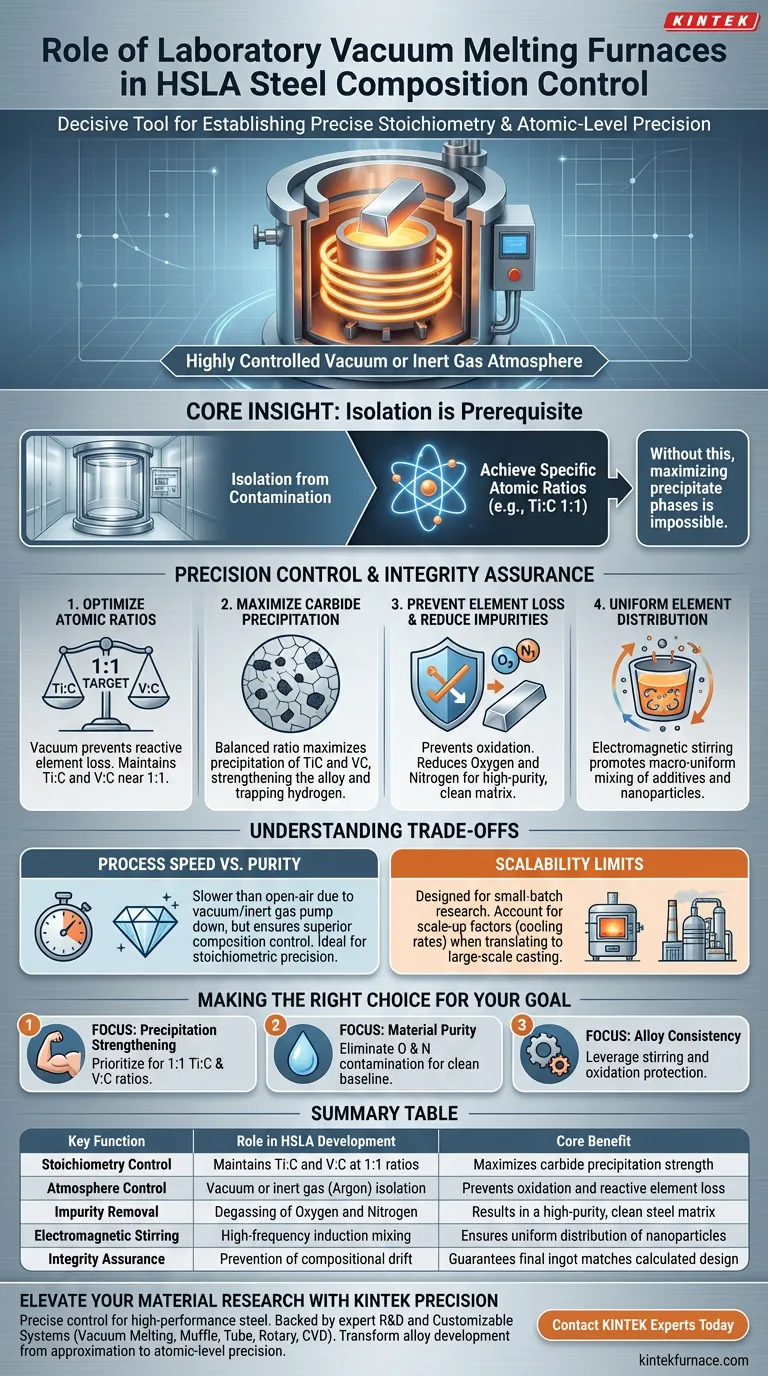
A Laboratory Vacuum Melting Furnace is the decisive tool for establishing precise stoichiometry in High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steel. By operating in a highly controlled vacuum or inert gas atmosphere, this equipment allows researchers to strictly regulate the atomic ratios of strengthening phases, specifically keeping Titanium Carbide (TiC) and Vanadium Carbide (VC) near a 1:1 ratio. This exact control is necessary to maximize carbide precipitation, which serves as the primary mechanism for strengthening the alloy and trapping hydrogen.
Core Insight: The furnace’s ability to isolate the melt from atmospheric contamination is not just about purity; it is the prerequisite for achieving specific atomic ratios (like Ti:C 1:1). Without this environment, maximizing precipitate phases for advanced material research becomes impossible.
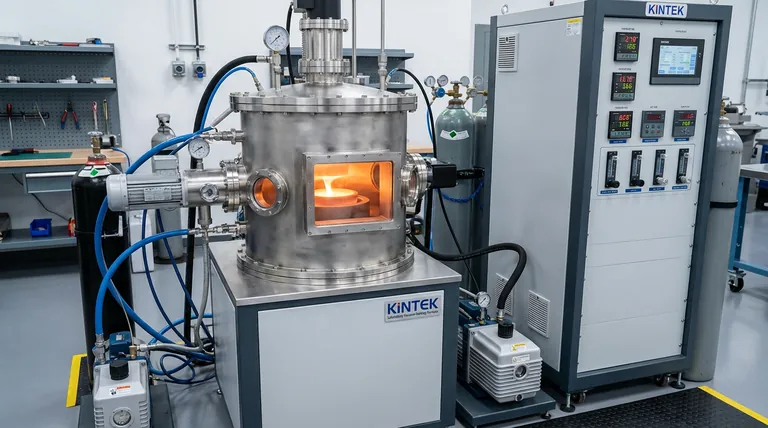

Precision Control of Strengthening Phases
Optimizing Atomic Ratios
The primary function of this furnace in HSLA applications is the regulation of alloy composition to specific atomic standards.
To achieve optimal material properties, the atomic ratios of Titanium to Carbon (Ti:C) and Vanadium to Carbon (V:C) must be maintained near 1:1. The vacuum environment prevents the loss of these reactive elements, allowing you to hit these targets with high precision.
Maximizing Carbide Precipitation
Achieving the correct atomic ratio is directly linked to the efficiency of the steel's strengthening mechanism.
When the ratio is balanced correctly, the precipitation of carbides (TiC and VC) is maximized. This maximization is fundamental for researchers studying the relationship between precipitation strengthening and the steel's ability to trap hydrogen, a critical factor in preventing embrittlement.
Ensuring Compositional Integrity
Prevention of Element Loss
Beyond ratio control, the furnace plays a defensive role against compositional drift.
In open-air melting, alloying elements can easily oxidize and burn off. The vacuum or inert gas (such as argon) atmosphere effectively prevents oxidation, ensuring that the chemical composition of the final ingot matches the intended design or the original base material.
Reduction of Impurities
High-performance steels require a pristine matrix to function correctly.
Melting in a vacuum environment actively reduces the inclusion of impurity elements, specifically oxygen and nitrogen. This results in a high-purity ingot that provides a reliable baseline for studying microstructural transformations, such as those found in bainitic steel.
Uniform Element Distribution
Achieving the right ingredients is useless if they are not mixed thoroughly.
These furnaces utilize high-frequency induction heating, which generates electromagnetic stirring forces within the liquid metal. This promotes a macro-uniform distribution of additives and nanoparticles throughout the melt pool, ensuring consistent properties across the entire ingot.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Speed vs. Purity
While vacuum melting ensures superior composition control, it is inherently slower than open-air processing.
The requirement to pump down to a vacuum and backfill with inert gas adds cycle time. This method is best reserved for applications where stoichiometric precision outweighs the need for high-throughput production.
Scalability Limits
Laboratory Vacuum Melting Furnaces are designed for experimental ingots and small-batch research.
While they are excellent for developing the "recipe" for HSLA steel, the specific cooling rates and solidification dynamics in a small crucible may differ from large-scale industrial casting. You must account for these scale-up factors when translating lab results to mass production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The utility of a Laboratory Vacuum Melting Furnace depends on the specific parameters of your research or production needs.
- If your primary focus is Precipitation Strengthening: Prioritize this furnace to lock in the 1:1 Ti:C and V:C ratios required to maximize carbide formation.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Use this equipment to eliminate oxygen and nitrogen contamination, ensuring a clean baseline for microstructural analysis.
- If your primary focus is Alloy Consistency: Leverage the electromagnetic stirring and oxidation protection to ensure your final chemical composition mirrors your calculated input.
Ultimately, this furnace transitions HSLA steel development from rough approximation to atomic-level precision.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Role in HSLA Development | Core Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Stoichiometry Control | Maintains Ti:C and V:C at 1:1 ratios | Maximizes carbide precipitation strength |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum or inert gas (Argon) isolation | Prevents oxidation and reactive element loss |
| Impurity Removal | Degassing of Oxygen and Nitrogen | Results in a high-purity, clean steel matrix |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | High-frequency induction mixing | Ensures uniform distribution of nanoparticles |
| Integrity Assurance | Prevention of compositional drift | Guarantees final ingot matches calculated design |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Precise control over alloy stoichiometry is the difference between average and high-performance steel. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum Melting, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems—all customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are maximizing carbide precipitation in HSLA steel or developing advanced bainitic structures, our equipment provides the purity and control your research demands.
Ready to transform your alloy development from approximation to atomic-level precision?
Visual Guide
References
- Tim Boot, Vera Popovich. Hydrogen trapping and embrittlement of titanium- and vanadium carbide-containing steels after high-temperature hydrogen charging. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-024-09611-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does the alternating current power supply contribute to the induction heater's operation? Unlock Efficient, Contactless Heating
- What solutions are implemented for vacuum induction melting (VIM)? Achieve Superior Alloy Purity and Performance
- What types of materials can be smelted in an induction furnace? Master the Art of Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is induction heating and how does it work? Discover Its Fast, Precise, and Efficient Heating
- Why is repeated melting and flipping of alloy ingots necessary? Achieving Homogeneity in Mn–Ni–Fe–Si Alloys
- What are the advantages of using a medium frequency vacuum induction furnace for NAB alloys? Precision & Purity
- What are the main advantages of using an induction furnace for metal melting? Unlock Superior Efficiency & Quality
- Why are induction gold melting furnaces considered cost-effective in the long run? A Smart Investment for Higher Profits



















