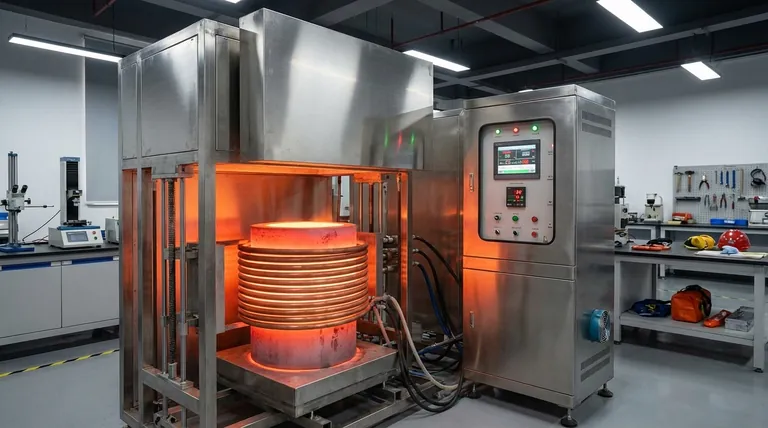
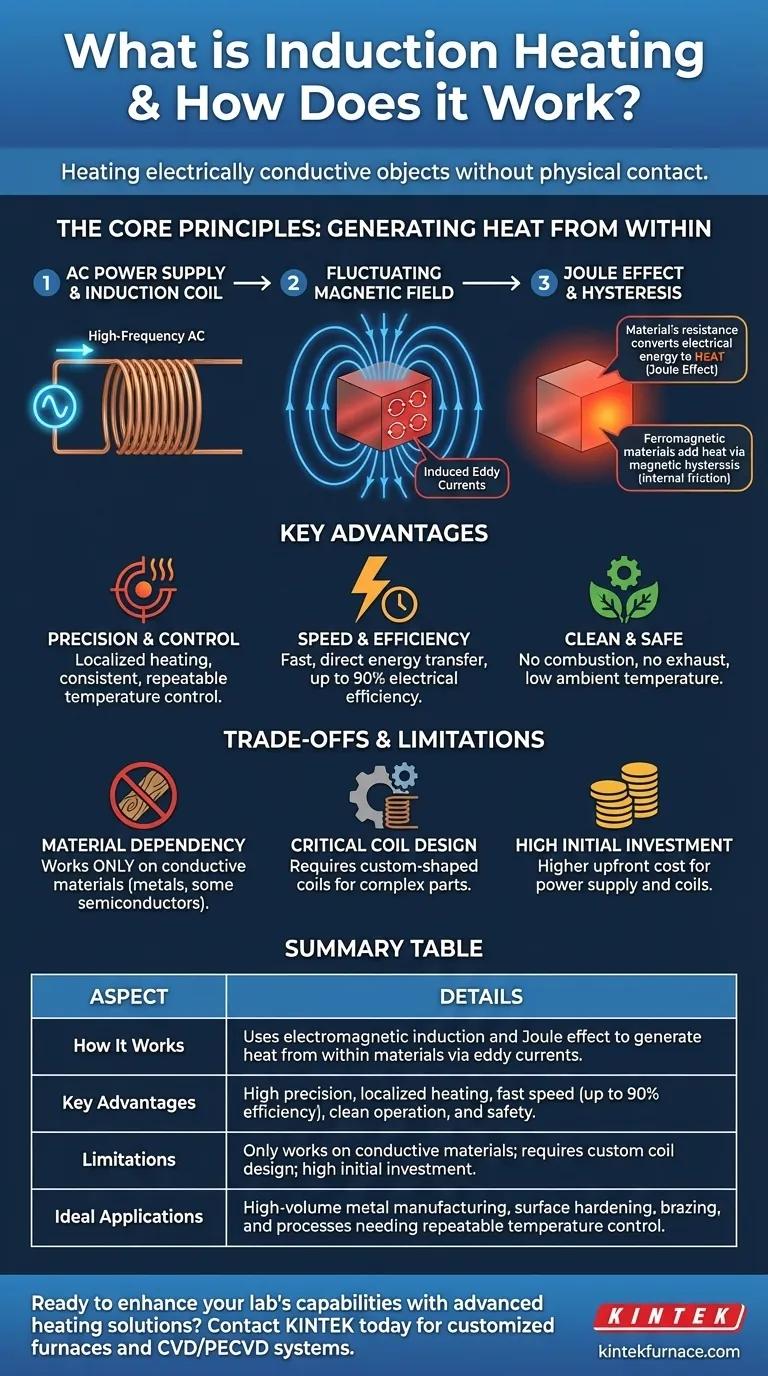
At its core, induction heating is a method of heating an electrically conductive object without any physical contact. It uses a fluctuating magnetic field to generate electrical currents directly inside the material itself. These internal currents, known as eddy currents, create intense heat due to the material's natural electrical resistance, heating the object from the inside out.
While conventional heating methods transfer heat from an external source, induction heating turns the object into its own heat source. This fundamental difference is the key to its exceptional speed, precision, and efficiency.

The Core Principles: How Induction Generates Heat
Induction heating is a direct application of two fundamental physics principles: electromagnetic induction and the Joule effect. The process unfolds in a precise, controllable sequence.
Step 1: Creating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with an induction coil, typically made of copper. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil. This flow of electricity generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space around and within the coil.
Step 2: Inducing Eddy Currents
When an electrically conductive workpiece, such as a piece of metal, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces small, circular electrical currents within the workpiece. These are called eddy currents, and their creation is governed by Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction.
Step 3: Generating Heat (The Joule Effect)
As these eddy currents flow through the workpiece, they encounter the material's inherent electrical resistance. This resistance impedes the flow of the current, converting the electrical energy into thermal energy, or heat. This phenomenon is known as the Joule effect, and it is the primary source of heat in the induction process.
A Secondary Heat Source: Magnetic Hysteresis
For ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt, an additional heating mechanism contributes. The rapid reversal of the magnetic field forces the material's microscopic magnetic domains to constantly realign. This internal friction generates supplementary heat, a process known as hysteresis loss. While secondary, it can significantly accelerate heating in these specific materials.
Key Advantages of Induction Technology
The unique method of generating heat from within gives induction several powerful advantages over traditional flame, resistance, or furnace heating.
Unmatched Precision and Control
Heat is generated only within the part of the workpiece exposed to the magnetic field. This allows for extremely localized and targeted heating. By precisely adjusting the current's frequency and power, you can achieve highly repeatable and consistent temperature control, which is critical for quality-sensitive processes like surface hardening or brazing.
Superior Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the material, the process is exceptionally fast. There is no need to first heat an oven chamber or wait for heat to conduct from an external surface. This direct energy transfer can achieve an electrical efficiency of up to 90%, drastically reducing the energy wasted on heating the surrounding environment.
Clean and Safe Operation
Induction heating involves no combustion, meaning there are no exhaust fumes or harmful byproducts. The process can be performed in a vacuum to prevent oxidation and contamination. Furthermore, the induction coil itself does not get hot, and ambient temperatures remain low, creating a safer and more comfortable working environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technology is a universal solution. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging where induction heating might not be the best fit.
Material Dependency
The most significant limitation is that induction heating only works on electrically conductive materials. Metals and some semiconductors are excellent candidates. However, non-conductive materials like plastics, wood, glass, and most ceramics cannot be heated directly by this method.
Coil Design is Critical
The efficiency and uniformity of heating are heavily dependent on the design of the induction coil. The coil must be shaped and sized appropriately for the workpiece geometry. Complex parts may require custom-engineered coils, which can add to the initial setup cost and engineering effort.
High Initial Investment
The capital equipment for an induction heating system—specifically the high-frequency power supply and the inductor coils—can represent a higher upfront cost compared to simpler gas-fired furnaces or resistance heaters. This investment is typically justified by higher throughput, lower energy costs, and improved product quality over time.
Is Induction Heating Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right heating technology depends entirely on your material, production goals, and operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable manufacturing of metal parts: Induction is likely the ideal choice due to its speed, consistency, and potential for full automation.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening, brazing, or localized treatment: Induction's ability to precisely control the heating zone makes it far superior to methods that heat the entire part.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials or running low-volume, varied jobs: Simpler, lower-cost methods like convection ovens or direct resistance heating may be more practical and cost-effective.
By understanding that induction generates heat from within, you can leverage its unique advantages for any process demanding precision, speed, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| How It Works | Uses electromagnetic induction and Joule effect to generate heat from within materials via eddy currents. |
| Key Advantages | High precision, localized heating, fast speed (up to 90% efficiency), clean operation, and safety. |
| Limitations | Only works on conductive materials; requires custom coil design; high initial investment. |
| Ideal Applications | High-volume metal manufacturing, surface hardening, brazing, and processes needing repeatable temperature control. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced heating solutions? Contact KINTEK today to explore how our high-temperature furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—can be customized to meet your unique experimental needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we deliver precise, efficient, and reliable equipment tailored for your success. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















