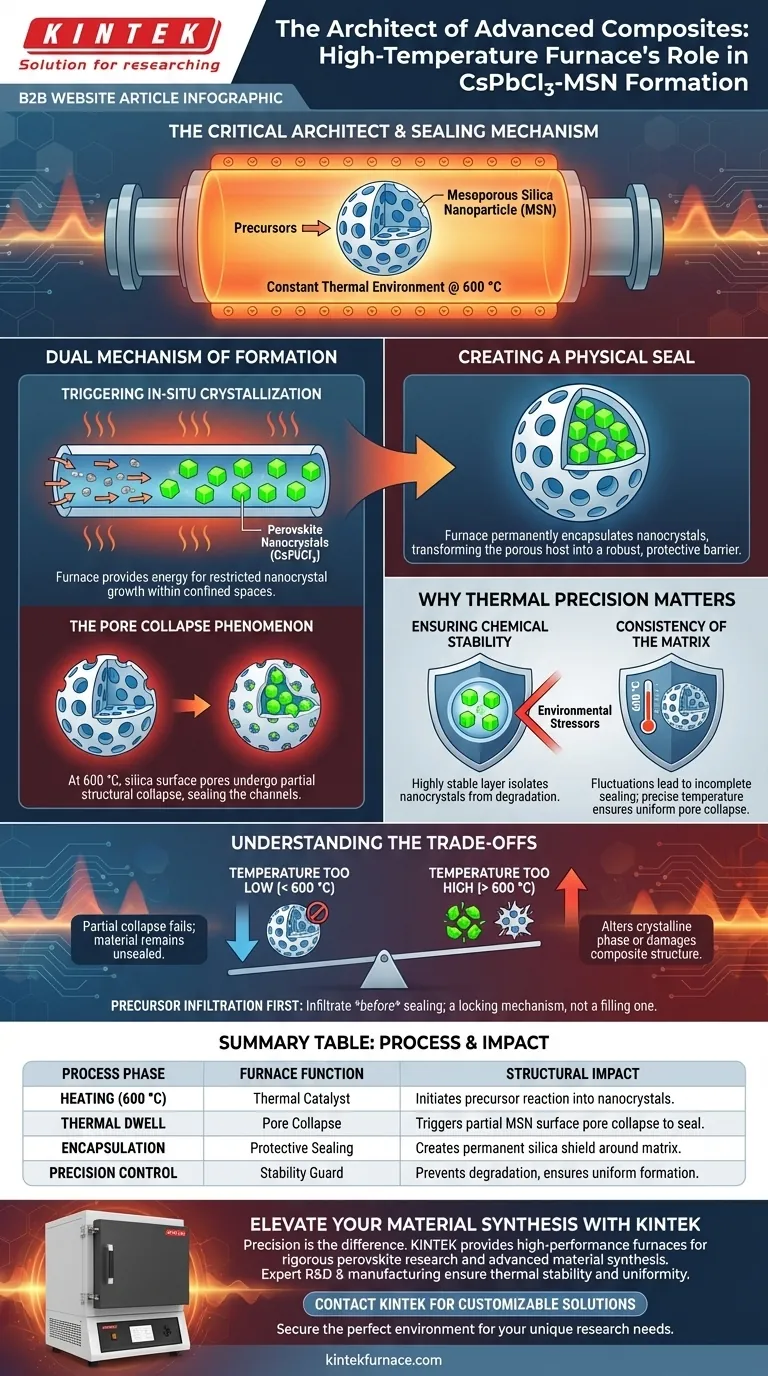
The high-temperature furnace acts as the critical architect for both synthesis and containment. Specifically, for CsPbCl3-MSN composites, the furnace maintains a constant thermal environment at 600 °C. This specific temperature triggers the chemical reaction of precursors to form nanocrystals while simultaneously altering the physical structure of the silica host to lock those crystals in place.
Core Takeaway The furnace functions as more than a heat source; it is a sealing mechanism. By holding the material at 600 °C, it forces the surface pores of the Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN) to partially collapse, physically trapping the newly formed perovskite nanocrystals inside a permanent, protective silica shield.

The Dual Mechanism of Formation
The role of the furnace in this process is twofold. It orchestrates a chemical transformation and a physical structural change simultaneously.
Triggering In-Situ Crystallization
The process begins with precursors already infiltrated within the mesoporous channels of the silica.
The furnace provides the energy required to initiate the reaction between these precursors. Because this happens inside the confined space of the silica channels, the growth of the CsPbCl3 is restricted, resulting in the formation of nanocrystals.
The Pore Collapse Phenomenon
The most distinct function of this heating stage is its effect on the Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN) themselves.
At 600 °C, the silica structure reaches a critical transition point. The surface pores, which were previously open to allow precursor entry, undergo a partial structural collapse.
Creating a Physical Seal
This collapse effectively closes the "doors" of the mesoporous channels.
By sealing the surface pores, the furnace ensures the generated perovskite nanocrystals are permanently encapsulated within the silica matrix. This transforms the porous host into a robust, protective barrier.
Why Thermal Precision Matters
The success of this composite material relies heavily on the specific thermal environment provided by the tube or crucible furnace.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
Perovskite nanocrystals (CsPbCl3) can be sensitive to environmental factors.
The encapsulation process, driven by the furnace heat, creates a highly stable protective layer. This shield isolates the nanocrystals from external stressors that might otherwise degrade them.
Consistency of the Matrix
The reference emphasizes a "constant thermal environment." Fluctuations during this phase could lead to uneven pore collapse.
If the temperature is not maintained precisely at 600 °C, the sealing process may be incomplete, leaving the nanocrystals exposed and vulnerable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the high-temperature treatment is essential for stability, it introduces specific constraints that must be managed.
The Temperature Narrow Window
The process relies on a specific balance at 600 °C.
If the temperature is too low, the partial collapse of the MSN pores may not occur, failing to seal the material. Conversely, temperatures significantly exceeding this range could alter the crystalline phase of the perovskite or damage the composite structure.
Precursor Infiltration Dependency
The furnace step is a "locking" mechanism, not a "filling" mechanism.
The precursors must be successfully infiltrated into the channels before the furnace reaches the critical sealing temperature. Once the pores collapse, no further material can be added to the internal matrix.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the CsPbCl3-MSN formation, align your thermal processing with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is maximum stability: Ensure the furnace maintains a strict 600 °C profile to guarantee complete pore collapse and effective encapsulation.
- If your primary focus is crystal quality: Verify that the "in-situ" reaction has sufficient time to complete within the channels before the cooling cycle begins.
Precise thermal control during this stage effectively turns the silica host into a permanent vault for the perovskite nanocrystals.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Function | Structural Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Heating (600 °C) | Thermal Catalyst | Initiates chemical reaction of precursors into nanocrystals |
| Thermal Dwell | Pore Collapse | Triggers partial collapse of MSN surface pores to seal channels |
| Encapsulation | Protective Sealing | Creates a permanent silica shield around the perovskite matrix |
| Precision Control | Stability Guard | Prevents phase degradation and ensures uniform composite formation |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a successful composite and a failed experiment. KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces designed for the rigorous demands of perovskite research and advanced material synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems offer the thermal stability and uniformity required for critical processes like pore collapse and in-situ crystallization.
Ready to optimize your lab’s thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today for a customizable solution and secure the perfect environment for your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Jiaze Wu, Kai Huang. Generative Synthesis of Highly Stable Perovskite Nanocrystals via Mesoporous Silica for Full‐Spectrum White LED. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202507240
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of vacuum devices in Polymer Impregnation Method? Enhance Deep Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a vacuum oven required for drying NMC811 precursors? Essential Steps for High-Nickel Cathode Purity
- What role does a vacuum heat treatment furnace play in the preparation of SKD6 side dies? Enhance Tool Steel Longevity
- How does a laboratory vacuum drying oven facilitate the thermal treatment of graphene/polyimide films? Enhance Purity
- How does a vertical vacuum furnace separate magnesium, zinc, and aluminum? Exploit Boiling Points for Metal Recovery
- What role does a vacuum annealing furnace play in NCG synthesis? Precision Carbonization for Nanomaterials
- Why might a vacuum furnace maintain vacuum during cooling? Protect Workpieces from Oxidation and Control Metallurgy
- What role do vacuum furnaces play in electronic component manufacturing? Essential for Purity and Precision



















