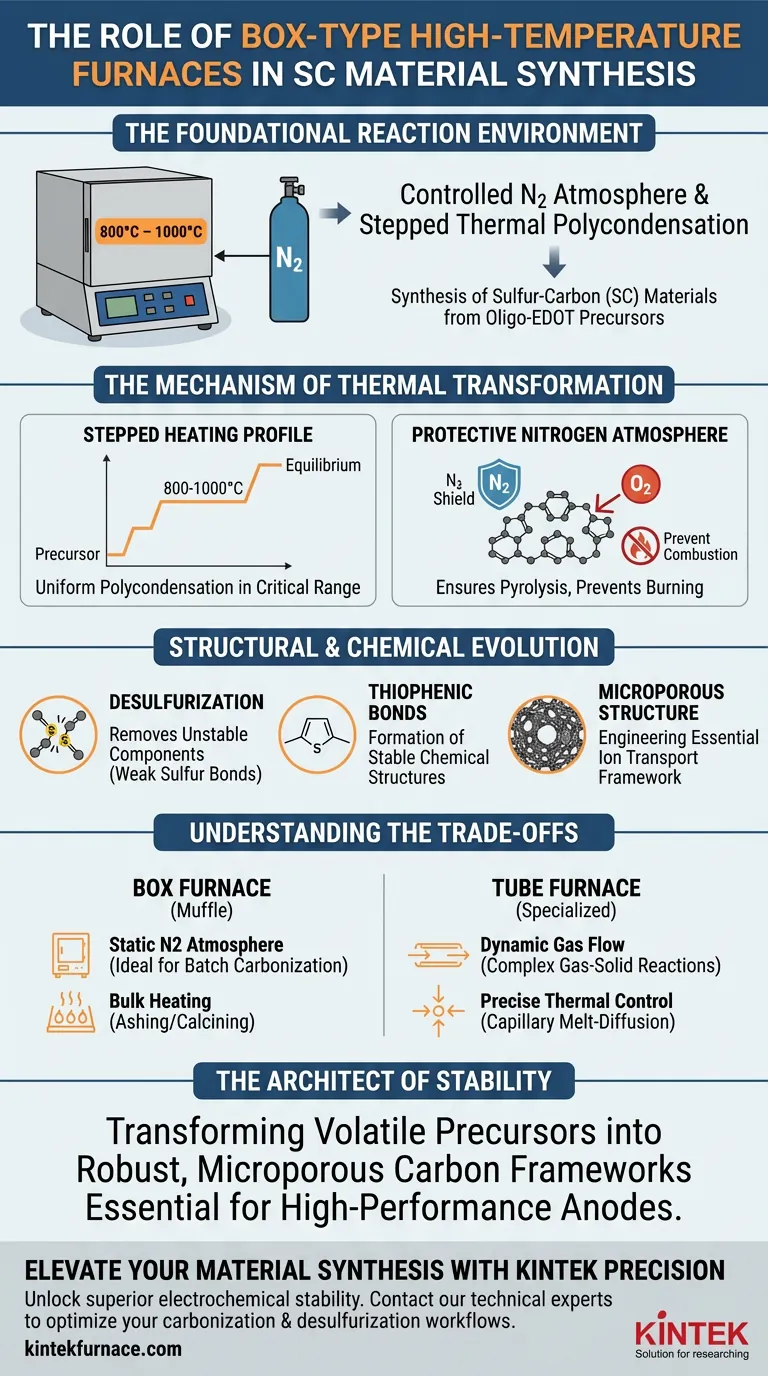
The box-type high-temperature furnace serves as the foundational reaction environment for synthesizing sulfur-carbon (SC) materials from oligo-EDOT precursors. By maintaining a controlled nitrogen atmosphere and executing a stepped thermal polycondensation process between 800 °C and 1000 °C, the furnace enables the simultaneous carbonization of the skeleton and the removal of unstable sulfur components.
The furnace’s primary function is to drive a precise chemical evolution, converting raw precursors into stable, microporous anode materials rich in thiophenic chemical environments through controlled thermal treatment.
The Mechanism of Thermal Transformation
The box-type furnace (often called a muffle or ashing furnace) is not merely a heating element; it is a chamber for chemical synthesis. Its role is defined by the rigorous control of temperature and atmosphere.
Stepped Thermal Polycondensation
The furnace executes a stepped heating profile, typically operating in the critical range of 800 °C to 1000 °C.
This is not a linear heating process. The "stepped" nature allows the material to reach equilibrium at specific thermal plateaus, ensuring the polycondensation reaction proceeds uniformly throughout the precursor bulk.
Protective Nitrogen Atmosphere
Carbonization requires high heat, but oxygen is the enemy. The furnace maintains a nitrogen protective atmosphere to prevent combustion.
This inert environment ensures that the precursor undergoes pyrolysis (chemical decomposition by heat) rather than burning, allowing the carbon structure to form without degrading into ash.
Structural and Chemical Evolution
The "desulfurization and carbonization" mentioned in your query are actually two sides of the same thermal process facilitated by the furnace.
Desulfurization of Unstable Components
As the temperature rises, the furnace facilitates the removal of unstable components.
In the context of sulfur-carbon materials, this acts as a selective desulfurization process. It eliminates weak sulfur bonds that would degrade battery performance, leaving behind only the robust chemical structures.
Formation of Thiophenic Environments
The high-temperature treatment promotes the formation of thiophenic sulfur-carbon bonds.
Unlike elemental sulfur which can be unstable, thiophenic sulfur is chemically bonded within the carbon lattice. This structure is critical for the electrochemical stability of the final anode material.
Microporous Structure Engineering
The thermal stresses and gas evolution during heating create a specific microporous structure.
This architecture is essential for ion transport. The furnace's ability to hold high temperatures allows these pores to "set" into a rigid framework, defining the physical surface area of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the box-type furnace is excellent for high-temperature carbonization, it differs significantly from other furnace types utilized in material science.
Static vs. Dynamic Atmosphere
Box furnaces generally provide a static or low-flow inert atmosphere, which is ideal for batch carbonization.
However, they often lack the precise, continuous gas flow capabilities of a tube furnace. If your process requires complex gas-solid reactions (such as using H2S gas flow for active sulfurization) or capillary melt-diffusion, a tube furnace is often the superior tool.
Thermal Uniformity Limitations
Box furnaces are designed for bulk heating, commonly used for ashing or calcining.
For processes requiring extreme temperature gradient control or rapid cooling rates to freeze specific crystal structures, the thermal mass of a large box furnace can be a limiting factor compared to smaller, specialized tube reactors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your sulfur-carbon material synthesis, align your equipment choice with your specific processing stage.
- If your primary focus is creating the conductive carbon skeleton: Rely on the box furnace for its ability to handle high-temperature (800–1000 °C) stepped polycondensation under nitrogen.
- If your primary focus is maximizing electrochemical stability: Use the box furnace to drive the thermodynamic conversion of loose sulfur precursors into stable thiophenic chemical structures.
Ultimately, the box-type furnace is the architect of stability, transforming volatile precursors into robust, microporous carbon frameworks essential for high-performance anodes.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Temperature Range | Primary Function in SC Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonization | 800°C – 1000°C | Creates conductive carbon skeleton through pyrolysis |
| Desulfurization | High Heat Plateau | Removes unstable sulfur bonds to improve chemical stability |
| Atmosphere Control | Constant N2 Flow | Prevents combustion and ensures inert chemical evolution |
| Pore Engineering | Stepped Heating | Develops microporous structures essential for ion transport |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock superior electrochemical stability for your SC materials with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production needs.
Whether you require the bulk processing power of a high-temperature box furnace or the precise gas-solid reaction control of a specialized tube furnace, our engineering team is ready to help you optimize your carbonization and desulfurization workflows.
Ready to refine your results? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temp furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Enis Oğuzhan Eren, Paolo Giusto. Microporous Sulfur–Carbon Materials with Extended Sodium Storage Window. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202310196
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the thermochemical conversion research of animal-derived waste? Optimize Pyrolysis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the thermal processing of crystal synthesis? Master Precise Crystal Growth
- What are the primary applications of muffle furnaces in materials research? Unlock Precision in Synthesis and Analysis
- What are some common applications of muffle furnaces in high-temperature processes? Discover Precision Heating Solutions
- How does heat distribution differ between muffle furnaces and drying ovens? Uncover Key Insights for Your Lab
- How is a muffle furnace utilized for defect engineering in delta-MnO2? Precision Thermal Treatment for Optimal Defects
- Why is a desktop drying oven used for CeZrPAl supports? Essential Tips for Structural Integrity
- What are the key features of box type electric furnaces in heat treatment processes? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Superior Metallurgy



















