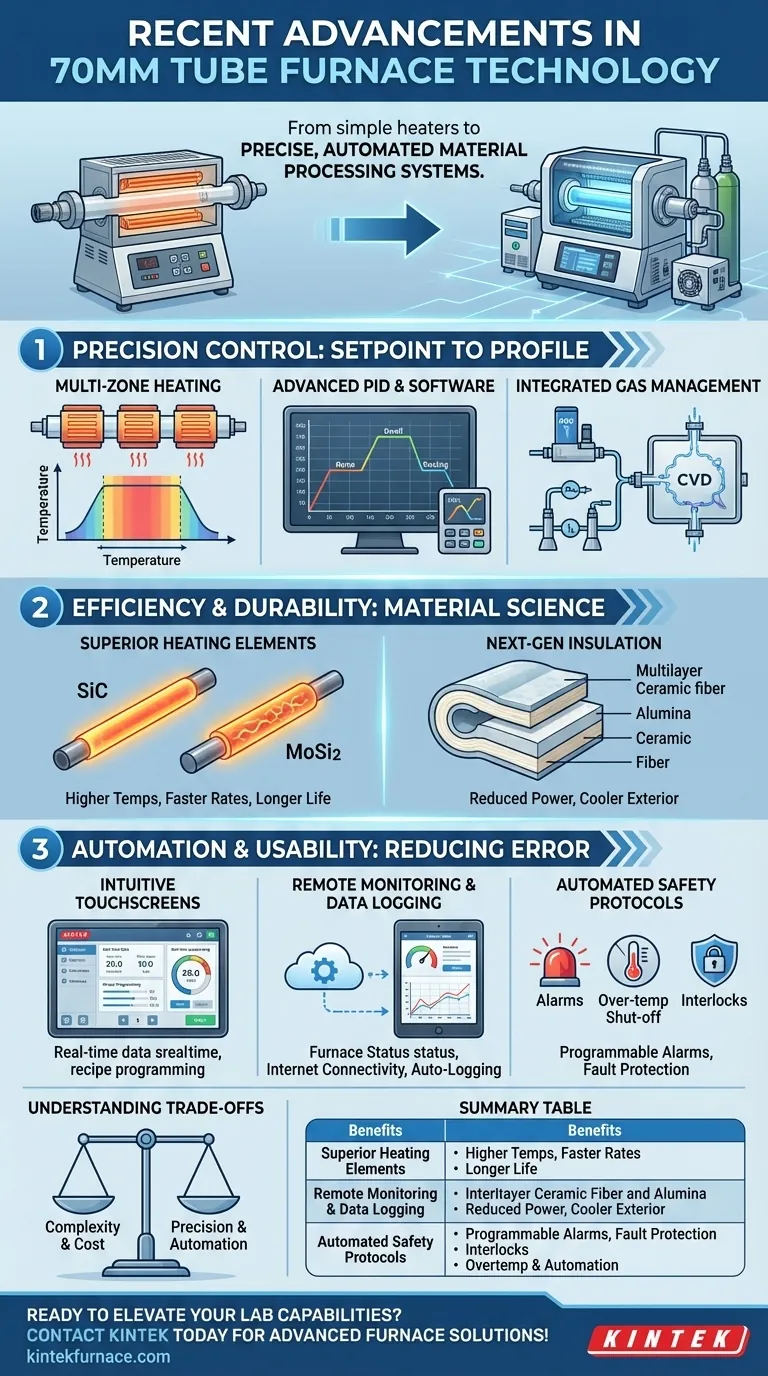
Recent advancements in 70mm tube furnace technology have moved these devices from simple heaters to precise, automated material processing systems. Key upgrades focus on delivering superior temperature uniformity, tighter control over the processing atmosphere, and enhanced operational efficiency and safety. These changes are driven by improvements in control software, insulation materials, and the heating elements themselves.
The core takeaway is that modern tube furnaces are no longer just about reaching a target temperature. They are sophisticated tools where thermal profiles, gas flow, and data logging are integrated into a single, programmable, and highly repeatable process.
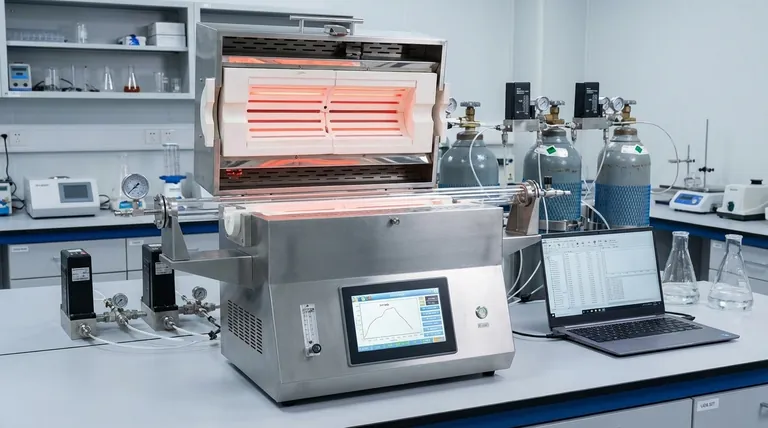

Precision Control: From Setpoint to Process Profile
The primary goal of any furnace is temperature control, but modern systems have redefined what "control" means. The focus has shifted from merely holding a static temperature to precisely executing a complex, multi-stage process profile.
The Rise of Multi-Zone Heating
For a 70mm diameter tube, maintaining a uniform temperature across a significant length is a major challenge. Single-zone furnaces inherently have cooler ends.
Multi-zone heating, typically with three or even five independent heating zones, directly solves this. Each zone has its own sensor and controller, allowing the system to compensate for end losses and create a much larger, highly uniform flat temperature zone in the center of the tube.
Advanced PID Controllers and Software
Modern furnaces use advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers with auto-tuning capabilities. This minimizes temperature overshoot and allows the furnace to reach its setpoint quickly and stably.
This hardware is paired with sophisticated software that allows users to program complex, multi-step recipes involving specific ramp rates, dwell times, and cooling profiles.
Integrated Gas Management
Previously, controlling the gas atmosphere was a separate, manual task. Today's advanced systems feature integrated mass flow controllers (MFCs).
These MFCs are programmed directly within the thermal recipe. This means you can automatically change gas types or flow rates at specific points in the heating cycle, enabling fully automated processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or complex annealing cycles.
Efficiency and Durability: The Core Material Science
Advancements are not just in the electronics but also in the fundamental materials used to build the furnace. These improvements lead to better performance, lower running costs, and a longer operational lifespan.
Superior Heating Elements
Many modern furnaces have moved beyond traditional metallic elements. High-performance models now use heating elements made from Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
These materials offer significantly higher maximum operating temperatures, faster ramp rates, and greater longevity, especially when used in reactive chemical environments.
Next-Generation Insulation
Improvements in graded, high-purity alumina and ceramic fiber insulation have a direct impact on performance. This superior insulation reduces heat loss, which lowers overall power consumption.
A secondary benefit is a cooler external furnace body, which enhances operator safety and reduces the thermal load on the laboratory environment.
Automation and Usability: Reducing Human Error
A major trend is the move toward automation and user-friendly interfaces, designed to simplify operation, improve repeatability, and ensure process integrity.
Intuitive Touchscreen Interfaces
Clunky, button-based controllers are being replaced by high-resolution touchscreen interfaces. These graphical displays simplify the programming of complex recipes and provide clear, real-time visualization of the process parameters.
Remote Monitoring and Data Logging
Many furnaces now feature internet connectivity for remote operation and monitoring. Operators can track a long process from their office and receive automated alerts if issues arise.
Crucially, these systems provide automatic data logging of all key parameters—temperature, time, and gas flow—creating an essential record for quality control, research reports, and process validation.
Automated Safety Protocols
Modern safety features are built directly into the control system. This includes programmable alarms, automatic over-temperature shut-off, and interlocks that can automatically stop gas flow in the event of a system fault.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While these advancements offer significant capabilities, they come with considerations that must be weighed against your specific needs.
Complexity vs. Simplicity
A multi-zone furnace with integrated gas management is a powerful tool, but it is also more complex to program and maintain than a basic single-zone unit. For simple, non-critical heat treatments, the added complexity may not be necessary.
The Cost of Advanced Features
Each major feature—multi-zone control, mass flow controllers, advanced software—adds to the initial purchase price. You must perform a cost-benefit analysis to ensure the investment is justified by the required process precision and automation.
Material Compatibility
The choice of heating element and tube material (e.g., quartz, alumina, sapphire) is critical and depends entirely on your process chemistry and maximum temperature. An element like MoSi2 is robust but can be degraded by certain atmospheres, so it must be matched carefully to the application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and uniformity: Prioritize a multi-zone heating system with an advanced, programmable PID controller.
- If your primary focus is controlled atmosphere processing: You must invest in a system with fully integrated mass flow controllers.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput research or quality control: Look for a furnace with an intuitive touchscreen, recipe storage, and automated data logging.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature work (above 1500°C): Specify MoSi2 heating elements and the appropriate high-purity alumina insulation and furnace tube.
By understanding these specific advancements, you can select a furnace that functions as a precise instrument tailored to your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Advancement | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Multi-Zone Heating | Improved temperature uniformity across the tube length |
| Advanced PID Controllers | Precise and stable temperature control with auto-tuning |
| Integrated Gas Management | Automated gas flow control for processes like CVD |
| Superior Heating Elements | Higher temperatures, faster ramp rates, and longer lifespan |
| Enhanced Insulation | Reduced power consumption and improved safety |
| Touchscreen Interfaces | User-friendly programming and real-time monitoring |
| Remote Monitoring | Internet connectivity for remote operation and alerts |
| Automated Safety Protocols | Built-in alarms and shut-offs for process integrity |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with cutting-edge tube furnace technology? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on precision control, automation, or high-temperature processing, we're here to help. Contact us today to discuss how our innovations can benefit your research or production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















