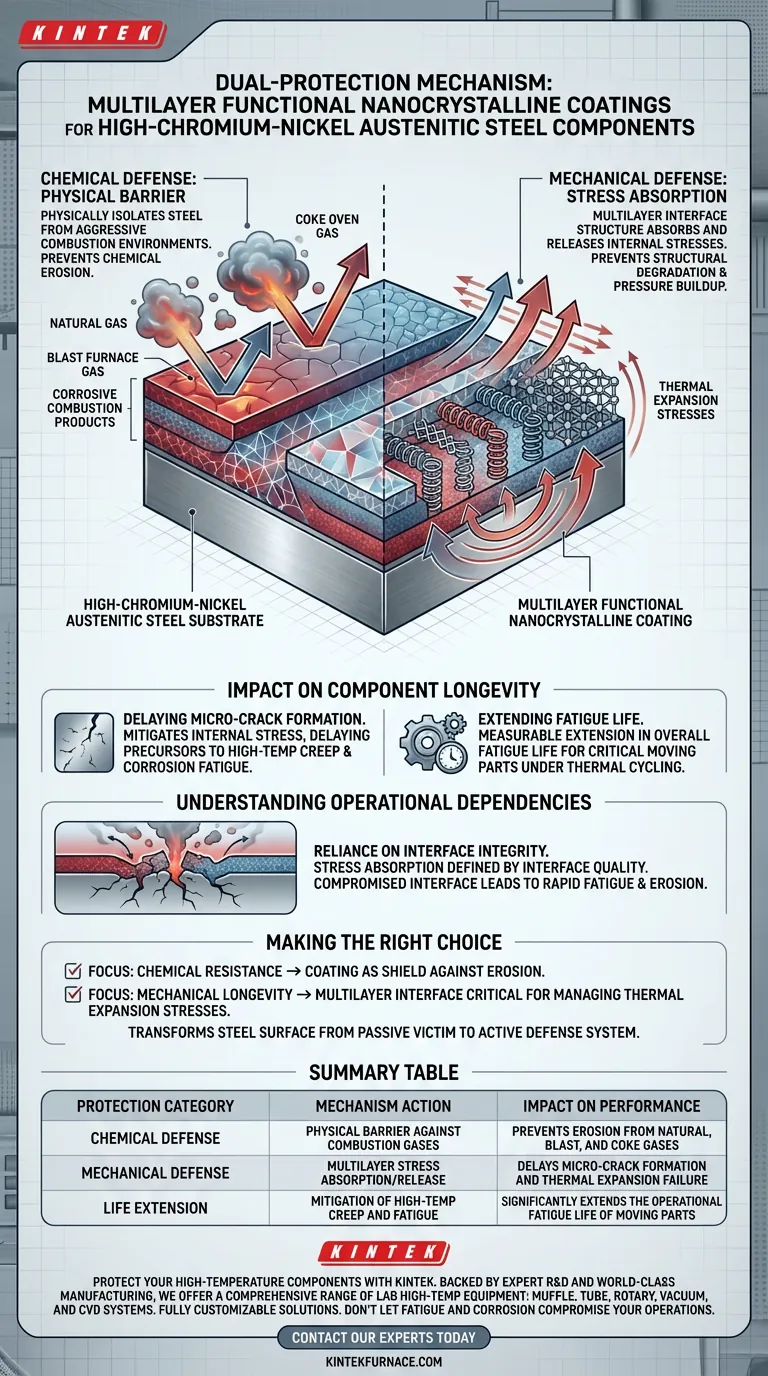
Multilayer functional nanocrystalline coatings provide a dual-protection mechanism comprising a physical shield and a stress-management system. Specifically, they act as a high-performance barrier that physically isolates high-chromium-nickel austenitic steel from aggressive combustion environments while simultaneously managing internal structural pressures to prevent mechanical failure.
The core value of this technology lies in its ability to decouple chemical defense from mechanical endurance. By preventing gas erosion and absorbing thermal stress at the interface, the coating delays the onset of micro-cracks and significantly extends the fatigue life of critical moving parts.

The Mechanics of Protection
Chemical Defense: The Physical Barrier
The primary function of these coatings is to serve as a robust physical barrier.
This layer prevents chemical erosion by blocking the interaction between the steel surface and aggressive combustion products. This is particularly effective against corrosive mixtures involving natural gas, blast furnace gas, and coke oven gas.
Mechanical Defense: Stress Absorption
Beyond simple isolation, the coating utilizes a unique multilayer interface structure to manage mechanical loads.
This structure is engineered to absorb and release internal stresses that arise from thermal expansion. By effectively managing these expansion forces, the coating prevents the buildup of pressure that typically leads to structural degradation.
Impact on Component Longevity
Delaying Micro-Crack Formation
The combination of chemical shielding and stress absorption directly targets the root causes of component failure.
By mitigating internal stress, the coating delays the formation of micro-cracks. These cracks are typically the precursors to failure caused by high-temperature creep and corrosion fatigue.
Extending Fatigue Life
The ultimate result of this dual-protection mechanism is a measurable extension in the overall fatigue life of the component.
For critical moving parts made of high-chromium-nickel austenitic steel, this means reliable operation for longer periods, even under the duress of thermal cycling and corrosive gas exposure.
Understanding the Operational Dependencies
Reliance on Interface Integrity
While these coatings offer significant protection, their effectiveness is heavily reliant on the integrity of the multilayer interface.
The system's ability to absorb stress is defined by the quality of this interface structure. If the interface is compromised, the mechanism for releasing thermal expansion stresses fails, potentially exposing the substrate to rapid fatigue and erosion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating this coating technology for your specific engineering challenges, consider the primary failure modes of your components:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Resistance: The coating acts as a necessary shield against erosion from mixed combustion gases like blast furnace or coke oven gas.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Longevity: The multilayer interface is critical for managing thermal expansion stresses and preventing the micro-cracking associated with creep and fatigue.
This solution effectively transforms the steel surface from a passive victim of its environment into an active defense system against thermal and chemical stress.
Summary Table:
| Protection Category | Mechanism Action | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Defense | Physical barrier against combustion gases | Prevents erosion from natural, blast, and coke gases |
| Mechanical Defense | Multilayer stress absorption/release | Delays micro-crack formation and thermal expansion failure |
| Life Extension | Mitigation of high-temp creep and fatigue | Significantly extends the operational fatigue life of moving parts |
Protect Your High-Temperature Components with KINTEK
Are thermal expansion stresses and chemical erosion shortening the lifespan of your critical steel components? KINTEK provides the advanced material solutions you need to ensure long-term reliability in aggressive environments.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of lab high-temp equipment, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production needs.
Don't let fatigue and corrosion compromise your operations. Contact our experts today to discover how our high-temperature expertise can enhance your laboratory efficiency and material durability.
Visual Guide
References
- А.M. Yalova, Nazarii Bondar. The problem of increasing the working resource of energy equipment details. DOI: 10.31498/2225-6733.49.2.2024.321349
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature range is required for CVD synthesis of graphene? Optimize Your Growth for Superior Carbon Quality
- What are the general applications of CVD furnaces? Unlock High-Performance Thin Films for Your Industry
- What are the disadvantages of chemical vapor deposition? Managing High Heat, Hazardous Gases, and Complex Geometries
- Why is a solvent bubbler used in CVD for 2D COF synthesis? Optimize Polymerization & Crystallinity
- What are the advantages of CVD coating? Achieve Superior, Uniform Coatings for Complex Parts
- What is the mechanism of CVD reaction? Master the Steps from Gas to Thin Film
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- How does CVD enhance cutting tools and industrial machinery? Boost Durability and Productivity














