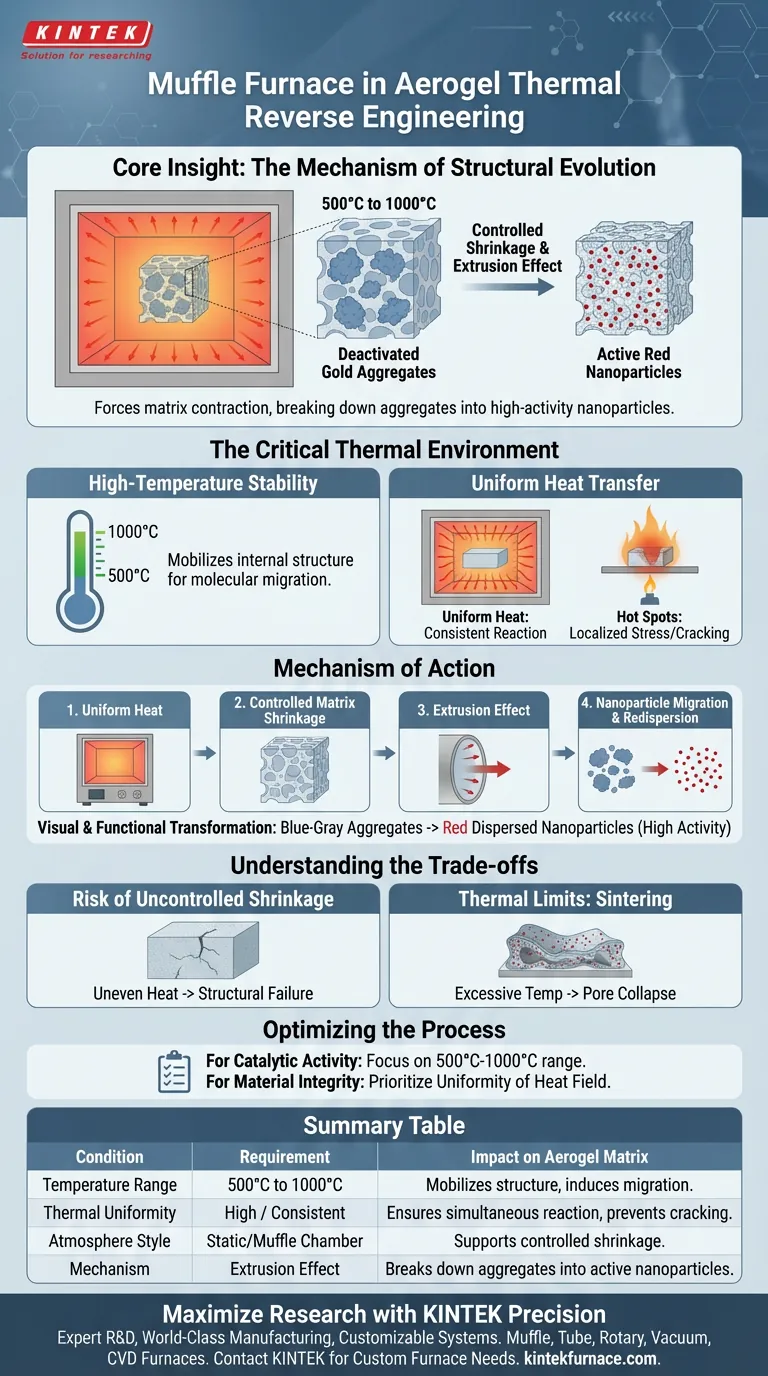
During the thermal reverse engineering of aerogels, a muffle furnace provides a precisely controlled thermal field typically ranging from 500°C to 1000°C. This high-energy environment delivers the uniform heat transfer necessary to induce controlled physical changes within the aerogel matrix without destroying it.
Core Insight: The muffle furnace does not merely heat the material; it acts as a mechanism for structural evolution. By maintaining a uniform high-temperature field, it forces the aerogel matrix to undergo "controlled shrinkage." This physical contraction creates an extrusion effect that breaks down large, deactivated gold aggregates and redistributes them as highly active nanoparticles.

The Critical Thermal Environment
To successfully reverse engineer aerogels, specifically to reactivate catalytic components, precise environmental conditions are required.
High-Temperature Stability
The process relies on a thermal window between 500°C and 1000°C.
This high-energy input is required to mobilize the internal structure of the material. Temperatures below this threshold may fail to induce the necessary molecular migration.
Uniform Heat Transfer
A defining characteristic of the muffle furnace is its ability to provide a highly uniform temperature field.
Unlike direct heating methods that might create hot spots, a muffle furnace envelops the aerogel in consistent heat. This ensures that the entire sample reacts simultaneously, preventing localized stress or uneven structural evolution.
Mechanism of Action on Aerogels
The thermal conditions provided by the furnace trigger a specific chain of physical and chemical events within the aerogel.
Controlled Matrix Shrinkage
The uniform heat causes the aerogel matrix to shrink in a controlled manner.
This is not a collapse, but a tightening of the structure. This shrinkage generates internal pressure—an extrusion effect—that acts upon the materials embedded within the aerogel pores.
Nanoparticle Migration and Redispersion
The extrusion force drives the migration of large, deactivated gold aggregates.
Under these conditions, these large clusters are broken down and redispersed throughout the matrix. This transforms the material from a deactivated state back into a functional catalytic state.
Visual and Functional Transformation
The process results in a tangible change in the material's properties.
Deactivated aggregates, which appear blue-gray, are transformed into red dispersed gold nanoparticles. This color change serves as a visual indicator that the material has regained its high activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is effective, the process relies heavily on the balance between temperature and structural integrity.
The Risk of Uncontrolled Shrinkage
The key term in this process is "controlled" shrinkage.
If the heat transfer is not uniform, different parts of the aerogel will shrink at different rates. This can lead to cracking or structural failure rather than the desired extrusion effect, rendering the material useless.
Thermal Limits
While the furnace can reach 1000°C, exceeding the material's specific thermal tolerance can lead to sintering.
If the temperature is too high for the specific aerogel composition, the pores may collapse entirely rather than just shrinking, trapping the nanoparticles rather than redispersing them.
Optimizing the Reverse Engineering Process
To ensure successful reactivation of aerogel catalysts, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is restoring catalytic activity: Ensure your furnace reaches the 500°C to 1000°C range to guarantee enough energy is available to break down large aggregates.
- If your primary focus is material integrity: Prioritize the uniformity of the heat field over heating speed to ensure the shrinkage remains controlled and consistent throughout the matrix.
By leveraging the precise thermal environment of a muffle furnace, you can effectively recycle deactivated aerogels into high-performance materials.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Requirement | Impact on Aerogel Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 500°C to 1000°C | Mobilizes internal structure & induces molecular migration |
| Thermal Uniformity | High / Consistent | Ensures simultaneous reaction & prevents localized stress/cracking |
| Atmosphere Style | Static/Muffle Chamber | Protects sample from direct flame & supports controlled shrinkage |
| Mechanism | Extrusion Effect | Breaks down deactivated gold aggregates into active nanoparticles |
Maximize Your Aerogel Research with KINTEK Precision
Precision thermal control is the difference between material reactivation and structural collapse. At KINTEK, we understand the delicate balance required for thermal reverse engineering. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all of which are fully customizable to meet your unique lab requirements.
Whether you are redistributing gold nanoparticles or exploring novel catalytic matrices, our high-temperature furnaces deliver the uniformity your research demands. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs and ensure your materials reach their peak functional state.
Visual Guide
References
- Hanna Judit Csupász-Szabó, István Lázár. Thermal Reverse-Engineered Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Nanogold-Containing Silica Aerogels. DOI: 10.3390/gels11020087
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What PPE is necessary when adjusting controls or handling equipment during furnace operation? Essential Safety Gear for High-Temperature Tasks
- Why is a box furnace required for the calcination of hydroxide precursors? Master P2-Type Oxide Synthesis
- How are muffle furnaces utilized in the aerospace industry? Essential for Safety Testing and Material Development
- What processes can be performed using box furnaces? Unlock Versatile Thermal Solutions for Your Lab
- What are the main applications of box type electric furnaces? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the OBD process for Ti-6Al-4V? Enhance Alloy Surface Hardening Precision
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- What is the significance of using a laboratory high-temperature box furnace for Fe3O4@Al2O3 nanopowders?



















