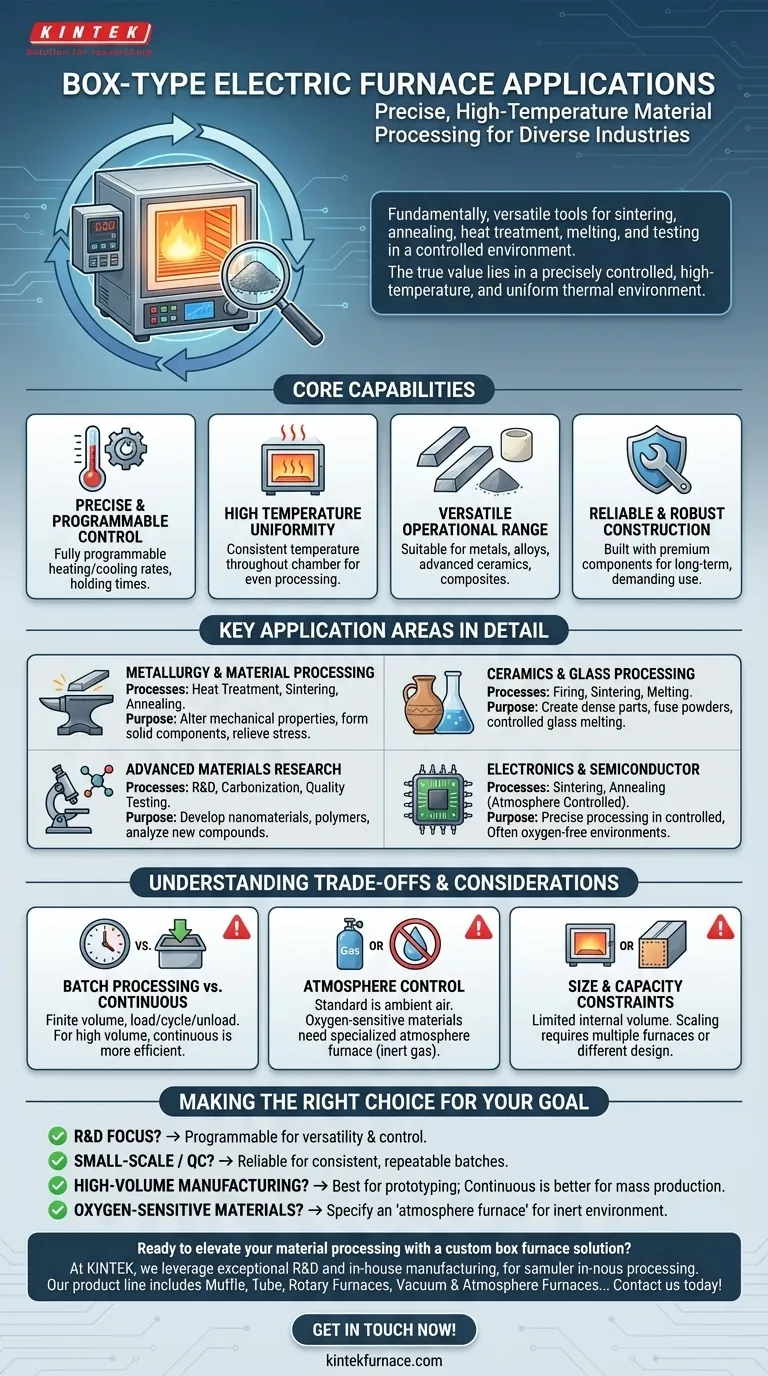
Fundamentally, box type electric furnaces are versatile tools for high-temperature material processing. They are essential equipment in industries like metallurgy, ceramics, glass, and chemicals, as well as in advanced materials research. Their primary function is to execute precise thermal processes such as sintering, annealing, heat treatment, material melting, and quality testing in a controlled environment.
While they have broad applications, the true value of a box furnace lies in its ability to provide a precisely controlled, high-temperature, and uniform thermal environment. This makes it an indispensable tool for developing and testing materials where consistency and repeatability are paramount.

Core Capabilities: Why Box Furnaces Are So Widely Used
The utility of a box furnace stems from a few key design principles that make it a reliable workhorse in both laboratory and industrial settings. Understanding these capabilities is key to understanding its applications.
Precise and Programmable Temperature Control
Box furnaces offer fully programmable control over heating rates, holding times, and cooling rates. This allows users to design and execute complex thermal profiles required for specific material transformations.
High Temperature Uniformity
A critical feature is temperature uniformity, meaning the temperature is consistent throughout the entire heating chamber. This ensures that a component or batch of material is processed evenly, which is crucial for achieving desired properties and preventing defects.
Versatile Operational Range
These furnaces are designed to operate at high temperatures, making them suitable for processing a wide variety of materials, from metals and alloys to advanced ceramics and composites.
Reliable and Robust Construction
Designed for long-term, demanding use, box furnaces are built with premium components and sturdy construction. This reliability is essential for research labs and production environments where downtime is costly.
Key Application Areas in Detail
The combination of control, uniformity, and high-temperature capability makes the box furnace suitable for a range of specific tasks across different fields.
Metallurgy and Material Processing
In metallurgy, box furnaces are standard for the heat treatment of metals to alter their mechanical properties, such as hardening or softening. They are also used for sintering powdered metals into solid components and for annealing to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility.
Ceramics and Glass Processing
The high temperatures achievable are perfect for firing ceramic green bodies into dense, durable final parts. The process of sintering ceramic powders and the controlled melting of glass compositions also rely heavily on the precise environment of a box furnace.
Advanced Materials Research
In university and government laboratories, these furnaces are essential for R&D. They are used to develop new materials, such as nanomaterials and polymers, and for analytical processes like the carbonization of organic matter or performing quality tests on new compounds.
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
The manufacturing of certain electronic components, semiconductors, and display devices requires extremely precise thermal processing. Box-type atmosphere furnaces are used to sinter or anneal components in a controlled environment, often free of oxygen.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While incredibly useful, a box furnace is not the right tool for every thermal processing task. Objectively understanding its limitations is critical.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
A box furnace is inherently a batch processor. You load material, run a cycle, cool it down, and then unload it. For high-volume, continuous manufacturing, a tunnel furnace or roller hearth furnace is a more efficient design.
Atmosphere Control
A standard box furnace operates in ambient air. If your material is sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures (e.g., most metals), you must use a specialized atmosphere furnace. These models allow the chamber to be purged with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation.
Size and Capacity Constraints
The "box" design has a finite internal volume. This naturally limits the size and throughput of the parts that can be processed. Scaling up requires either multiple furnaces or a different type of furnace altogether.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines whether a box furnace is the appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A programmable box furnace is ideal for testing new materials and developing thermal processes due to its versatility and precise control.
- If your primary focus is small-scale production or quality control: Its reliability and temperature uniformity make it perfect for consistent heat treatment or firing of small, repeatable batches.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: A box furnace is best for prototyping, but a continuous furnace is likely a more efficient solution for mass production.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials: You must specify an "atmosphere furnace" with gas-handling capabilities to create an inert environment.
Ultimately, understanding these core capabilities allows you to leverage the box furnace as a precise and reliable thermal processing tool for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Heat treatment, sintering, annealing | Precise temperature control, high uniformity |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing, sintering, melting | High-temperature capability, robust construction |
| Advanced Materials | R&D, carbonization, quality testing | Programmable profiles, versatile operational range |
| Electronics | Sintering, annealing in controlled atmospheres | Atmosphere control options, reliability |
Ready to elevate your material processing with a custom box furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in metallurgy, ceramics, or advanced research, contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results—Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is a muffle furnace utilized for AlN crystal post-processing? Optimize Surface Purity via Staged Oxidation
- Why is immediate water-quenching required after thermal simulation? Preserve (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Alloy Microstructure
- What is the function of laboratory high-temperature box furnaces in T6 aluminum treatment? Key to Material Strength
- What is the significance of the thermal environment in calcination? Achieve Pure Ceramic Phases with KINTEK
- How is a laboratory muffle furnace utilized during the debinding stage of HAp green bodies? Precision Thermal Control



















