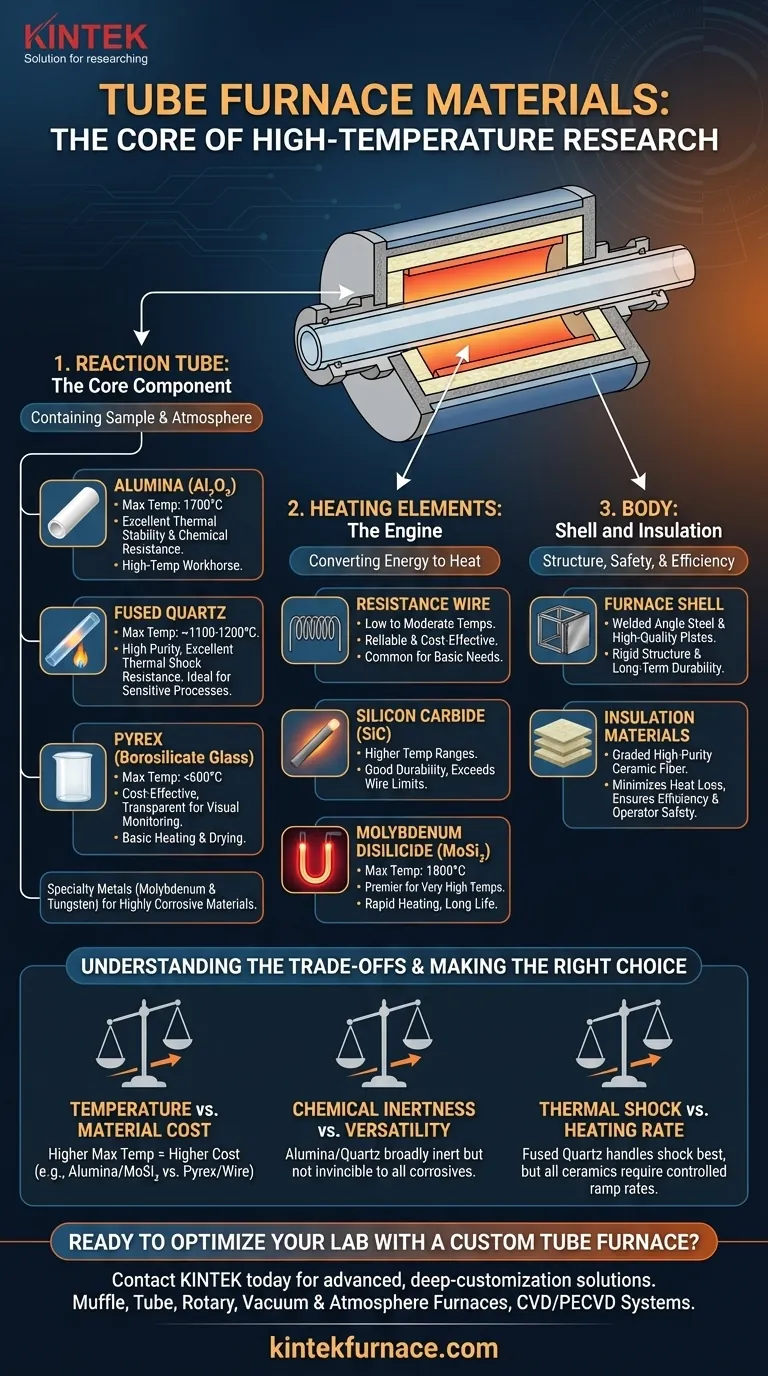
In short, a tube furnace is constructed from three primary material groups. The central reaction tube is typically made of alumina, fused quartz, or Pyrex, chosen for temperature and chemical resistance. The heating elements that surround the tube are made from materials like resistance wire, silicon carbide, or molybdenum disilicide. Finally, the outer body consists of a steel shell and high-performance ceramic fiber insulation to ensure efficiency and safety.
The selection of materials for a tube furnace is not arbitrary; it is a direct function of the intended application. The core challenge is balancing the required operating temperature, the chemical inertness needed to protect your sample, and the overall cost.

The Core Component: The Reaction Tube
The reaction tube is the heart of the furnace, containing the sample and atmosphere. Its material directly impacts the maximum temperature and the types of chemical processes you can run.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide)
Alumina is the workhorse for high-temperature applications. It offers excellent thermal stability, capable of reaching temperatures up to 1700°C.
It is also highly resistant to chemical attack, making it suitable for a wide range of experiments without risking contamination or tube degradation.
Fused Quartz
Fused quartz is prized for its high purity and excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning it can handle rapid temperature changes better than some ceramics.
While its maximum operating temperature is typically lower than alumina's (around 1100-1200°C), its inertness makes it ideal for sensitive processes where sample purity is paramount.
Pyrex (Borosilicate Glass)
Pyrex is a cost-effective option for lower-temperature work, generally below 600°C.
While it lacks the extreme heat tolerance of ceramics, it is transparent, allowing for visual monitoring of the process, and is suitable for many basic heating and drying applications.
Specialty Metals (Molybdenum & Tungsten)
For processes involving highly corrosive materials that could damage even robust ceramics, specialty metal tubes are used.
Molybdenum and tungsten tubes provide superior resistance to certain aggressive chemical environments, ensuring the integrity of both the sample and the furnace itself.
The Engine: Heating Elements
The heating elements convert electrical energy into thermal energy. The choice of material dictates the furnace's maximum temperature and heating speed.
Resistance Wire
Materials like Kanthal (an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy) are common in furnaces designed for lower to moderate temperatures. They are reliable and cost-effective.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
For higher temperature ranges, silicon carbide rods are used. They offer good durability and can operate efficiently at temperatures well beyond the limits of metallic resistance wires.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
These are the premier heating elements for very high-temperature applications (up to 1800°C). MoSi2 elements, often marketed as "Super 1800," enable rapid heating rates and have a long service life.
The Body: Shell and Insulation
The external structure provides support, safety, and thermal efficiency.
Furnace Shell
The outer body, or shell, is typically constructed from welded angle steel and high-quality steel plates. This provides the rigid structure needed to support the internal components and ensure long-term durability.
Insulation Materials
To achieve and maintain high internal temperatures efficiently, furnaces use high-performance insulation. This is often a graded package of high-purity alumina fiber or other ceramic fiber materials.
This insulation minimizes heat loss, which lowers power consumption and keeps the external shell at a safe temperature for operators.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right materials involves balancing performance requirements against practical limitations.
Temperature vs. Material Cost
There is a direct correlation between maximum operating temperature and cost. A furnace with Pyrex tubes and resistance wire is far less expensive than one with alumina tubes and molybdenum disilicide elements. Over-specifying your furnace leads to unnecessary expense.
Chemical Inertness vs. Versatility
While alumina and quartz are broadly inert, they are not invincible. Highly alkaline or specific corrosive atmospheres at high temperatures can still cause degradation. Understanding the precise chemical interactions of your process is crucial to prevent premature tube failure.
Thermal Shock vs. Heating Rate
Fused quartz is superior in handling thermal shock, but all ceramic tubes can crack if heated or cooled too quickly. The material's properties dictate the maximum safe ramp rate, which can impact process time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your experimental goal is the single most important factor in material selection.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (1200°C to 1700°C): You must select a furnace with an alumina tube and either silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and thermal shock resistance: A fused quartz tube is the ideal choice for applications up to around 1100°C.
- If your primary focus is processing corrosive materials: You will need to invest in a system with a specialized molybdenum or tungsten reaction tube.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, low-temperature heating (below 600°C): A cost-effective furnace with a Pyrex tube and standard resistance wire elements is sufficient.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of these core materials empowers you to select a tube furnace that serves as a reliable tool for achieving your scientific goals.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Tube | Alumina, Fused Quartz, Pyrex, Specialty Metals | High temp resistance, chemical inertness, thermal shock resistance |
| Heating Elements | Resistance Wire, Silicon Carbide, Molybdenum Disilicide | High temp operation, durability, rapid heating |
| Shell & Insulation | Steel, Ceramic Fiber | Structural support, thermal efficiency, safety |
Ready to optimize your lab with a custom tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace facilitate the transformation of natural wood into a Carbonized Wood carrier? Master Pyrolysis
- What are the advantages of using a condensing tube furnace for magnesium extraction? Achieve High Purity and Efficient Metal Recovery
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide during Ni-TiN catalyst calcination? Master Precise Catalysis
- What role does a high-temperature Tube Furnace play in ScSZ thin film post-treatment? Master Structural Refinement
- What is the maximum temperature for a tube furnace? Unlock the Right Heat for Your Application
- What materials are commonly used for the heating element in tubular furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- How does a horizontal electric furnace ensure precise thermal control? Achieve Superior Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a tubular furnace play in the thermal activation of sulfide ores? Precision Control for High-Yield Leaching



















