At its core, titanium's suitability for harsh environments comes from a unique and powerful combination of properties. It possesses exceptional corrosion resistance, a high strength-to-weight ratio, and thermal stability that other metals cannot easily match, making it a premier material for long-term durability under extreme stress.
The true source of titanium's resilience is not the metal itself, but the chemically inert, tenacious, and self-healing layer of titanium dioxide (TiO₂) that instantly forms on its surface. This passive film is the key to its survival in aggressive conditions.

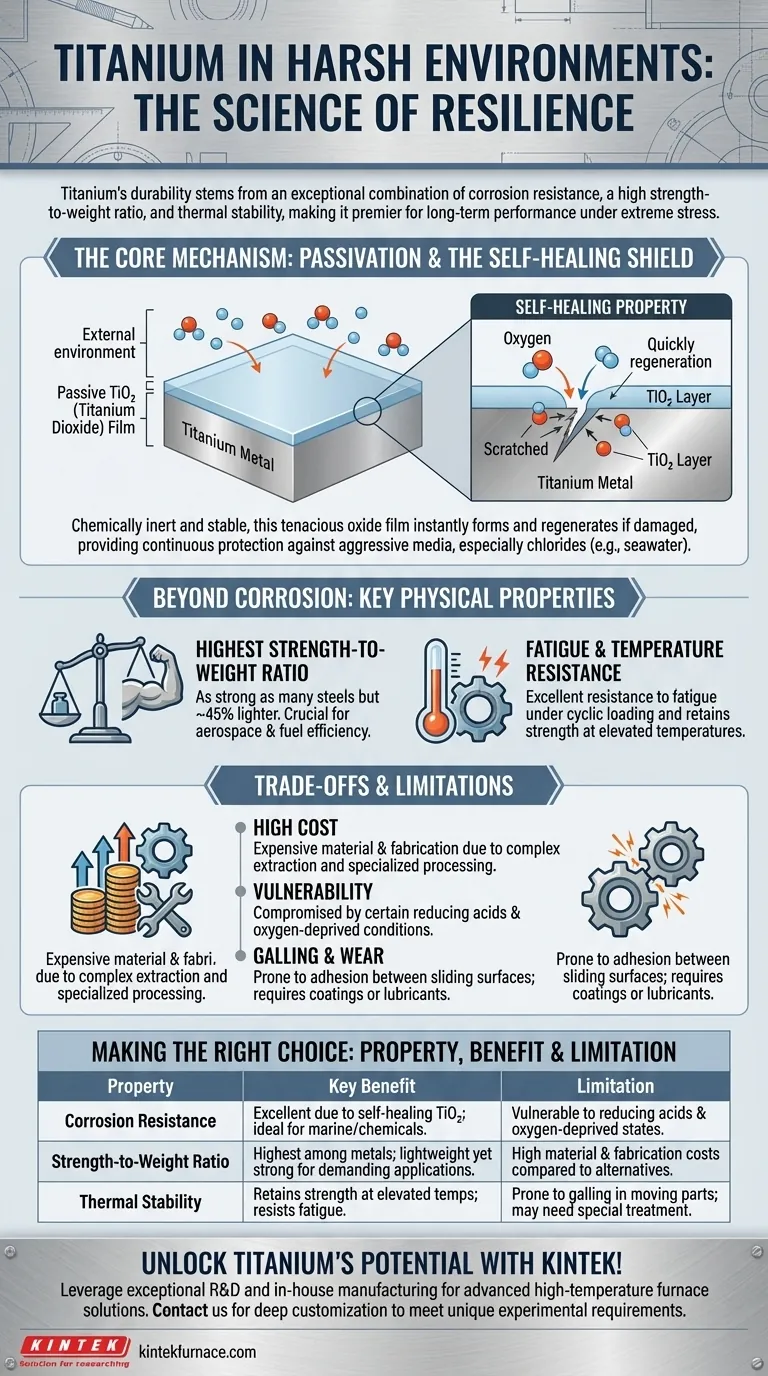
The Core Mechanism: The Power of the Oxide Layer
The secret to titanium’s legendary corrosion resistance lies in a phenomenon called passivation. This is not just a coating, but an integral part of the material itself.
How the Passive Film Forms
When titanium is exposed to oxygen in the air or water, its surface instantly reacts to form a very thin, stable, and non-porous layer of titanium dioxide (TiO₂).
This oxide film is chemically inert and tightly bonded to the base metal, acting as a formidable barrier that prevents corrosive substances from reaching and attacking the titanium underneath.
The Self-Healing Property
One of the most critical features of this oxide layer is its ability to self-heal. If the surface is scratched or damaged, the exposed titanium immediately reacts with any available oxygen to regenerate the protective film almost instantaneously.
This self-repairing nature ensures the barrier remains intact, providing continuous protection even in abrasive or dynamic environments.
Stability in Aggressive Media
The TiO₂ film is exceptionally stable, particularly against attack from chlorides, which are notoriously corrosive to most other metals, including many stainless steels.
This is why titanium excels in applications involving seawater, brine solutions, and wet chlorine gas. The passive layer remains effective where others would break down and lead to pitting or crevice corrosion.
Beyond Corrosion: Key Physical Properties
While corrosion resistance is its most famous trait, titanium’s physical characteristics are equally important for performance in demanding applications.
The Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium alloys have the highest strength-to-density ratio of any metallic element. They are as strong as many steels but are about 45% lighter.
This property is invaluable in aerospace, performance vehicles, and mobile equipment, where reducing weight is critical for fuel efficiency and performance without compromising structural integrity.
Fatigue and Temperature Resistance
Titanium exhibits excellent resistance to fatigue and cracking under cyclic loading, making it reliable for components that experience constant vibration or stress reversals.
It also retains its strength well at moderately elevated temperatures where materials like aluminum alloys would begin to weaken significantly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging titanium's limitations is critical for making an informed engineering decision.
High Cost of Material and Fabrication
Titanium is significantly more expensive than steel or aluminum. The cost is driven by the complex and energy-intensive process required to extract the metal from its ore.
Furthermore, machining and welding titanium require specialized equipment, techniques, and inert gas shielding to prevent contamination, adding to the overall fabrication cost.
Vulnerability to Specific Environments
While dominant in oxidizing or neutral environments, the protective oxide layer can be compromised by certain reducing acids (like hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acid) and in high-temperature, oxygen-deprived conditions.
Galling and Wear Resistance
Pure titanium and some of its alloys are prone to galling, a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces. In applications with moving parts, this often necessitates the use of special coatings, lubricants, or specific alloys designed for better wear resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting titanium should be a deliberate decision based on its unique advantages weighed against its costs and limitations.
- If your primary focus is marine or chemical exposure: Titanium is the definitive choice for its unmatched resistance to chloride-induced corrosion, ensuring extreme longevity.
- If your primary focus is lightweight structural performance: The superior strength-to-weight ratio of titanium alloys makes them ideal for aerospace and high-performance applications where every gram matters.
- If your primary focus is managing a tight budget: You should carefully evaluate if the extreme performance of titanium is a true necessity, as high-grade stainless steels or other alloys may offer a more cost-effective solution for less severe conditions.
Understanding these properties empowers you to specify titanium not just as a default strong material, but as the correct engineering solution for a specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent due to self-healing TiO₂ layer, ideal for seawater and chemicals | Vulnerable to reducing acids and oxygen-deprived conditions |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Highest among metals, lightweight yet strong for aerospace and vehicles | High material and fabrication costs compared to steel or aluminum |
| Thermal Stability | Retains strength at elevated temperatures, resists fatigue | Prone to galling in moving parts, may require coatings or alloys |
Unlock the full potential of titanium for your harsh environment applications with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental requirements, ensuring optimal performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your projects and deliver reliable results in extreme conditions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















