In short, quartz ceramic tubes are suitable for high-pressure applications because of a unique combination of inherent mechanical strength, extreme thermal stability, and chemical inertness. These properties work in synergy, allowing the material to resist the simultaneous stresses of pressure, high temperature, and corrosive environments that often define such demanding conditions.
The suitability of a quartz tube for high pressure is not determined by a single property, but by its holistic ability to resist mechanical, thermal, and chemical stress simultaneously. Its true strength lies in its stability when these forces are combined.
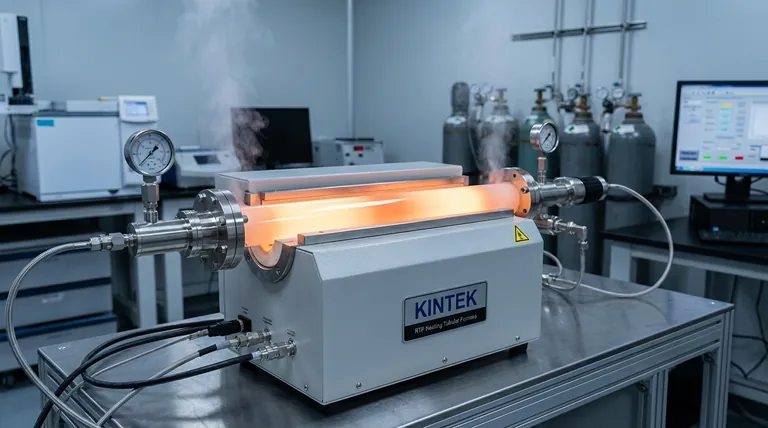

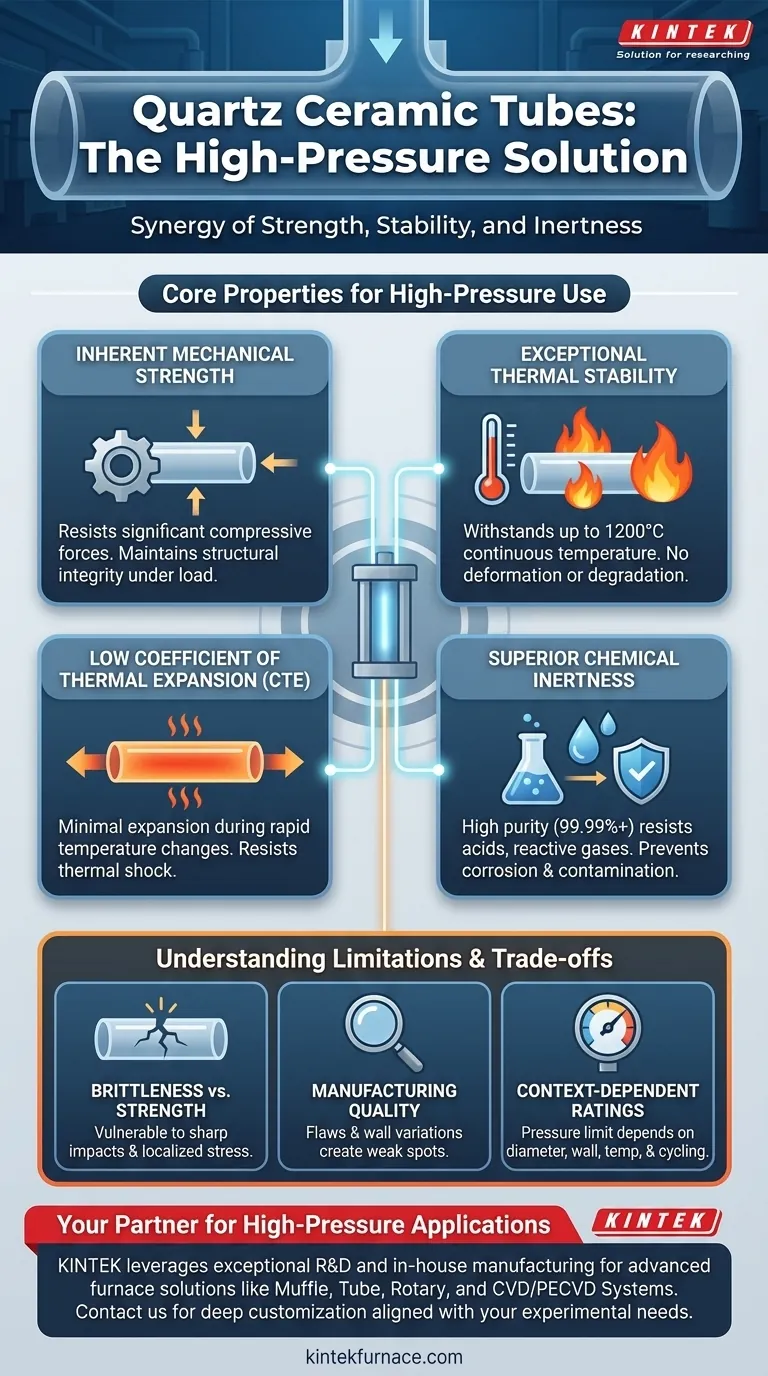
The Core Properties Enabling High-Pressure Use
To understand why quartz is a reliable choice, we must look beyond a simple strength rating. Its performance in high-pressure systems is a result of several interconnected material characteristics.
Inherent Mechanical Strength
Quartz possesses significant compressive strength, which is the fundamental ability to resist the physical force exerted by high-pressure gases or liquids. This durability ensures the tube maintains its structural integrity under load.
When properly manufactured with uniform wall thickness and no surface defects, a quartz tube can reliably contain substantial internal pressures.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
High-pressure processes frequently involve extreme heat. Quartz tubes can withstand continuous operating temperatures up to 1200°C without deforming, softening, or degrading.
This thermal stability ensures that the tube's mechanical strength is not compromised even when the system is heated, a critical factor for safety and process consistency.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
Quartz barely expands or contracts when its temperature changes. This is a crucial feature for high-pressure systems that undergo rapid heating and cooling cycles.
A low CTE minimizes internal stress buildup within the material during temperature fluctuations. This dramatically reduces the risk of thermal shock, where rapid temperature changes can cause other materials to crack and fail catastrophically.
Superior Chemical Inertness
The high purity of quartz (often 99.99%) makes it exceptionally resistant to acids, reactive gases, and other chemicals. It does not react with or corrode from contact with most substances.
In a high-pressure environment, any chemical degradation could weaken the tube wall and create a failure point. The chemical inertness of quartz preserves its structural integrity, ensuring containment is not compromised from the inside out.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While quartz is a powerful material, no choice is without compromise. Acknowledging its limitations is critical for safe and effective implementation.
Brittleness vs. Strength
Like many ceramics, quartz is strong but brittle. It resists uniform pressure well but is vulnerable to catastrophic failure from sharp impacts or localized stress points.
A small surface scratch or internal flaw can act as a stress concentrator, significantly reducing the tube's effective pressure rating and making it susceptible to shattering under pressure.
The Critical Role of Manufacturing Quality
The performance of a quartz tube is directly tied to its manufacturing quality. The "excellent tolerances" and high purity mentioned in specifications are not just marketing points—they are critical for safety.
Inclusions, bubbles, or variations in wall thickness can create weak spots. For any high-pressure application, sourcing tubes from a reputable manufacturer with certified quality control is non-negotiable.
Pressure Ratings Are Context-Dependent
There is no single "high-pressure rating" for quartz. The maximum allowable pressure for any given tube is a function of its diameter, wall thickness, operating temperature, and the specific cycling conditions of the application.
Always consult the manufacturer's engineering data. You must verify that the specific tube's specifications meet or exceed the calculated requirements for your unique operational parameters.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct quartz tube requires aligning the material's properties with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum pressure and safety: Prioritize tubes with greater wall thickness, a flawless surface finish, and certified pressure ratings from the manufacturer.
- If your primary focus is process purity: Select a tube with the highest available purity (e.g., 99.99%+) to prevent sample contamination from material leaching.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal cycling: Confirm the material has an extremely low CTE and is specifically rated for high thermal shock resistance.
Ultimately, choosing the right quartz tube is about matching its proven material strengths to the specific combination of stresses in your application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit for High-Pressure Applications |
|---|---|
| Inherent Mechanical Strength | Resists compressive forces to maintain structural integrity under pressure |
| Exceptional Thermal Stability | Withstands temperatures up to 1200°C without deformation or degradation |
| Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | Minimizes internal stress and thermal shock risk during temperature changes |
| Superior Chemical Inertness | Prevents corrosion and maintains purity in harsh chemical environments |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your lab's unique high-pressure requirements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental needs, enhancing safety and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment
- What happens to convective and radiative heat transfer effects at high furnace gas temperatures? Radiation Dominates for Superior Heating



















