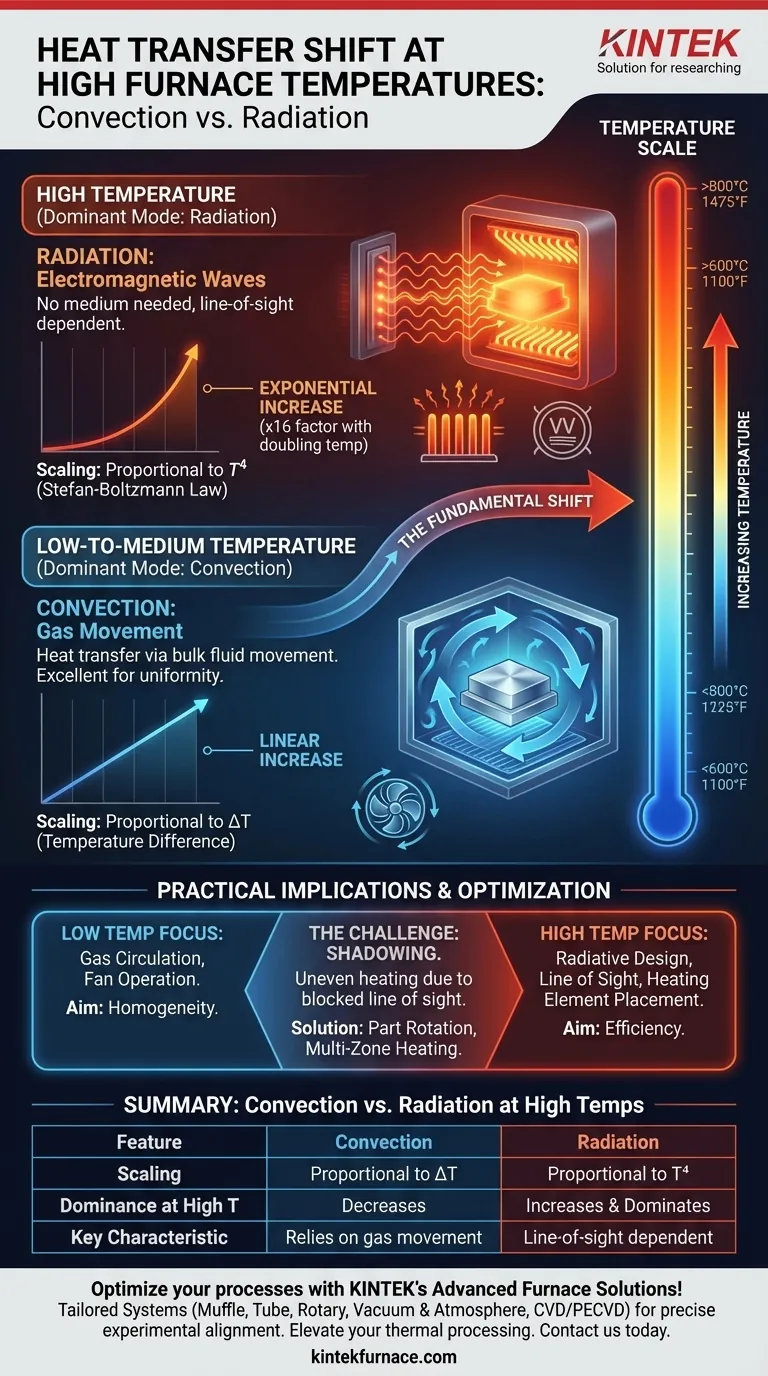
At high furnace temperatures, the physics of heat transfer undergoes a fundamental shift. While convective heat transfer's relative impact decreases, radiative heat transfer increases dramatically, quickly becoming the dominant mechanism for heating the workpiece.
The core principle to grasp is that heat transfer is not a single process. As temperatures escalate, the mechanism shifts from being dominated by the movement of hot gas (convection) to being governed by the emission of electromagnetic energy (radiation), a change with profound implications for furnace design and material processing.

The Two Modes of Heat Transfer in a Furnace
To understand the shift, we must first clearly define the two processes at play inside a typical furnace.
Convection: The Role of Gas Movement
Convection is heat transfer through the bulk movement of a fluid—in this case, the furnace atmosphere.
Hot gas molecules circulate within the chamber, transferring their thermal energy to the cooler workpiece upon contact. As noted in the references, this process is excellent for maintaining a uniform temperature and accelerating heat transfer at lower temperatures.
Radiation: The Power of Electromagnetic Waves
Radiation is heat transfer via electromagnetic waves (specifically infrared radiation). It requires no medium to travel.
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The hotter the object, the more energy it radiates. This energy travels at the speed of light and is absorbed by other objects in its "line of sight."
Why Radiation Dominates at High Temperatures
The transition from convection to radiation is not arbitrary; it is governed by fundamental physical laws.
The T⁴ Relationship (Stefan-Boltzmann Law)
The key is how each mechanism scales with temperature. Radiative heat transfer is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature (T⁴).
In contrast, convective heat transfer is roughly proportional to the simple temperature difference (ΔT) between the hot gas and the workpiece.
A Practical Comparison
Because of this T⁴ relationship, even a modest increase in temperature has an exponential effect on radiation.
If you double the absolute temperature of a furnace, the potential for convective heat transfer roughly doubles. However, the potential for radiative heat transfer increases by a factor of 16 (2⁴). This massive increase quickly overwhelms the linear gains of convection.
The Relative Decline of Convection
At extreme temperatures, radiation becomes so powerful and efficient that convection's contribution becomes a small fraction of the total energy being transferred.
This is why its effect is said to "decrease"—not because it stops working, but because it is dwarfed by the immense power of radiation.
Understanding the Practical Implications
This shift from convection to radiation is not merely academic. It dictates how high-temperature furnaces must be designed and operated.
Designing for Radiation
In high-temperature applications, furnace design must prioritize managing radiation. This involves the careful selection and placement of heating elements to ensure they have a clear line of sight to the workpiece.
The choice of refractory and insulation materials also becomes critical, as their ability to reflect or absorb radiative energy directly impacts furnace efficiency and temperature uniformity.
The Challenge of "Shadowing"
A major trade-off is the risk of uneven heating. Since radiation travels in straight lines, any part of the workpiece that is "shadowed" from the heating elements will receive significantly less energy.
This can create hot and cold spots, which is why part rotation or furnaces with heating elements on multiple sides are common in high-temperature processes.
The Extreme Case: Vacuum Furnaces
A vacuum furnace is the ultimate example of radiative dominance. By removing the atmosphere, convection is almost completely eliminated.
In this environment, heat transfer occurs almost exclusively through radiation. This makes the design of heating elements and thermal shielding the absolute primary concern for achieving efficient and uniform heating.
Optimizing Your Furnace for the Dominant Heat Transfer Mode
Your operational strategy must align with the physics governing your target temperature range.
- If your primary focus is low-to-medium temperature uniformity (below ~600°C / 1100°F): Ensure proper gas circulation and fan operation to maximize the homogenizing effect of convective heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature efficiency (above ~800°C / 1475°F): Prioritize the design, placement, and condition of heating elements to maximize direct line-of-sight radiative energy transfer to the workpiece.
- If your primary focus is preventing uneven heating at high temperatures: Implement strategies like part rotation or multi-zone heating to counteract radiative shadowing and ensure all surfaces are heated evenly.
By understanding which heat transfer mechanism is in control, you can master your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mode | Scaling with Temperature | Dominance at High Temperatures | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convection | Proportional to ΔT | Decreases | Relies on gas movement, uniform at lower temps |
| Radiation | Proportional to T⁴ | Increases and dominates | No medium needed, line-of-sight dependent |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can elevate your thermal processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















