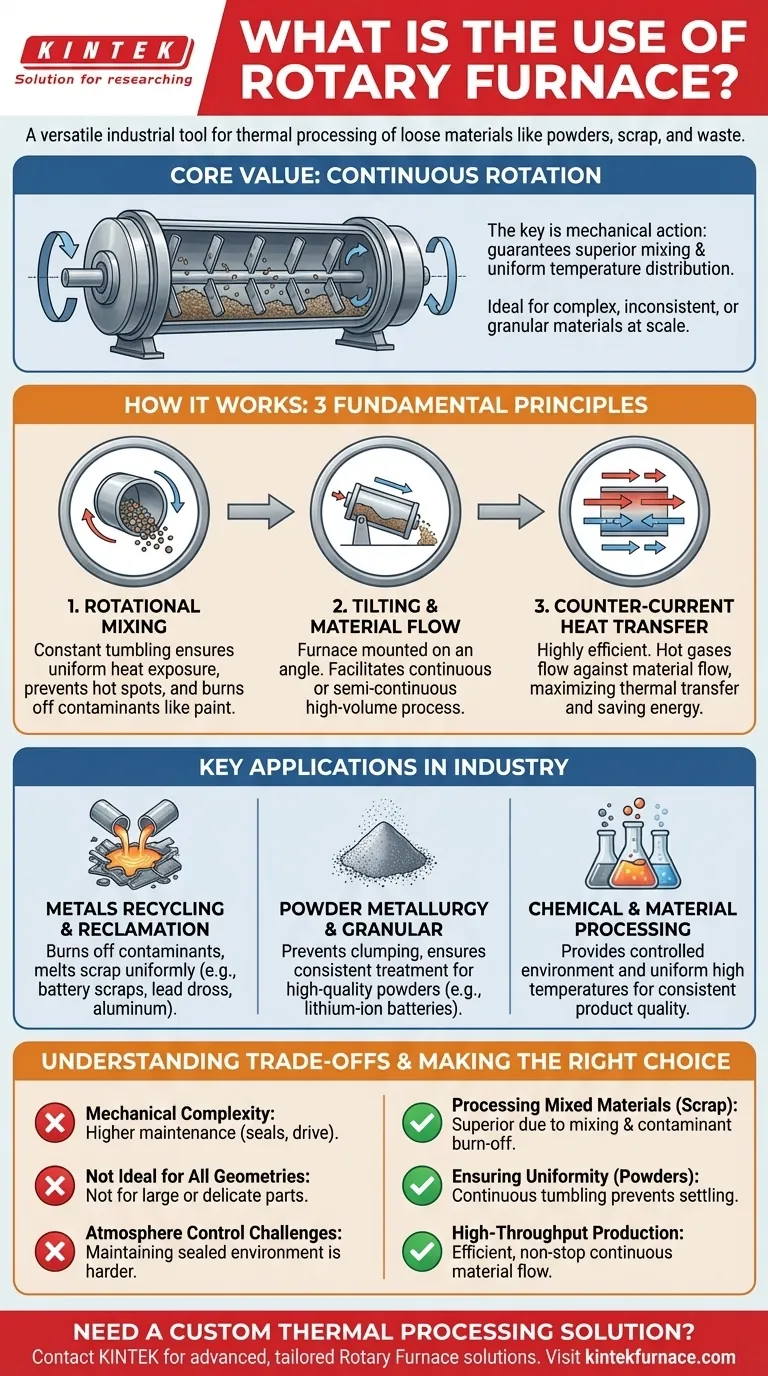
In essence, a rotary furnace is a highly versatile industrial tool used for thermal processing of loose materials like powders, scrap metal, and industrial waste. Its primary applications are found in metals recycling, powder metallurgy, and chemical processing, where its unique ability to mix and heat materials simultaneously provides significant advantages over static furnace designs.
The core value of a rotary furnace is not simply its ability to generate heat, but its continuous rotation. This mechanical action guarantees superior mixing and uniform temperature distribution, making it the ideal solution for processing complex, inconsistent, or granular materials at scale.

How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Its Versatility
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace comes from three fundamental design principles working in concert. These principles are what separate it from a standard box furnace.
The Principle of Rotational Mixing
A rotary furnace is a large, rotating cylinder, similar in concept to an industrial dryer or cement mixer. As the furnace barrel rotates, it continuously tumbles the material inside.
This constant agitation ensures that every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source. It prevents hot spots and ensures that volatile components, like paint or plastics on scrap metal, are effectively burned off.
The Role of Tilting and Material Flow
The furnace is mounted on a slight angle. This tilt, combined with the rotation, causes the material to gradually move from the charging end to the discharge end.
This design facilitates a continuous or semi-continuous process, making it highly efficient for high-volume industrial applications. Operators can continuously feed raw material in one end and collect the processed material at the other.
Efficient Heat Transfer with Counter-Current Flow
Heat is typically introduced by a burner or hot gases, which often flow in the opposite direction of the material. This "counter-current" design is extremely efficient.
As the hot gas travels through the furnace, it transfers its heat to the material. The coolest material entering the furnace meets the coolest gas, while the hottest material about to exit meets the hottest gas, maximizing the thermal transfer efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Key Applications in Industry
The unique combination of mixing, movement, and efficient heating makes the rotary furnace indispensable in several sectors.
Metals Recycling and Reclamation
This is a primary use case. The furnace's ability to handle diverse feed materials is critical for recycling battery scraps, lead dross, and blast furnace waste.
In aluminum recycling, it excels at melting scrap that may still have paint, lacquer, or plastic coatings. The rotational mixing helps burn off these contaminants while ensuring the metal melts uniformly.
Powder Metallurgy and Granular Materials
For processes like calcining, roasting, or drying powders, uniformity is paramount. A static furnace can lead to settled layers and inconsistent results.
The rotary furnace’s tumbling action prevents clumping and guarantees that every granule is treated identically. This is essential for producing high-quality powders used in applications like lithium-ion battery manufacturing.
Chemical and Material Processing
The furnace provides a controlled environment for various chemical reactions that require high temperatures. Its ability to achieve and maintain uniform temperature throughout a batch is critical for consistent product quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating barrel, seals, and drive system introduce more mechanical complexity than a static furnace. This can lead to higher maintenance requirements to ensure the rotating seals and drive train remain in good working order.
Not Ideal for All Geometries
This furnace is specifically designed for materials that can tumble freely. It is not suitable for processing large, single, or delicate parts that would be damaged by the tumbling action or cannot be fed into the system.
Atmosphere Control
While possible, maintaining a perfectly sealed, controlled atmosphere inside a rotating furnace can be more challenging than in a static, sealed chamber. The dynamic seals at either end of the barrel are critical points of potential leakage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace technology depends entirely on the material you are processing and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is processing mixed or non-uniform materials (like scrap metal): The rotary furnace is superior due to its ability to mix, burn off contaminants, and melt feedstock uniformly.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process uniformity for powders or granules: The furnace's continuous tumbling action is the most effective way to prevent settling and achieve consistent results.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous production: Its tilted, rotating design enables an efficient, non-stop flow of material perfect for large-scale industrial operations.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace is a specialized tool engineered to solve the difficult problem of uniformly heating materials that do not stay still.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Metals Recycling | Burns off contaminants, melts scrap uniformly |
| Powder Metallurgy | Prevents clumping, ensures consistent granule treatment |
| Chemical Processing | Provides controlled, uniform high-temperature reactions |
| High-Volume Production | Enables continuous, efficient material flow |
Need a custom thermal processing solution for your materials?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced rotary furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you're in metals recycling, powder processing, or chemical production, our expertise ensures superior mixing, uniform heating, and high-throughput efficiency.
Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, and more, all backed by deep customization capabilities. Let us help you optimize your industrial process—contact our experts today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What makes rotary tube furnaces user-friendly? Achieve Superior Process Uniformity and Efficiency
- What is the purpose of the rotating device in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Efficient Mixing
- What temperature capabilities and control features do rotary tube furnaces offer? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Your Lab
- How do material properties influence rotary kiln design? Optimize Efficiency and Reliability
- What are some specialized applications of rotary furnaces? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis and Environmental Solutions
- Can metal materials be processed in a rotary kiln without nitriding? Yes, with inert atmosphere control.
- How does material processing occur in a rotary furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Efficient Mixing
- What is the working principle of a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion



















