In short, the rotating device in a rotary tube furnace serves one primary purpose: to turn the central tube during heating. This rotation is fundamental to the furnace's operation, as it continuously tumbles the material inside, ensuring every particle is heated uniformly and thoroughly mixed.
The core function of rotation is to solve the inherent problem of uneven heating found in static furnaces. By creating a dynamic environment, rotation guarantees superior temperature uniformity and process consistency, leading to higher quality results and more efficient processing.

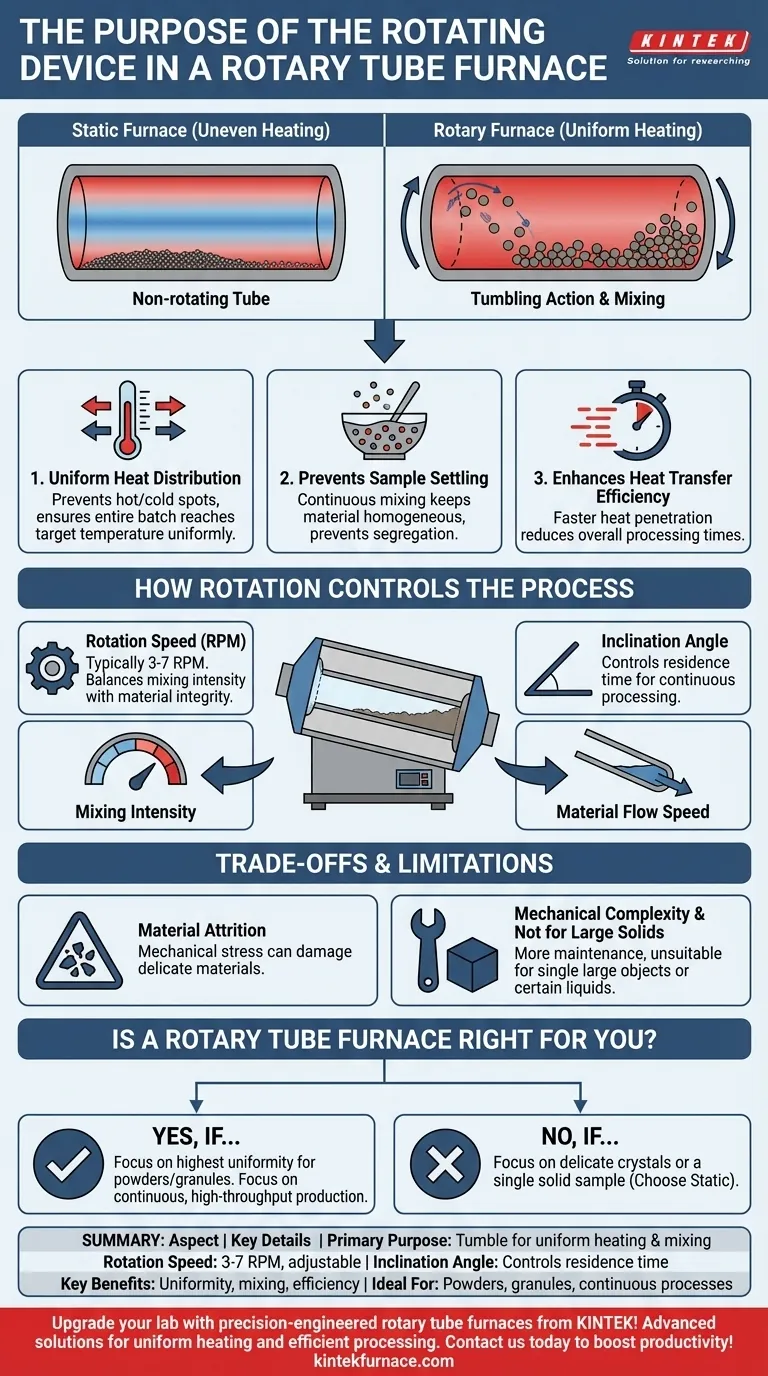
The Core Principle: Overcoming Static Heating Limitations
A standard, non-rotating furnace heats material from the outside in. This often creates a temperature gradient where the material touching the furnace wall is much hotter than the material in the center, leading to inconsistent results. The rotating mechanism directly solves this challenge.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Distribution
The constant tumbling action exposes all surfaces of the sample material to the hot inner wall of the tube. This prevents localized hot spots and cold spots, ensuring that the entire batch reaches the target temperature uniformly.
Preventing Sample Settling
For powders, granules, or multi-component mixtures, gravity is an enemy in a static furnace, causing denser particles to settle. The rotation acts as a continuous mixing force, keeping the material homogeneous and preventing segregation or incomplete reactions.
Enhancing Heat Transfer Efficiency
By constantly disturbing the material, the rotation breaks up the bulk sample and improves heat penetration. This enhanced heat transfer allows the material to reach its target temperature faster, significantly reducing overall processing times compared to a static furnace.
How Rotation Controls the Process
The rotating mechanism isn't just an on/off feature; it's a variable that gives you precise control over the material processing environment. Operators can fine-tune the furnace's behavior by adjusting two key parameters.
The Role of Rotation Speed (RPM)
The speed, typically between 3 to 7 RPM, dictates the degree of mixing. A higher speed provides more aggressive tumbling, which can enhance heat transfer but may also cause damage to delicate materials. Adjusting the speed allows you to balance mixing intensity with material integrity.
The Impact of Inclination Angle
Many rotary tube furnaces can be tilted. This inclination angle, combined with rotation, controls the residence time—how long the material spends inside the heated zone. A steeper angle causes material to flow through more quickly, making it ideal for continuous processing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, the rotating mechanism introduces considerations that are not present in simpler static furnaces.
Material Attrition
The primary trade-off is mechanical stress. The tumbling action can cause delicate, brittle, or friable materials to break down, a phenomenon known as attrition. This makes rotary furnaces unsuitable for processing materials where particle size and shape must be perfectly preserved.
Increased Mechanical Complexity
A rotating system involves motors, drives, and specialized seals to contain the atmosphere within the moving tube. This added complexity requires more maintenance than a simple, static tube furnace.
Unsuitability for Certain Samples
Rotary furnaces are designed for particulate matter like powders and granules. They are not appropriate for processing a single large solid object or certain liquids where the tumbling action is not beneficial.
Is a Rotary Tube Furnace Right for Your Process?
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on your material and your goal. The rotation is the key differentiating factor.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible uniformity for powders or granules: A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice for ensuring every particle receives identical thermal treatment.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-throughput production: The ability to control material flow via rotation and inclination makes a rotary furnace ideal for moving beyond slow, batch-based processes.
- If your primary focus is processing delicate crystals or a single solid sample: You should choose a static tube furnace to avoid the mechanical damage caused by the tumbling action.
Ultimately, the rotating device transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a dynamic processing reactor, offering unparalleled control over material uniformity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Turns the tube to tumble material for uniform heating and mixing |
| Rotation Speed | Typically 3-7 RPM, adjustable for mixing intensity |
| Inclination Angle | Controls residence time for continuous processing |
| Key Benefits | Uniform heat distribution, prevents settling, enhances heat transfer |
| Limitations | Material attrition, mechanical complexity, unsuitable for large solids |
| Ideal For | Powders, granules, continuous high-throughput processes |
Upgrade your lab with precision-engineered rotary tube furnaces from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced solutions like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for uniform heating and efficient processing. Don't settle for inconsistent results—contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your material processing and boost productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces enhance efficiency in materials processing? Boost Throughput and Quality
- What are the advantages of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Material Processing
- How is the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace used in the carbon activation process? Achieve Uniform, High-Porosity Activated Carbon
- What optional features enhance the processing capabilities of rotary tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Advanced Customizations
- What makes rotary tube furnaces user-friendly? Achieve Superior Process Uniformity and Efficiency



















