At its core, a rotary kiln is not a generic machine; it is a custom-engineered solution shaped entirely by the material it processes. The thermal, physical, and chemical properties of your material directly dictate every major design decision, from the kiln's physical dimensions and energy requirements to the power of its mechanical drive system. Understanding these properties is the first and most critical step in designing an efficient and reliable thermal processing system.
The design of a rotary kiln is a direct translation of a material's physical and thermal characteristics into mechanical specifications. Misinterpreting these properties leads to process inefficiency, high operating costs, and poor product quality.

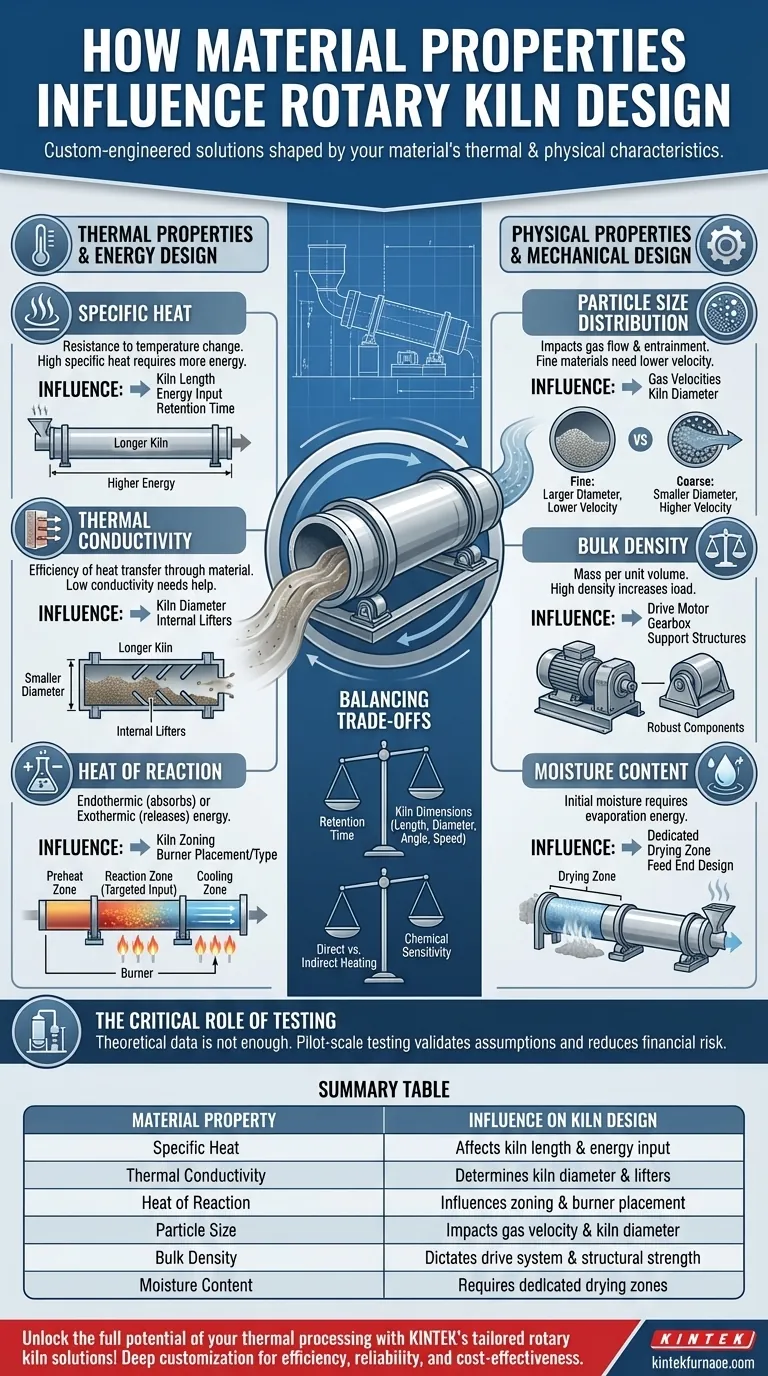
The Foundation: Thermal Properties and Energy Design
The primary function of a kiln is to transfer heat. Therefore, how a material responds to thermal energy is the most fundamental consideration, directly influencing the kiln's length, diameter, and fuel consumption.
Specific Heat
Specific heat measures a material's resistance to temperature change. A material with high specific heat requires more energy to heat up.
This directly translates to a need for either a longer kiln to increase retention time, a higher energy input from the burner, or a combination of both to ensure the material reaches its target temperature.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is how efficiently heat transfers through the material bed. This property is crucial for ensuring the entire volume of material is processed evenly.
If a material has low thermal conductivity, heat struggles to penetrate from the surface to the core. This may force the design toward a smaller kiln diameter to reduce the depth of the material bed, or require internal lifters that cascade the material to improve mixing and heat exposure.
Heat of Reaction
Many processes involve chemical reactions that either consume energy (endothermic) or release it (exothermic).
An endothermic reaction requires a significant, targeted energy input at a specific point in the process. This influences the zoning of the kiln and the placement or type of burner. An exothermic reaction may require controlled airflow or other design features to manage the release of heat and prevent overheating.
Shaping the Machine: Physical Properties and Mechanical Design
A material's physical form dictates how it moves through the kiln and the mechanical stress it places on the equipment. These properties influence the kiln's size, angle, and structural components.
Particle Size Distribution
The size of the material particles has a profound impact on gas flow and material handling.
Fine materials and powders can become easily entrained in the hot process gas flowing through the kiln. This necessitates lower gas velocities, which in turn requires a larger kiln diameter to handle the required throughput. Conversely, pelletized or coarse feeds can tolerate higher gas velocities, allowing for a smaller, more cost-effective kiln diameter.
Bulk Density
Bulk density is the mass of the material per unit of volume. This simple metric has major consequences for the kiln's structural and mechanical design.
A high-density material places immense weight on the entire system. This requires more robust—and more expensive—components, including the drive motor, gearbox, support tires, and trunnion wheels. Underestimating bulk density can lead to premature mechanical failure.
Moisture Content
For processes involving drying, the initial moisture content is a critical energy factor.
A high moisture content requires a large amount of energy simply for evaporation. This often dictates the design of the kiln's feed end, which may be configured as a dedicated drying zone before the material moves into the higher-temperature reaction zones.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing a kiln is an exercise in balancing interconnected variables. Changing one parameter to accommodate a material property will inevitably affect another.
Retention Time vs. Kiln Dimensions
The time a material must spend in the kiln to be processed, known as retention time, is a direct outcome of its thermal properties. This is achieved by manipulating four key design variables: kiln length, diameter, inclination angle, and rotational speed.
For example, a material that heats slowly might require a 20-minute retention time. This could be achieved with a very long, slow-turning kiln or a shorter kiln with a shallower angle of inclination. The final choice depends on balancing capital cost, plant footprint, and operational efficiency.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The choice between a direct-fired kiln (where combustion gas contacts the material) and an indirect-fired kiln (where the shell is heated from the outside) is determined by the material's chemical sensitivity.
If a material cannot be exposed to combustion byproducts, an indirect kiln is mandatory. This completely changes the heat transfer mechanism, efficiency, and overall construction of the unit, making it a pivotal, material-dependent decision.
The Critical Role of Testing
The references make it clear: theoretical data is not enough. If the material's behavior under heat is not well-documented, proceeding without testing is a significant financial risk.
Pilot-scale testing is used to validate all the material property assumptions. It refines the required retention time, temperature profile, and off-gas characteristics, providing the empirical data needed to design a commercial-scale kiln that will perform as expected.
How to Ensure an Optimal Kiln Design
To translate material properties into a successful design, you must prioritize the right data for your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Prioritize accurate thermal data (specific heat, conductivity, heat of reaction) to correctly size the kiln length and energy systems, avoiding over- or under-processing.
- If your primary focus is mechanical reliability and operational cost: Pay close attention to physical properties like bulk density and particle size to ensure the drive system and structural supports are not undersized for the load.
- If you are working with a new or unproven material: Insist on pilot-scale testing to generate empirical data and validate all assumptions before committing to a full-scale design.
A successful thermal processing operation begins with a deep, data-driven understanding of the material itself.
Summary Table:
| Material Property | Influence on Kiln Design |
|---|---|
| Specific Heat | Affects kiln length and energy input for proper heating |
| Thermal Conductivity | Determines kiln diameter and use of internal lifters |
| Heat of Reaction | Influences zoning and burner placement |
| Particle Size | Impacts gas velocity and kiln diameter |
| Bulk Density | Dictates drive system and structural strength |
| Moisture Content | Requires dedicated drying zones and energy planning |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processing with KINTEK's tailored rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your kiln design precisely meets your material's unique properties, boosting efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Don't leave your process to chance—contact us today to discuss your needs and see how we can optimize your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions



















