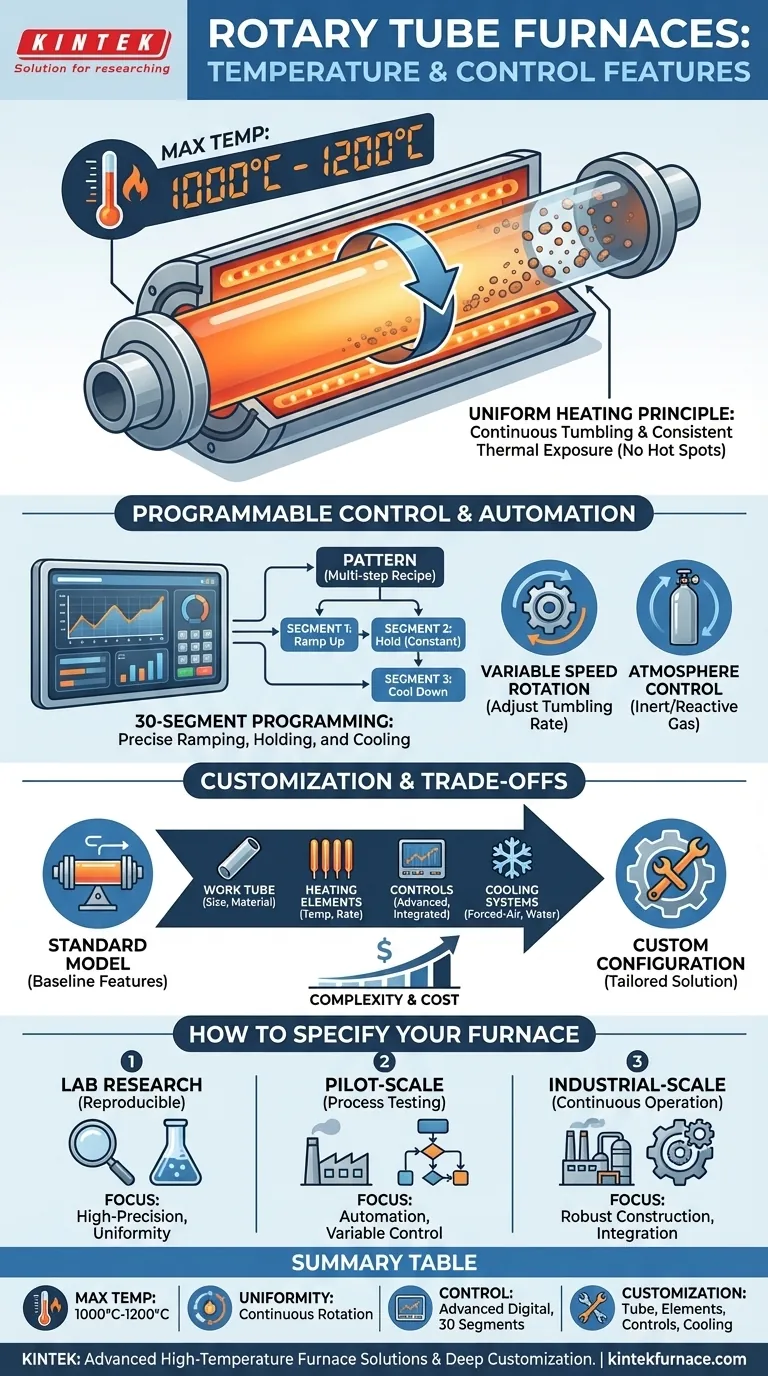
At their core, rotary tube furnaces provide high-temperature processing capabilities, typically reaching a maximum of 1000°C to 1200°C, depending on the work tube material. This thermal capacity is governed by advanced digital controllers that ensure precise temperature regulation and enable highly specific, programmable heating and cooling cycles for uniform material processing.
The true value of a rotary tube furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity for dynamic, uniform heating. The combination of physical rotation and programmable control allows for exceptionally consistent and repeatable thermal treatment of loose or powdered materials.

Deconstructing Thermal Capabilities
To understand if a rotary tube furnace meets your needs, you must first break down its core thermal components and how they work together.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The furnace's peak temperature is fundamentally limited by its construction, primarily the work tube material. Common options include stainless steel or quartz tubes, which generally allow for a maximum operating temperature between 1000°C and 1200°C.
The Principle of Uniform Heating
A key advantage of this furnace type is its ability to deliver exceptionally uniform heating. The cylindrical design and constant, slow rotation of the tube ensure that the material inside is continuously tumbled. This dynamic movement prevents hot spots and guarantees that the entire sample is exposed to the same temperature conditions, which is critical for consistent results.
The Role of Advanced Digital Controllers
Modern rotary tube furnaces are equipped with intelligent or automated control systems. These digital controllers are the brain of the operation, precisely managing temperature, heating rates, and holding times. This level of automation simplifies operation and significantly reduces the risk of human error.
Mastering Processes with Programmable Control
The most powerful feature of these furnaces is the ability to program complex thermal profiles. This moves beyond simple heating to executing a precise, multi-step recipe.
Understanding Segments and Patterns
Many controllers offer 30-segment programming, often arranged as two patterns of 15 segments each. A "segment" is a single step in your thermal process, such as ramping the temperature up at a specific rate, holding it at a constant temperature for a set duration, or cooling it down.
A "pattern" is a sequence of these segments that forms a complete process cycle. This programmability allows you to design and automate highly customized heating, constant temperature, and cooling processes tailored to your material's specific needs.
Integrating Speed and Atmosphere Control
Effective thermal processing is about more than just temperature. Many furnaces integrate other critical controls:
- Variable Speed Rotation: DC variable speed control allows you to adjust the tumbling rate of the material. This can be crucial for optimizing heat transfer and preventing material degradation.
- Atmosphere Control: For sensitive processes, the ability to introduce and manage an inert or reactive gas atmosphere inside the tube is essential. This is often available as a custom feature.
Understanding Customization and Trade-offs
While standard models are available, the true strength of rotary tube furnaces often lies in their adaptability to specific applications.
Standard vs. Custom Configurations
Off-the-shelf furnaces provide a baseline of features, but many research and industrial processes have unique requirements that demand a tailored solution. Customization allows you to build a tool that precisely matches your objective.
Key Areas for Customization
Nearly every aspect of the furnace can be modified to meet specific needs. Common customizations include:
- Work Tube: Adjustments to the size, shape, and material.
- Heating Elements: Selection based on required temperature and ramp rates.
- Controls: Upgrading controllers or integrating them with other lab systems.
- Cooling Systems: Adding forced-air or water-cooling systems for faster cycle times.
The Impact on Complexity and Cost
It is important to recognize that every customization adds a layer of complexity and cost to the system. While a highly tailored furnace can deliver superior results, it requires a clear understanding of your process parameters to justify the investment.
How to Specify the Right Furnace for Your Goal
Use your primary objective to guide your selection and customization choices.
- If your primary focus is reproducible lab research: Prioritize a high-precision programmable controller with multi-segment capabilities and ensure the system guarantees temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is pilot-scale production: Focus on automation features, variable speed rotation, and the option for atmosphere control to test process variables.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale processing: Emphasize robust construction for continuous operation, deep customization of all parameters, and integration with plant-wide control systems.
Ultimately, selecting the right rotary tube furnace is about matching its control precision to the specific demands of your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | 1000°C to 1200°C, depending on work tube material |
| Heating Uniformity | Ensured by cylindrical design and constant rotation to prevent hot spots |
| Control Systems | Advanced digital controllers with programmable segments (e.g., 30 segments) |
| Programmability | Supports multi-step thermal profiles for heating, holding, and cooling |
| Additional Controls | Variable speed rotation and atmosphere control for optimized processing |
| Customization | Options for work tube, heating elements, controls, and cooling systems |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with a tailored rotary tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your material processing with reliable, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















