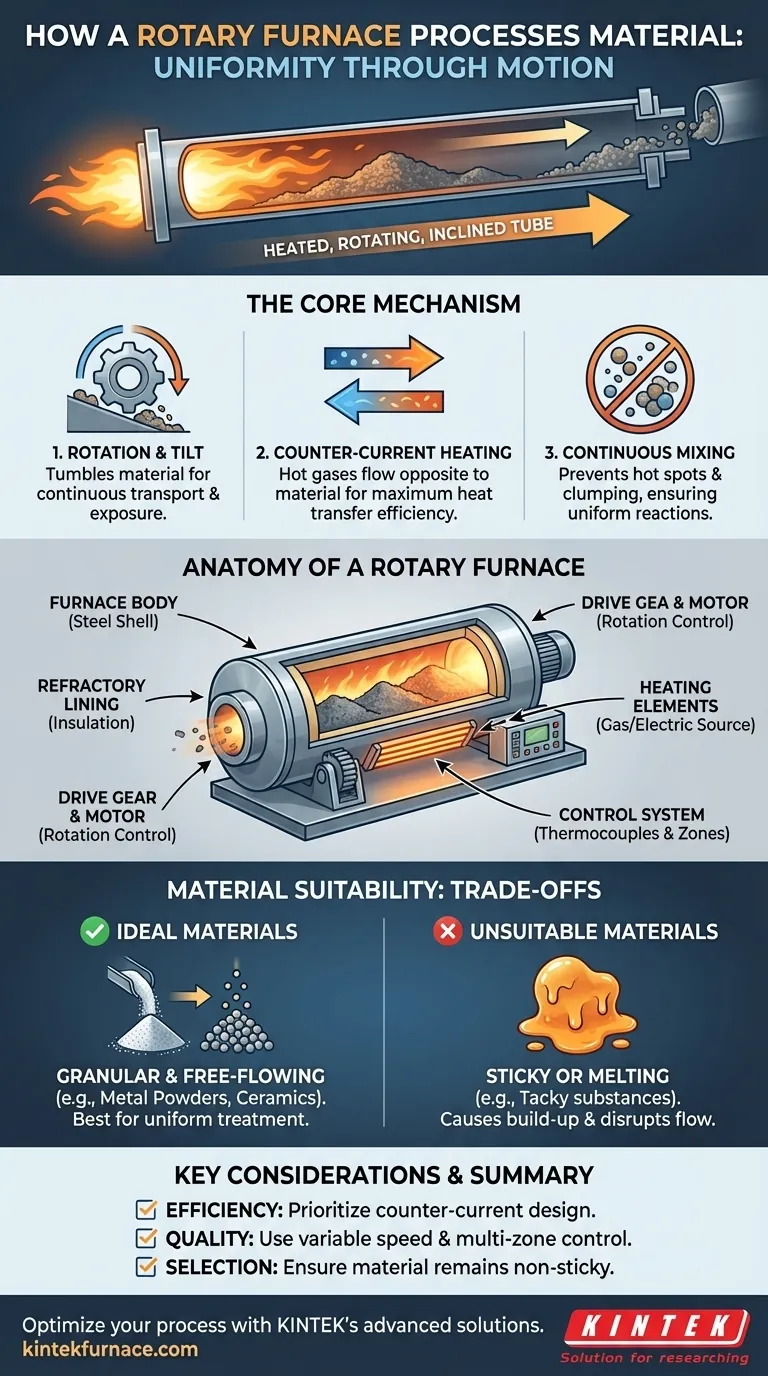
At its core, a rotary furnace processes material by tumbling it continuously through a heated, rotating, and slightly inclined tube. This mechanism combines constant material transport with aggressive mixing, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to a controlled thermal environment as it moves from the furnace inlet to the outlet.
The defining principle of a rotary furnace is not just heating, but achieving exceptional thermal uniformity through constant motion. This design ensures that granular or particulate materials are processed consistently, preventing the hot spots, clumping, and sticking that can compromise results in static furnace designs.

How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Uniform Processing
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace comes from the interplay of its mechanical movement and thermal design. It is engineered to solve the problem of uneven heating common in batch processes.
The Role of Rotation and Tilt
A rotary furnace is a cylindrical chamber that rotates slowly around its central axis. This chamber is also set at a slight downward angle.
The combination of rotation and tilt forces the material inside to tumble and cascade forward. This ensures the material travels the entire length of the furnace for continuous processing.
The Counter-Current Heating Principle
Heat is typically supplied by gas burners or electric elements. In many designs, hot gases flow in the counter-current direction—opposite to the movement of the material.
This strategy is highly efficient. It ensures that the coldest material entering the furnace meets the coolest gases, and the hottest material leaving the furnace meets the hottest gases, maximizing heat transfer along the entire tube.
The Benefit of Continuous Mixing
The tumbling action is the most critical aspect for material quality. It constantly exposes new particle surfaces to the heat source and the internal atmosphere.
This prevents any single particle from overheating, ensures even chemical reactions (like in calcination or smelting), and stops material from sticking to the hot furnace walls or forming clumps.
The Anatomy of a Rotary Furnace
A rotary furnace is a system of integrated components, each with a specific function designed for reliability and control at high temperatures.
The Furnace Body and Lining
The outer structure is the furnace body, typically a steel barrel of variable length depending on the application's required residence time.
Inside this steel shell is a furnace lining made of refractory materials like high-temperature bricks or castable cement. This lining insulates the furnace and resists the extreme heat and corrosive environments of the process.
The Drive Mechanism
A drive gear connected to a motor is responsible for the furnace's rotation.
Most modern systems feature a variable speed drive. This allows operators to precisely control the rotation speed, which in turn adjusts the residence time—how long the material spends inside the furnace.
The Heating and Control System
The heat source can be a series of gas burners or electric heating elements positioned to apply heat via conduction, convection, and radiation.
A sophisticated control system uses thermocouples to measure the internal temperature. These measurements are sent to a controller, which adjusts the power to the heating elements to maintain a precise, pre-programmed temperature profile. Many furnaces feature multi-zone heating for even greater control along the tube's length.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Suitability
While powerful, the rotary furnace design is not universally applicable. Its primary strength—continuous tumbling—is also its main limitation.
Ideal Materials: Granular and Free-Flowing
Rotary furnaces excel at processing materials that are granular or particulate and remain free-flowing at high temperatures.
Examples include metal powders, ceramics, glass, oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and various carbides. The process is ideal for applications like smelting, drying, or calcination where uniform treatment of individual particles is key.
Unsuitable Materials: The Stickiness Problem
The primary constraint is material behavior at processing temperature. Materials that become sticky, tacky, or begin to melt into a single mass are not suitable for a rotary furnace.
Sticky materials will adhere to the furnace walls and build up, disrupting flow and heat transfer, eventually forcing a shutdown for cleaning.
Key Considerations for Your Application
When evaluating or operating a rotary furnace, your material's properties and process goals dictate which design aspects are most important.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: The counter-current heat exchange design is the most critical feature, as it maximizes thermal transfer and reduces energy consumption.
- If your primary focus is material quality: The variable rotation speed and multi-zone heating controls are your key parameters for tuning residence time and achieving a precise thermal profile.
- If you are selecting a furnace: The most important consideration is whether your material remains granular and free-flowing at target temperatures, as stickiness is the primary operational constraint.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace excels by transforming a simple principle—tumbling—into a highly controlled and efficient method for uniform material processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotation and Tilt | Cylinder rotates and tilts to tumble material | Ensures uniform exposure and continuous transport |
| Counter-Current Heating | Hot gases flow opposite to material movement | Maximizes heat transfer and energy efficiency |
| Continuous Mixing | Tumbling action prevents clumping and hot spots | Improves material quality and reaction uniformity |
| Material Suitability | Ideal for granular, free-flowing materials like powders and ceramics | Avoids issues with sticky or melting substances |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on efficiency, material quality, or specific applications, KINTEK delivers reliable, controlled heating for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput



















