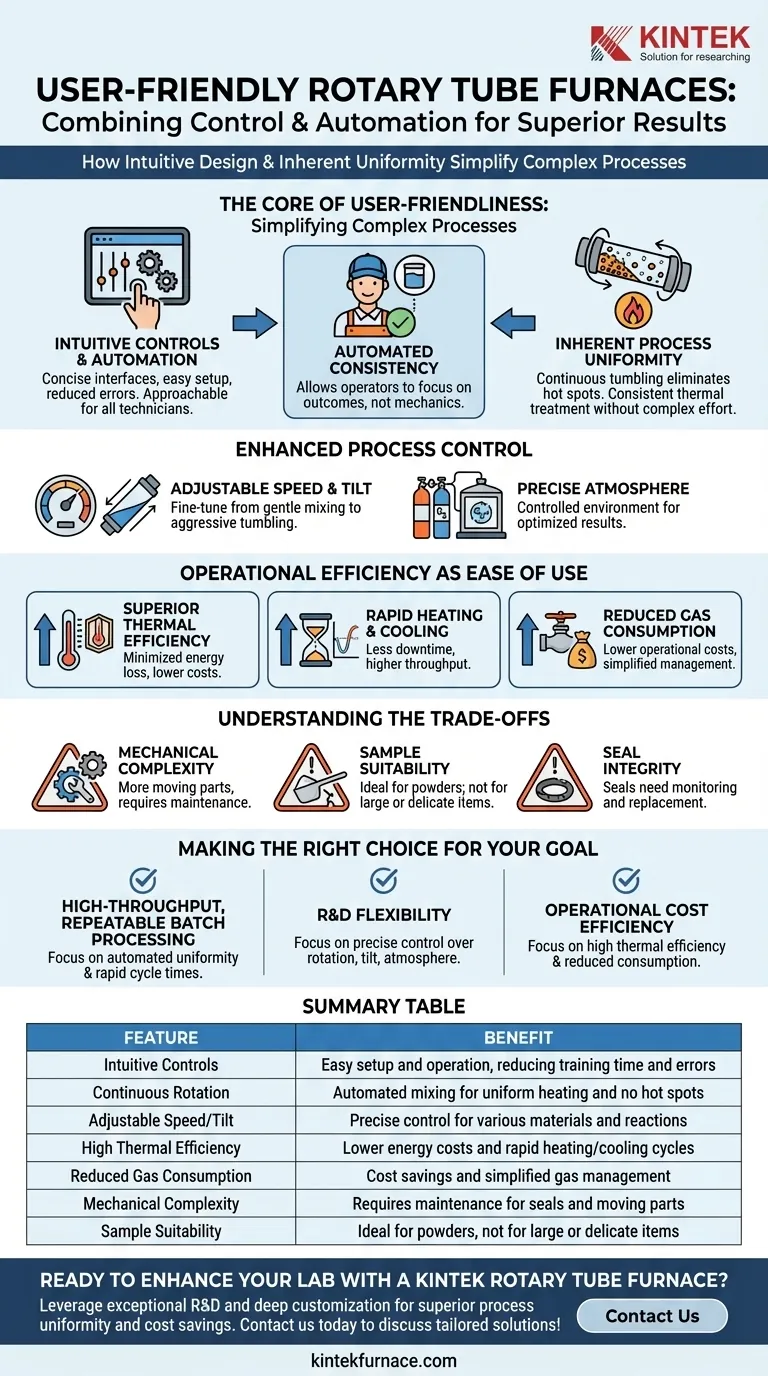
At its core, a rotary tube furnace is user-friendly because it combines intuitive operator controls with a physical design that inherently simplifies the achievement of uniform and repeatable results. The continuous rotation of the process tube automates the mixing of materials, eliminating the need for manual intervention and ensuring every particle receives consistent thermal treatment.
The true user-friendliness of a rotary tube furnace lies not just in its simple interface, but in how its fundamental design automates process uniformity. This allows operators to focus on the desired outcome rather than struggling with the mechanics of achieving it.
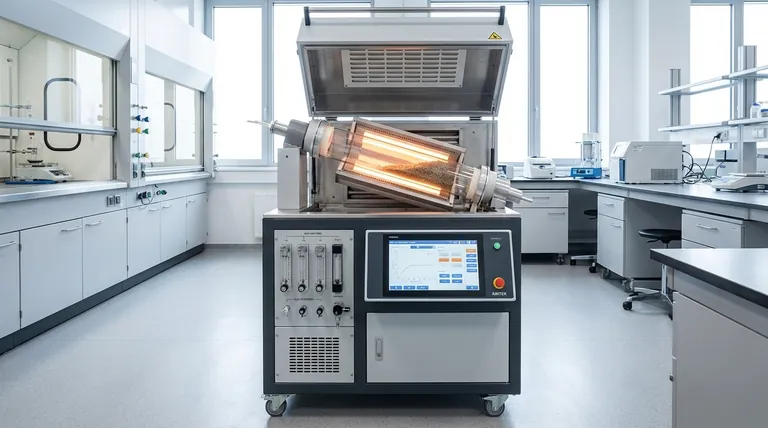

The Core of User-Friendliness: Simplifying Complex Processes
A user-friendly system removes obstacles between the operator and their goal. Rotary tube furnaces achieve this through both their software and their fundamental mechanical operation.
Intuitive Controls and Automation
Modern rotary tube furnaces feature concise and clear interfaces, often managed through a dedicated control panel or remote system. This allows users to easily set temperature profiles, start or stop processes, and make adjustments on the fly.
This accessibility makes the equipment approachable even for technicians new to furnace operations, reducing training time and minimizing operator error.
Inherent Process Uniformity
The primary advantage of the rotary design is the continuous tumbling of the material. This movement completely eliminates the risk of hot spots that can occur in static furnaces.
As the sample rotates, every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source and the controlled atmosphere, ensuring superior consistency throughout the entire batch without complex programming or manual repositioning.
Enhanced Process Control
Beyond simple rotation, these furnaces provide precise control over key variables. Operators can typically adjust the rotation speed and the tilt angle of the tube.
This allows for fine-tuning the process, from gentle mixing for delicate materials to aggressive tumbling for rapid reactions, all through simple, direct adjustments.
Operational Efficiency as a Form of Ease of Use
A system that is expensive or slow to operate creates friction and is fundamentally not user-friendly in a professional environment. Rotary furnaces are designed to be highly efficient.
Superior Thermal Efficiency
These furnaces utilize high-quality ceramic fiber insulation and efficient heating elements to minimize energy loss. The continuous movement of the sample also enhances heat transfer.
This results in high thermal efficiency, lower energy consumption, and reduced operating costs compared to other furnace designs.
Rapid Heating and Cooling
The efficient design enables rapid heating and cooling cycles. For a lab or production facility, this means less downtime between runs and significantly higher throughput.
Faster cycles allow researchers to conduct more experiments and manufacturers to process more material in the same amount of time.
Reduced Gas Consumption
The sealed, rotating tube design is highly efficient in its use of process gases. This controlled environment leads to reduced gas consumption, which lowers operational costs and simplifies gas supply management.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is universally perfect. True user-friendliness also means understanding a system's limitations to avoid misuse.
Increased Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the motor, drive system, and seals, adds moving parts not present in a static tube furnace. These components introduce potential points of failure and require periodic maintenance.
Sample Suitability
Rotary furnaces are ideal for powders, granules, and small, free-flowing solids. They are not suitable for processing single large components, delicate structures that could break during tumbling, or liquids.
Seal Integrity
The seals that allow the tube to rotate while maintaining a controlled atmosphere are critical components. They are subject to wear and thermal stress and must be monitored and replaced as part of a regular maintenance schedule to ensure process integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary tube furnace should be based on your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, repeatable batch processing: The furnace's automated uniformity and rapid cycle times are its greatest strengths.
- If your primary focus is research and development flexibility: The precise control over rotation, tilt, and atmosphere allows for a wide range of experimental conditions in a single machine.
- If your primary focus is operational cost efficiency: The high thermal efficiency and reduced consumption of energy and process gas will deliver significant long-term savings.
Ultimately, a rotary tube furnace empowers you to achieve superior process results with greater simplicity and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Intuitive Controls | Easy setup and operation, reducing training time and errors |
| Continuous Rotation | Automated mixing for uniform heating and no hot spots |
| Adjustable Speed/Tilt | Precise control for various materials and reactions |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Lower energy costs and rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| Reduced Gas Consumption | Cost savings and simplified gas management |
| Mechanical Complexity | Requires maintenance for seals and moving parts |
| Sample Suitability | Ideal for powders, not for large or delicate items |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a user-friendly rotary tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior process uniformity and cost savings. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces enhance efficiency in materials processing? Boost Throughput and Quality
- What is the role of rotary tube furnaces in the energy sector? Boost Efficiency in Biomass and Battery Material Processing
- What materials are rotary tube furnaces typically constructed from? Choose the Right Tube for Your Process
- How is the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace used in the carbon activation process? Achieve Uniform, High-Porosity Activated Carbon
- What are the advantages of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Material Processing



















