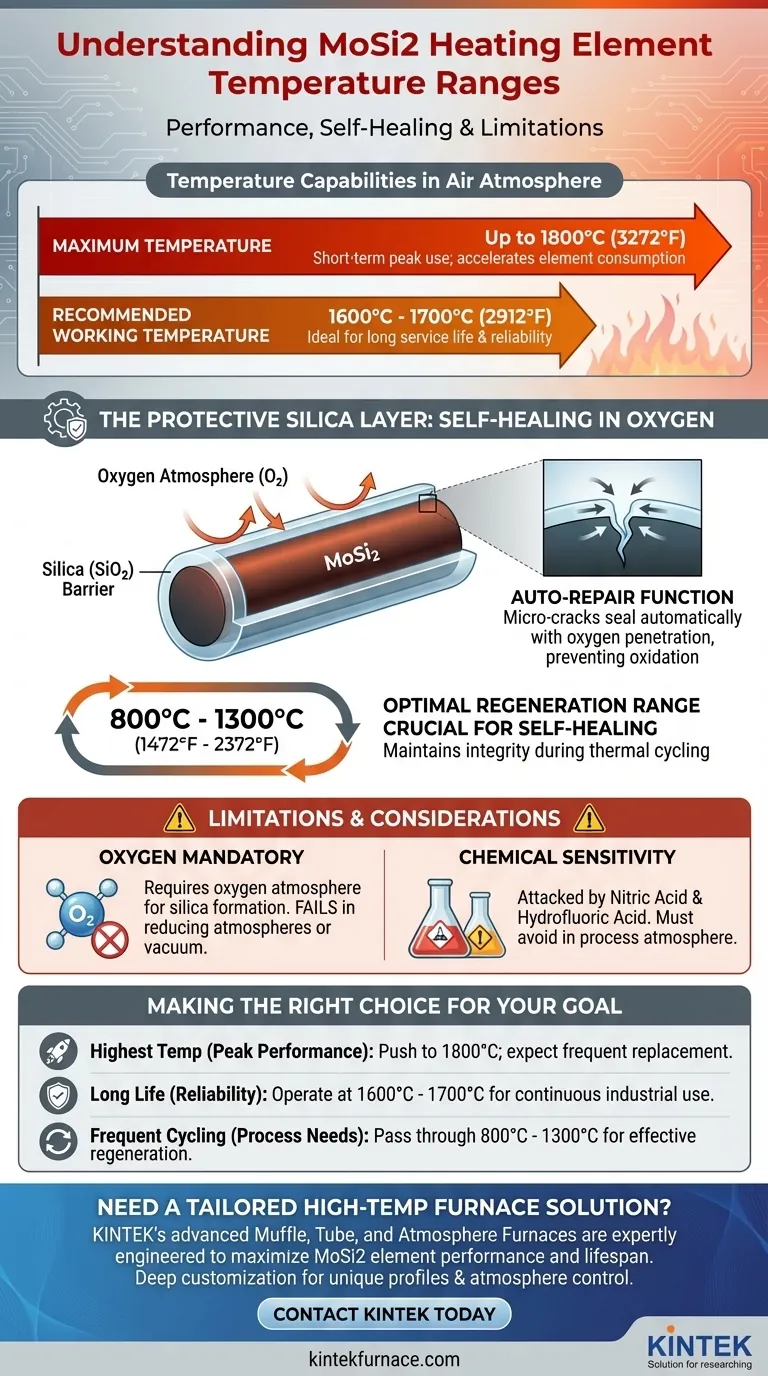
In short, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements can operate in air at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F). However, for continuous use and long service life, their recommended working temperature is typically between 1600°C and 1700°C (2912°F - 3092°F), depending on the specific grade of the element.
The exceptional high-temperature capability of a MoSi2 element is not just a property of the material itself, but a result of a dynamic process. It survives by forming a protective, self-healing glass-like layer of silica (SiO2) on its surface, a process that requires an oxygen atmosphere to function.

Understanding the Operating Principle: The Protective Silica Layer
To properly use a MoSi2 element, you must understand how it protects itself. Its high-temperature performance is entirely dependent on a chemical reaction with its environment.
How MoSi2 Achieves High Temperatures
When heated in the presence of oxygen (like in air), the molybdenum disilicide reacts to form a thin, non-porous layer of pure quartz glass (silica, SiO2) on its surface.
This silica layer acts as a barrier, preventing further oxidation and degradation of the underlying element material, even at extreme temperatures.
The Self-Healing Mechanism
This protective process is what gives MoSi2 its "auto-repair" function. If a micro-crack or defect develops on the surface, oxygen penetrates the opening and immediately forms new silica, effectively sealing the damage.
This continuous healing allows for a very long and stable service life, especially in processes involving continuous high-temperature work.
The Ideal Regeneration Range
This self-healing process is most effective and thermodynamically favorable in a specific temperature window.
The optimal range for the regeneration of the protective silica layer is between 800°C and 1300°C. Passing through or holding within this range is crucial for maintaining the element's integrity, especially in applications with frequent thermal cycling.
Differentiating Maximum vs. Working Temperatures
The distinction between the absolute maximum temperature and the recommended working temperature is critical for designing a reliable high-temperature process.
Maximum Temperature (Up to 1800°C)
This is the material's upper limit in an air atmosphere. Operating at or very near this temperature is possible but will significantly accelerate the consumption of the element and shorten its operational lifespan.
It should be considered a peak temperature for short durations, not a target for continuous industrial processes.
Recommended Working Temperature (1600°C - 1700°C)
This is the sustainable range for most commercial MoSi2 elements (often designated as "1700 grade" or "1800 grade" elements, which correspond to working and max temperatures, respectively).
Operating within this range provides the best balance between high heat output and long, reliable service life.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While superior in many high-temperature applications, MoSi2 elements are not universally applicable. Their unique operating principle comes with specific requirements and limitations.
An Oxygen Atmosphere is Mandatory
The entire protective mechanism relies on the availability of oxygen. Using MoSi2 elements in reducing atmospheres or a vacuum will prevent the formation of the silica layer, leading to rapid failure.
For these environments, other materials like pure molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite are required.
Superiority Over Other Materials
In oxygen-rich environments, MoSi2 elements can achieve significantly higher temperatures than common alternatives like Kanthal (FeCrAl), Nichrome, or even Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements.
Chemical Sensitivities
While the protective silica layer makes the element highly resistant to most acids and alkalis, it is vulnerable to certain chemicals.
MoSi2 elements will be attacked and dissolved by nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. This must be considered if your process atmosphere contains these compounds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy should be dictated by your primary objective for the furnace or process.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute highest temperature: You can push towards 1800°C, but you must budget for more frequent element replacement and potential process downtime.
- If your primary focus is long service life and reliability: Operate within the recommended working temperature of 1600°C to 1700°C for continuous industrial applications.
- If your primary focus is a process with frequent cycling: Ensure your heating schedule allows the elements to pass through or dwell in the 800°C to 1300°C range to effectively regenerate their protective layer.
Understanding these temperature ranges and the underlying science empowers you to optimize your high-temperature process for either peak performance or maximum reliability.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Type | Temperature Range (°C) | Temperature Range (°F) | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Up to 1800°C | Up to 3272°F | Short-term peak use; shortens element lifespan |
| Recommended Working Temperature | 1600°C - 1700°C | 2912°F - 3092°F | Ideal for long service life and reliability |
| Optimal Regeneration Range | 800°C - 1300°C | 1472°F - 2372°F | Crucial for self-healing of protective silica layer |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your specific process requirements?
KINTEK's advanced Muffle, Tube, and Atmosphere Furnaces are expertly engineered to maximize the performance and lifespan of critical components like MoSi2 heating elements. Our strong in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities allow for deep customization, ensuring your furnace precisely meets unique temperature profiles, atmosphere control, and thermal cycling needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can deliver a reliable, high-performance furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control



















