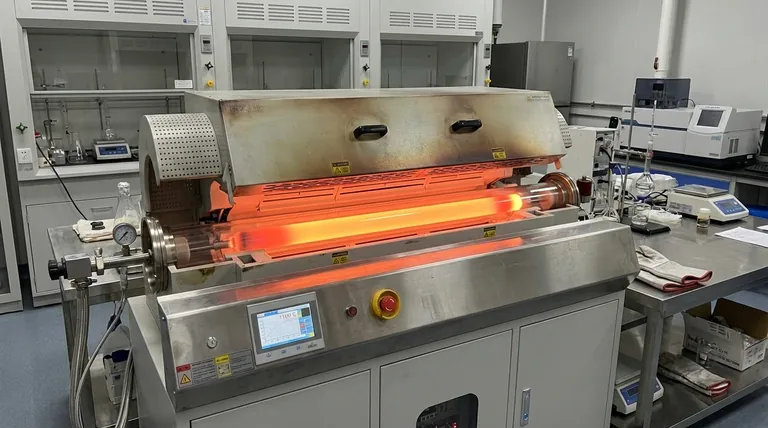
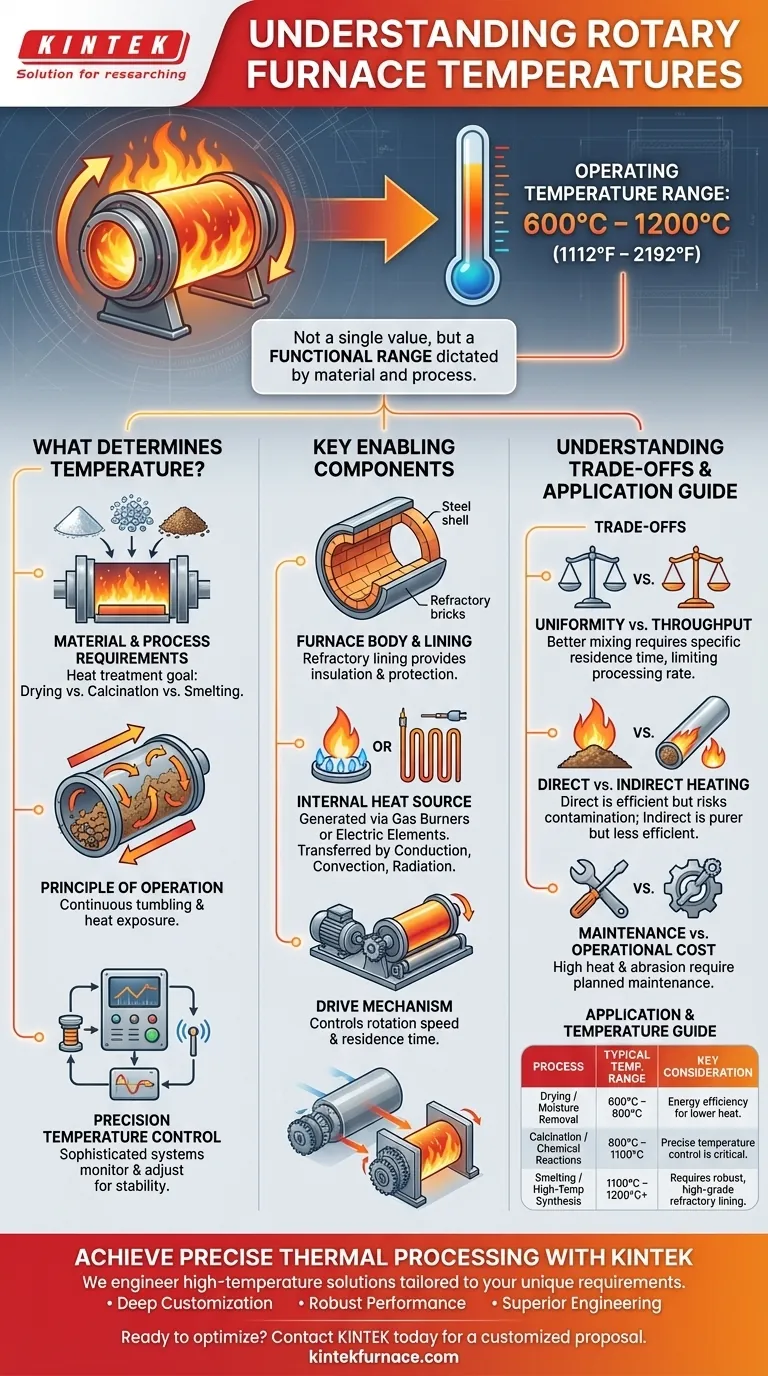
The operating temperature of a rotary furnace is not a single value but a functional range, typically falling between 600°C and 1200°C (1112°F to 2192°F). The exact temperature is dictated by the specific material being processed and the intended thermal reaction. Specialized units, such as electromagnetic rotary kilns, are engineered to consistently operate at high temperatures up to 1100°C and beyond for more demanding applications.
A rotary furnace's temperature is a direct function of its design and intended purpose. Instead of asking for the temperature, the critical question is what temperature your specific process requires, as the furnace must be engineered to achieve and sustain it reliably.

What Determines a Rotary Furnace's Temperature?
The operating temperature is a result of a balance between the furnace's construction, its heating system, and the demands of the material inside it. Understanding these factors is key to grasping its capabilities.
The Material and Process Requirements
The primary driver of temperature is the goal of the heat treatment. Different processes require vastly different thermal conditions.
For example, drying materials to remove moisture may only require lower temperatures, whereas calcination or the thermal decomposition of materials demands significantly higher, sustained heat.
The Principle of Operation
A rotary furnace is a cylindrical, barrel-shaped chamber that rotates on a slight incline. This rotation continuously tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source.
Hot gases typically flow through the chamber, often in the opposite direction of the material's travel (counter-current flow), to maximize heat transfer efficiency.
Precision Temperature Control
Modern rotary furnaces do not simply get "hot." They use a sophisticated control system to achieve and maintain a precise temperature profile.
Thermocouples or other sensors constantly monitor the internal temperature. This data is fed to a controller that adjusts the power to the heating elements or fuel to the burners, ensuring stable conditions essential for process consistency.
Key Components That Enable High Temperatures
A furnace's ability to reach and withstand temperatures over 1000°C is entirely dependent on the quality and design of its core components.
The Furnace Body and Lining
The outer shell is typically made of welded steel plate, but the critical component is the refractory lining on the inside.
This lining, made from refractory bricks, cement, or other moldable substances, provides the necessary insulation to protect the steel shell. It must also resist thermal shock and chemical corrosion from the materials being processed.
The Internal Heat Source
The heat is generated either by gas burners or electric heating elements. The choice depends on the application, required heat intensity, and operational costs.
Heat is transferred to the material through a combination of conduction (direct contact), convection (hot gas flow), and radiation from the hot lining and heating elements.
The Drive Mechanism
A motor and drive gear (or driven rollers) rotate the furnace body. The speed of this rotation is often variable.
Controlling the rotation speed and the furnace's tilt angle determines how long the material stays inside the furnace, known as its residence time, which is a critical process parameter.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary furnace is not a universal solution. Its design involves inherent trade-offs that are important to recognize.
Uniformity vs. Throughput
The slow tumbling action provides excellent mixing and heat uniformity. However, achieving this requires a specific residence time, which in turn limits the rate at which material can be processed (throughput).
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Most rotary furnaces use direct heating, where hot combustion gases are in direct contact with the material. This is very energy-efficient but carries a risk of contaminating the product.
For high-purity applications, an indirectly heated rotary tube furnace—where the tube is heated from the outside—may be necessary, though this is often less efficient.
Maintenance and Operational Cost
The combination of high temperatures, constant rotation, and abrasive materials causes wear on the refractory lining and mechanical components. This necessitates a planned maintenance schedule and factors into the furnace's long-term operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace specification is essential for achieving your processing goals efficiently and safely.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature drying or moisture removal: A furnace operating at the lower end of the range (near 600°C) will be sufficient and more energy-efficient.
- If your primary focus is calcination or specific chemical reactions: You will require a mid-to-high range furnace (800°C to 1100°C) with a highly precise temperature control system.
- If your primary focus is smelting or high-temperature material synthesis: You must source a specialized furnace capable of reaching 1200°C or higher, built with a robust, high-grade refractory lining.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's engineering to your specific thermal processing goal is the only way to ensure a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Process Application | Typical Temperature Range | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Drying / Moisture Removal | 600°C - 800°C | Energy efficiency for lower heat requirements. |
| Calcination / Chemical Reactions | 800°C - 1100°C | Precise temperature control is critical. |
| Smelting / High-Temp Synthesis | 1100°C - 1200°C+ | Requires robust, high-grade refractory lining. |
Achieve Precise Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Your specific material and process goals dictate the exact temperature your rotary furnace must deliver. At KINTEK, we don't just sell furnaces; we engineer high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique requirements.
Why choose KINTEK for your rotary furnace needs?
- Deep Customization: Leveraging our exceptional in-house R&D and manufacturing, we design Rotary Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, and other systems to precisely match your temperature profile, atmosphere, and throughput needs.
- Robust Performance: Our furnaces are built to reliably achieve and sustain temperatures from 600°C to over 1200°C, ensuring consistent results for applications like calcination, sintering, and heat treatment.
- Superior Engineering: We focus on the critical details—from advanced refractory linings that withstand thermal stress to precise control systems that guarantee uniform heating—so you can focus on your research or production.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Let our experts help you specify the perfect furnace. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your application and receive a customized solution proposal.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















