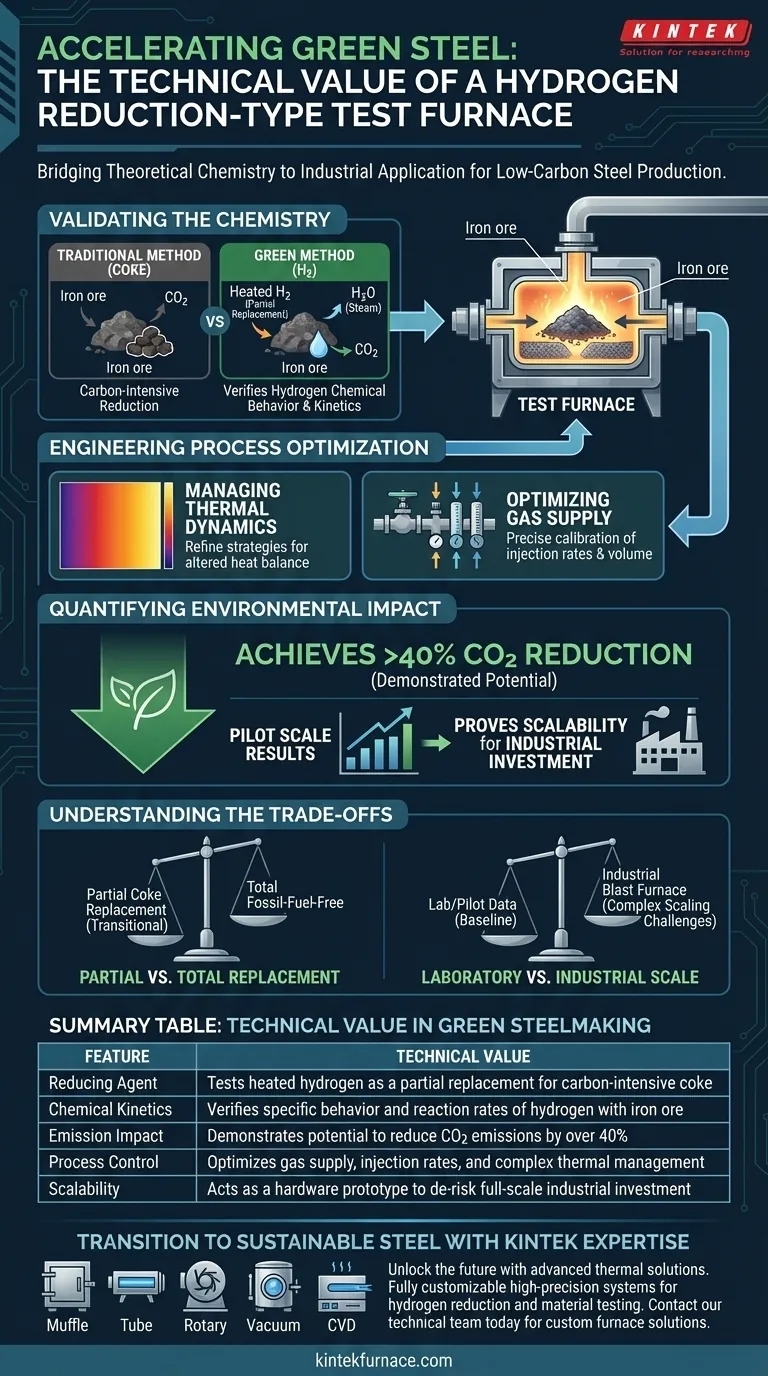
A Hydrogen Reduction-type Test Furnace serves as a critical bridge between theoretical chemistry and industrial application. It functions by introducing heated hydrogen as a partial replacement for coke during the iron ore reduction process. This apparatus allows engineers to verify the precise chemical behavior of hydrogen at laboratory and pilot scales, validating the technical feasibility of low-carbon steel production before mass implementation.
By optimizing gas supply and thermal management, these test furnaces have demonstrated the potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by over 40 percent, providing the essential data and hardware prototypes required to scale hydrogen steelmaking.

Validating the Chemistry of Green Steel
To move away from carbon-intensive methods, the industry must first prove that hydrogen can effectively reduce iron ore under controlled conditions.
Replacing Carbon with Hydrogen
Traditional blast furnaces rely heavily on coke as a reducing agent. This test furnace facilitates the technical evaluation of using heated hydrogen to partially replace that coke.
Verifying Chemical Behavior
Hydrogen reacts with iron ore differently than carbon does. The test furnace provides a controlled environment to observe and verify these specific chemical kinetics.
This verification is essential to ensure that the quality of the iron produced meets industrial standards.
Engineering Process Optimization
Beyond chemistry, the furnace serves as a hardware prototype to solve the engineering challenges associated with gas-based reduction.
Managing Thermal Dynamics
The equipment allows operators to test and refine thermal management strategies. This is crucial because introducing hydrogen alters the heat balance of the furnace compared to traditional methods.
Optimizing Gas Supply
The test furnace enables the precise calibration of gas injection rates. Engineers use this data to determine the optimal volume and pressure of hydrogen required for efficient reduction.
Quantifying Environmental Impact
The ultimate value of this equipment lies in its ability to generate concrete emissions data.
Achieving Significant Reductions
Experiments using this technology have demonstrated the potential to cut carbon dioxide emissions by more than 40 percent.
Proving Scalability
By achieving these results at the pilot scale, the furnace provides the empirical evidence needed to justify investment in full-scale industrial facilities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While valuable, it is important to recognize the specific scope and limitations of this testing equipment.
Partial vs. Total Replacement
The primary reference highlights the usage of hydrogen as a partial replacement for coke. This specific test setup verifies a transitional technology rather than a fully fossil-fuel-free process immediately.
Laboratory vs. Industrial Scale
Data gathered at the laboratory and pilot scales provides a strong baseline. However, scaling these thermal and chemical dynamics to a massive industrial blast furnace introduces complexities that smaller furnaces cannot fully replicate.
Advancing to Industrial Implementation
The data derived from a Hydrogen Reduction-type Test Furnace is the foundation for the next generation of steel manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is process validation: Analyze the chemical behavior data to understand how hydrogen kinetics differ from carbon reduction, ensuring product quality remains stable.
- If your primary focus is decarbonization strategy: Leverage the demonstrated >40% CO2 reduction metrics to validate the environmental ROI of retrofitting existing infrastructure.
This test furnace is not merely a research tool; it is the fundamental hardware prototype necessary to de-risk the global transition to sustainable steelmaking.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Technical Value in Green Steelmaking |
|---|---|
| Reducing Agent | Tests heated hydrogen as a partial replacement for carbon-intensive coke |
| Chemical Kinetics | Verifies specific behavior and reaction rates of hydrogen with iron ore |
| Emission Impact | Demonstrates potential to reduce CO2 emissions by over 40% |
| Process Control | Optimizes gas supply, injection rates, and complex thermal management |
| Scalability | Acts as a hardware prototype to de-risk full-scale industrial investment |
Transition to Sustainable Steel with KINTEK Expertise
Unlock the future of green metallurgy with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique hydrogen reduction and material testing needs.
Ready to validate your low-carbon processes and achieve superior environmental ROI? Contact our technical team today to design your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- The Technical Society, The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan. Production and Technology of Iron and Steel in Japan during 2024. DOI: 10.2355/isijinternational.65.7app_i
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a fixed-bed reactor in the slow pyrolysis process? Engineering High-Quality Biochar Production
- What is the primary function of drying bovine horn biomass for PVC biocomposites? Optimize Material Strength
- What is the technical objective of preheating the extrusion cylinder and molds to 460 ℃? Optimize Quality & Flow
- How do you maintain a vacuum pump? Ensure peak performance and longevity for your lab
- How does a refining furnace achieve the separation of impurities? Mastering High-Purity White Phosphorus Production
- What is the function of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in BAFPAE processing? Maintain Precursor Purity and Stability
- Why is it necessary to use a vacuum drying oven for porous graphene cathodes? Ensure Peak Battery Performance
- What is the necessity of an argon gas shielding system? Ensure Purity in Laser Remelting



















