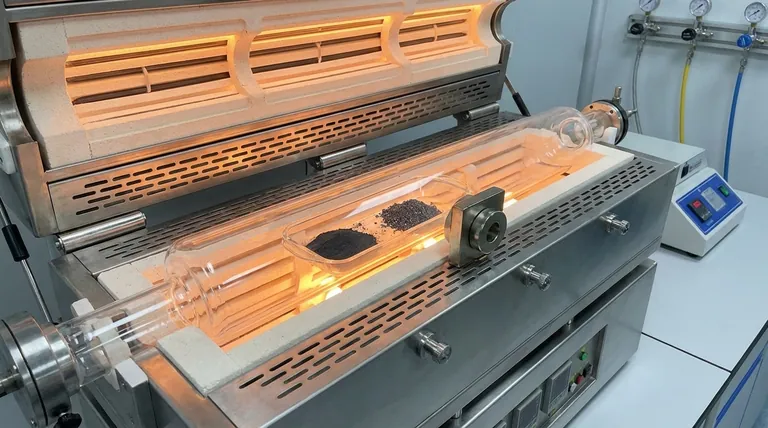
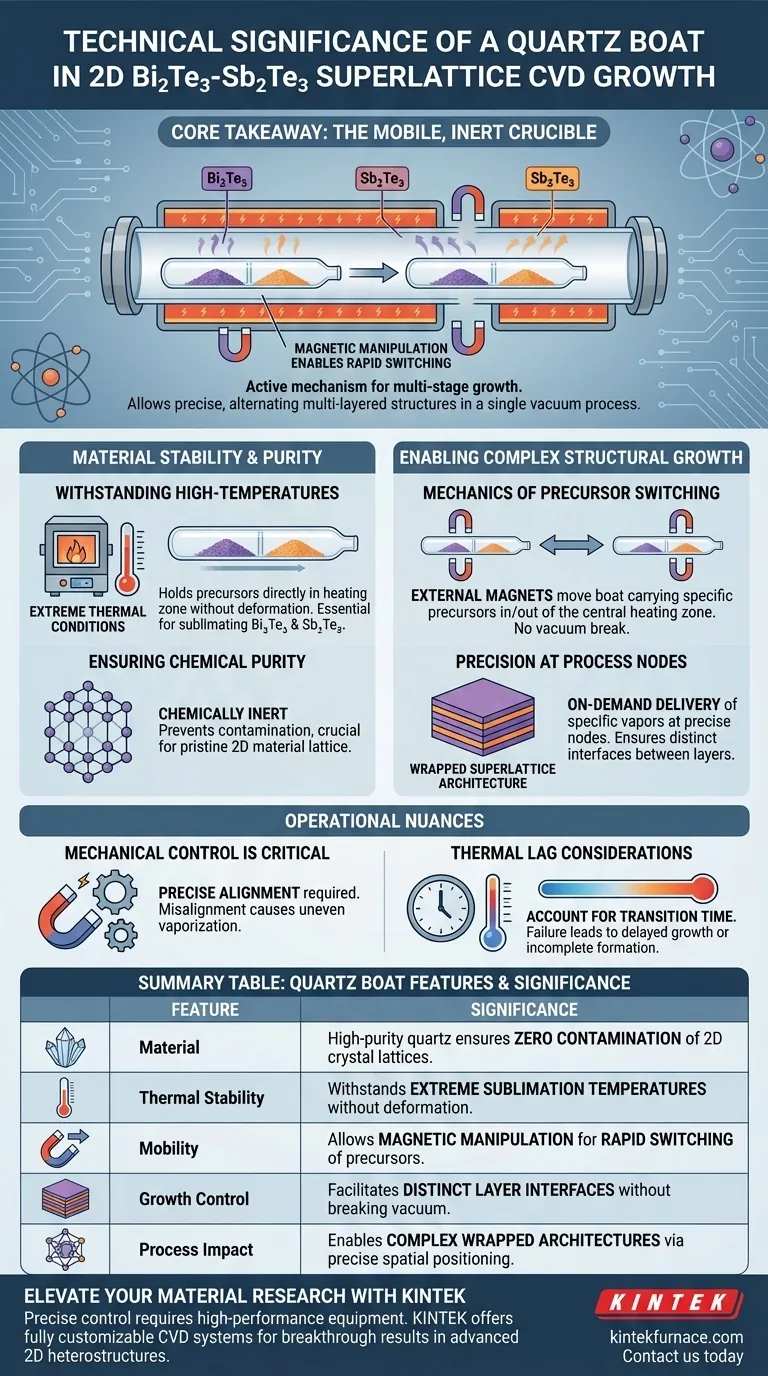
The quartz boat functions as a chemically inert, mobile crucible essential for the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) of 2D Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3 wrapped superlattices. Its technical significance is twofold: it withstands the extreme thermal conditions required to vaporize precursor powders, and it enables the physical transport necessary to switch materials during the growth process.
Core Takeaway The quartz boat is not merely a passive container; it is the active mechanism that enables multi-stage growth. By allowing for the rapid physical switching of precursors via magnetic manipulation, it solves the challenge of creating precise, alternating multi-layered structures in a single continuous vacuum process.

The Role of Material Stability
Withstanding High-Temperature Environments
The synthesis of materials like Bi2Te3 (Bismuth Telluride) and Sb2Te3 (Antimony Telluride) requires significant thermal energy to sublimate the solid precursor powders.
A quartz boat provides the necessary high-temperature resistance to hold these powders directly in the heating zone without deforming or degrading.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
In superlattice growth, purity is paramount. The slightest contamination can disrupt the crystal lattice of 2D materials.
Quartz is chosen for its chemical stability. It remains inert even at high processing temperatures, ensuring that the boat itself does not react with the precursors or introduce impurities into the delicate superlattice structure.
Enabling Complex Structural Growth
The Mechanics of Precursor Switching
Creating a "wrapped superlattice" requires alternating layers of different materials. In a static system, this is difficult to achieve without breaking the vacuum.
The technical innovation here is the use of external magnets to manipulate the quartz boat. This allows operators to physically move the boat carrying specific precursors into and out of the central heating zone.
Precision at Process Nodes
The quality of a superlattice depends on distinct interfaces between layers.
By moving the quartz boat, the system can introduce specific vapors at specific process nodes. This on-demand delivery allows for the controlled, sequential growth of alternating Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3 layers, resulting in the desired multi-layered architecture.
Understanding the Operational Nuances
Mechanical Control is Critical
While the quartz boat enables mobility, it introduces a mechanical variable to the CVD process.
The external magnetic control must be precise. Misalignment of the boat within the heating zone can lead to uneven vaporization rates, causing inconsistencies in layer thickness or composition.
Thermal Lag Considerations
Moving a quartz boat from a cool zone to a hot zone introduces a thermal transition period.
Operators must account for the time it takes for the boat and the powder to reach the target sublimation temperature. Failure to calculate this lag can result in delayed growth initiation or incomplete layer formation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If your primary focus is Structural Complexity:
- Utilize the magnetic mobility of the quartz boat to rapidly switch precursors, ensuring distinct boundaries between the alternating superlattice layers.
If your primary focus is Material Purity:
- Rely on the quartz boat’s chemical inertness to prevent cross-contamination between the boat material and the reactive precursor powders.
By leveraging the unique thermal and mechanical properties of the quartz boat, you transform a standard deposition process into a precision tool for engineering advanced 2D heterostructures.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Technical Significance in Superlattice Growth |
|---|---|
| Material | High-purity quartz ensures zero contamination of 2D crystal lattices. |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands extreme sublimation temperatures without deformation. |
| Mobility | Allows magnetic manipulation for rapid switching of precursors. |
| Growth Control | Facilitates distinct layer interfaces without breaking vacuum. |
| Process Impact | Enables complex wrapped architectures via precise spatial positioning. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise control over 2D material synthesis requires reliable, high-performance equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-temperature Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Whether you are developing advanced Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3 superlattices or complex heterostructures, our systems provide the thermal stability and precision necessary for breakthrough results.
Contact us today to find your custom lab solution
Visual Guide
References
- Han Wang, Wen Lei. Superlattice Engineering on 2D Bi<sub>2</sub>Te<sub>3</sub>‐Sb<sub>2</sub>Te<sub>3</sub> Chalcogenides. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202503492
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a vacuum pass-box and a high-capacity vacuum pump? Ensuring Safety in Battery Recycling
- What are the specific functions of a magnetic stirrer and a condenser reflux apparatus in the synthesis of KCC-1? Expert Insights
- Why is the pore size of refractory materials significant? Unlocking Precision in Bubble Formation and Oxygen Impact
- What is the primary function of a high-energy planetary ball mill? Unlock Nanoscale Ceramic Pretreatment
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump create negative pressure? Discover the Liquid-Ring Mechanism for Efficient Lab Vacuum
- What are the key characteristics of the circulating water multifunctional vacuum pump? Discover Clean, Oil-Free Lab Solutions
- What other industrial applications do graphite crucible furnaces have beyond metal melting? Unlock Advanced Material Processing
- What is the recommended cooling rate for the alumina furnace tube? Prevent Thermal Shock and Extend Tube Life

















