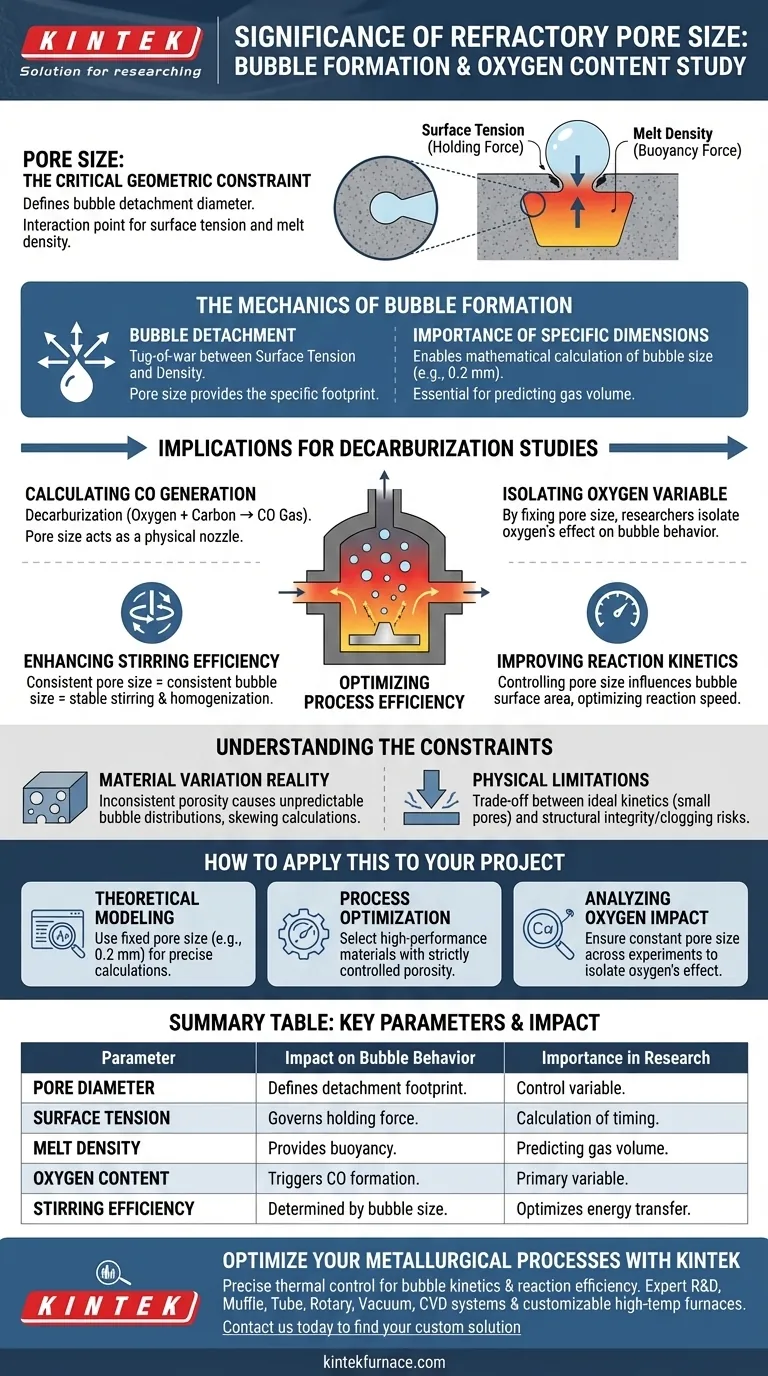
Pore size acts as the critical geometric constraint that defines the physical dimensions of bubbles generated during melt reactions. It serves as the specific diameter where the surface tension and density of the melt interact to determine the precise moment a bubble creates enough buoyancy to detach from the refractory wall.
By fixing the pore size variable, researchers can accurately model the interaction between melt properties and bubble formation. This control is essential for calculating the size of carbon monoxide bubbles during decarburization, directly influencing stirring efficiency and reaction kinetics.

The Mechanics of Bubble Formation
Determining Bubble Detachment
The formation of a bubble is not random; it is a tug-of-war between forces. The surface tension holding the bubble to the pore and the density of the melt pushing it upward are the primary factors.
However, these forces act upon a specific area. The pore size provides the defined footprint that dictates the bubble detachment diameter.
The Importance of Specific Dimensions
To understand how oxygen content affects the process, researchers must evaluate specific refractory pore sizes, such as 0.2 mm.
Using a known pore dimension allows for the mathematical calculation of bubble size. Without a defined pore size, it is impossible to predict the volume of gas released during detachment.
Implications for Decarburization Studies
Calculating Carbon Monoxide (CO) Generation
In the context of studying oxygen content, the primary reaction of interest is often decarburization. High oxygen content reacts with carbon in the melt to form CO gas.
The pore size of the refractory material is the physical nozzle through which these reaction gases or injected gases interact with the melt.
Isolating the Oxygen Variable
To accurately study the impact of oxygen, other variables must be controlled.
By fixing the pore size, researchers can isolate the effects of the melt's chemical composition (oxygen content) on the process. This ensures that observed changes in bubble behavior are due to the chemistry, not inconsistent material geometry.
Optimizing Process Efficiency
Enhancing Stirring Efficiency
Controlling the porosity of high-performance refractory materials is not just a theoretical exercise; it is critical for secondary metallurgy.
The size of the bubbles generated determines the energy transfer within the melt. Consistent pore sizes lead to consistent bubble sizes, which stabilizes the stirring action required for homogenization.
Improving Reaction Kinetics
Reaction kinetics depend heavily on the surface area available for reactions.
By controlling pore size, metallurgists can influence the surface area of the gas bubbles generated. This allows for the optimization of the speed and efficiency of chemical reactions within the vessel.
Understanding the Constraints
The Reality of Material Variation
While theoretical models often use a precise value like 0.2 mm, real-world refractory materials may have variable porosity.
Inconsistent pore sizes can lead to unpredictable bubble distributions. This variability can skew calculations regarding the impact of oxygen content, as large pores may release bubbles prematurely or late compared to the model.
Physical Limitations
There is a trade-off between the ideal pore size for kinetics and the structural integrity of the material.
Extremely small pores might offer high surface area for reactions but can be difficult to manufacture or prone to clogging. Conversely, overly large pores may reduce stirring efficiency by creating bubbles that rise too quickly without interacting sufficiently with the melt.
How to Apply This to Your Project
If your primary focus is theoretical modeling:
- Use a fixed pore size value (e.g., 0.2 mm) to calculate the precise bubble detachment diameter based on the melt's surface tension and density.
If your primary focus is process optimization:
- Select high-performance refractory materials with strictly controlled porosity to ensure consistent stirring efficiency and predictable reaction kinetics.
If your primary focus is analyzing oxygen impact:
- Ensure pore size remains constant across experiments so that variations in bubble formation can be attributed solely to changes in oxygen content and decarburization rates.
Standardizing refractory porosity is the key to turning random gas generation into a controlled, efficient metallurgical process.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Impact on Bubble Behavior | Importance in Research |
|---|---|---|
| Pore Diameter | Defines the physical footprint for bubble detachment. | Acts as the control variable to isolate chemical effects. |
| Surface Tension | Governs the force holding the bubble to the refractory wall. | Used to calculate detachment timing alongside pore size. |
| Melt Density | Provides the buoyancy required for bubble release. | Essential for predicting bubble volume and gas release. |
| Oxygen Content | Triggers decarburization and CO gas formation. | Primary variable studied via controlled material porosity. |
| Stirring Efficiency | Determined by consistent bubble size and distribution. | Optimizes energy transfer and melt homogenization. |
Optimize Your Metallurgical Processes with KINTEK
Precise control over your thermal environment is the key to mastering bubble kinetics and reaction efficiency. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research and production needs.
Whether you are studying decarburization or optimizing stirring efficiency, our high-performance equipment provides the stability your experiments require. Contact us today to find your custom solution and see how our expertise can drive your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Lukas Neubert, Olena Volkova. Effect of Oxygen on Thermophysical Properties of Molten High-Silicon Electrical Steels and Its Impact on Bubble Formation Behavior. DOI: 10.1007/s11663-025-03594-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of a vacuum pump in photocatalytic CO2 reduction? Ensure Pure Environments for Accurate Data
- What functions do carbon black and carbon fiber felt serve as insulation? Maximize Efficiency in 3000°C Furnaces
- What is the main purpose of BN coating on graphite in Ti-6Al-4V hot pressing? Ensure Purity & Easy Release
- How does a Mass Flow Controller (MFC) regulate TCNF morphology? Achieve Precise Carbon Nanofiber Growth
- Why is a precision constant temperature drying oven required for BZT ceramic powders? Ensure Perfect Powder Quality
- Why are high-purity alumina boats utilized as precursor containers in MoS2 synthesis? Ensure High-Quality 2D Materials
- Why is a vacuum drying oven essential for Pd-Ni/ZrO2 catalyst preparation? Ensure Uniform Metal Distribution
- What role do graphite molds play in graphite flake alignment? Engineered Precision for High Thermal Conductivity



















