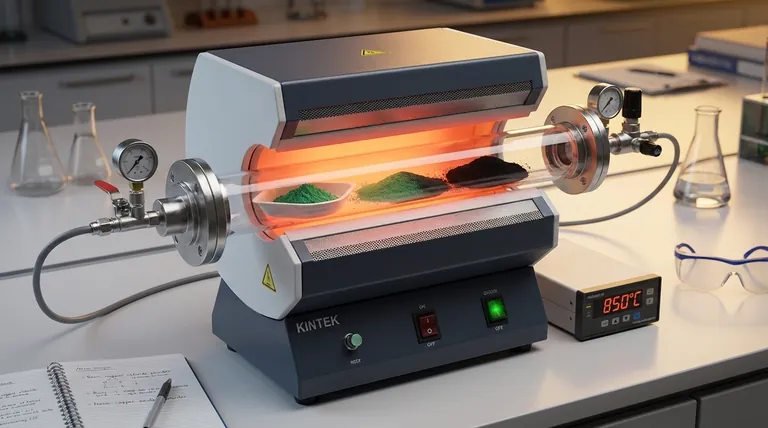
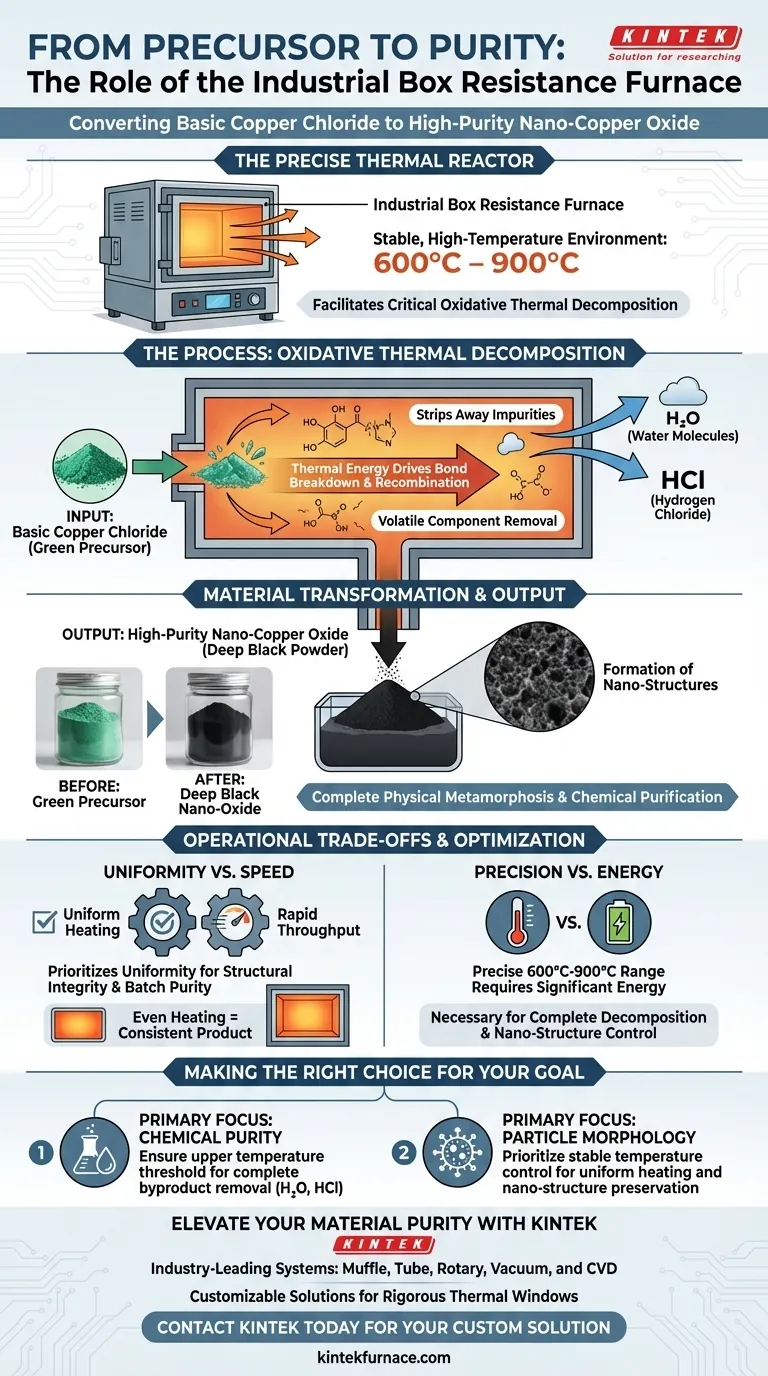
The industrial box resistance furnace serves as the precise thermal reactor required to convert basic copper chloride into high-purity copper oxide. It provides a stable, high-temperature environment, specifically between 600°C and 900°C, to facilitate the critical process of oxidative thermal decomposition.
By delivering controlled thermal energy, the furnace drives the breakdown of chemical bonds in the precursor material. This process effectively strips away water molecules and hydrogen chloride, leaving behind a pure, deep black nano-copper oxide structure.

The Mechanics of Thermal Decomposition
Precise Thermal Energy Application
The core function of the furnace is to maintain a rigorous temperature profile within the 600°C to 900°C range.
This specific thermal window is non-negotiable for this chemical reaction. The furnace ensures that the thermal energy provided is sufficient to initiate and sustain the decomposition without damaging the target material.
Driving Chemical Bond Recombination
Inside the furnace chamber, heat is used as a catalyst for chemical bond breaking and recombination.
The thermal energy destabilizes the basic copper chloride precursor. This forces the atomic structure to rearrange, transitioning the material from a complex chloride compound into a stable oxide form.
Purification via Byproduct Removal
A critical role of the furnace is the thermal extraction of impurities.
As the reaction progresses, the furnace heat drives off volatile components, specifically water molecules and hydrogen chloride. Removing these byproducts is essential to achieving the "high-purity" designation of the final product.
resulting Material Transformation
From Green to Deep Black
The furnace facilitates a complete physical metamorphosis of the material.
The starting material is a green precursor (basic copper chloride). Through the oxidative process, it is transformed into a deep black powder, which serves as the visual indicator of successful conversion.
Formation of Nano-Structures
Beyond just chemical changes, the furnace environment dictates the physical morphology of the product.
The controlled heating profile ensures the formation of nano-copper oxide. The uniformity of the heat is vital for consistent particle size and structure, preventing the material from aggregating into unusable clumps.
Understanding Operational Trade-offs
The Necessity of Uniformity vs. Speed
While high temperatures speed up reactions, the "box" design of the resistance furnace prioritizes uniform heating over rapid throughput.
In processes like sintering or annealing (as noted in broader industrial contexts), uniformity ensures structural integrity. Similarly, here, uneven heating would result in a mixture of unreacted green precursor and burnt oxide, ruining the batch purity.
Temperature Precision vs. Energy Consumption
Maintaining a precise 600°C–900°C environment requires significant energy input.
However, this consumption is a necessary trade-off. Fluctuations below this range result in incomplete decomposition (retaining chloride impurities), while uncontrolled spikes could alter the desired nano-crystalline structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your production of copper oxide, you must align your furnace settings with your specific quality metrics.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure the furnace maintains the upper threshold of the temperature range to guarantee the complete removal of hydrogen chloride and water.
- If your primary focus is Particle Morphology: Prioritize the stability of the temperature control system to ensure uniform heating, which preserves the delicate nano-structure of the copper oxide.
The industrial box resistance furnace is not just a heater; it is a precision instrument that dictates the purity, color, and structural integrity of your final copper oxide product.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Specification | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | 600°C – 900°C | Ensures complete oxidative thermal decomposition |
| Primary Reaction | Thermal Decomposition | Breaks chemical bonds to restructure copper chloride |
| Byproduct Removal | H2O & HCl Volatilization | Achieves high-purity status by extracting impurities |
| Physical Change | Green Precursor to Black Powder | Indicates successful transition to copper oxide |
| Structural Output | Nano-Copper Oxide | Uniform heating preserves delicate nano-morphology |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a contaminated batch and high-purity nano-structures. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically engineered to maintain the rigorous thermal windows required for complex chemical transformations.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique processing needs—whether you are prioritizing chemical purity or specific particle morphology.
Ready to optimize your production? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Dengliang He, Shishan Xue. Integrated Alkali Gradient pH Control Purification of Acidic Copper-Containing Etching Waste Solution and Cu2(OH)3Cl Conversion-Calcination Process for High-Purity CuO. DOI: 10.3390/pr13092807
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How should the furnace door be handled during use? Ensure Safe Operation and Prevent Damage
- What is the purpose of a high-temperature muffle furnace for rare earth oxalate calcination? Achieve High-Purity REOs
- What are the installation and maintenance benefits of electric furnaces? Achieve Simpler, Lower-Cost Heating
- What temperature range can box furnaces reach? Achieve 1800°C for Precise Thermal Processing
- What applications does a muffle furnace have in coal quality analysis? Essential for Precise Coal Testing
- How does the furnace wall and roof of a box type resistance furnace transfer heat to the metal? Discover the Key Mechanism for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a muffle furnace? Discover the Engineered System for Contamination-Free Heating
- Why is controlled and consistent heating important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Reliable Results in Your Lab



















