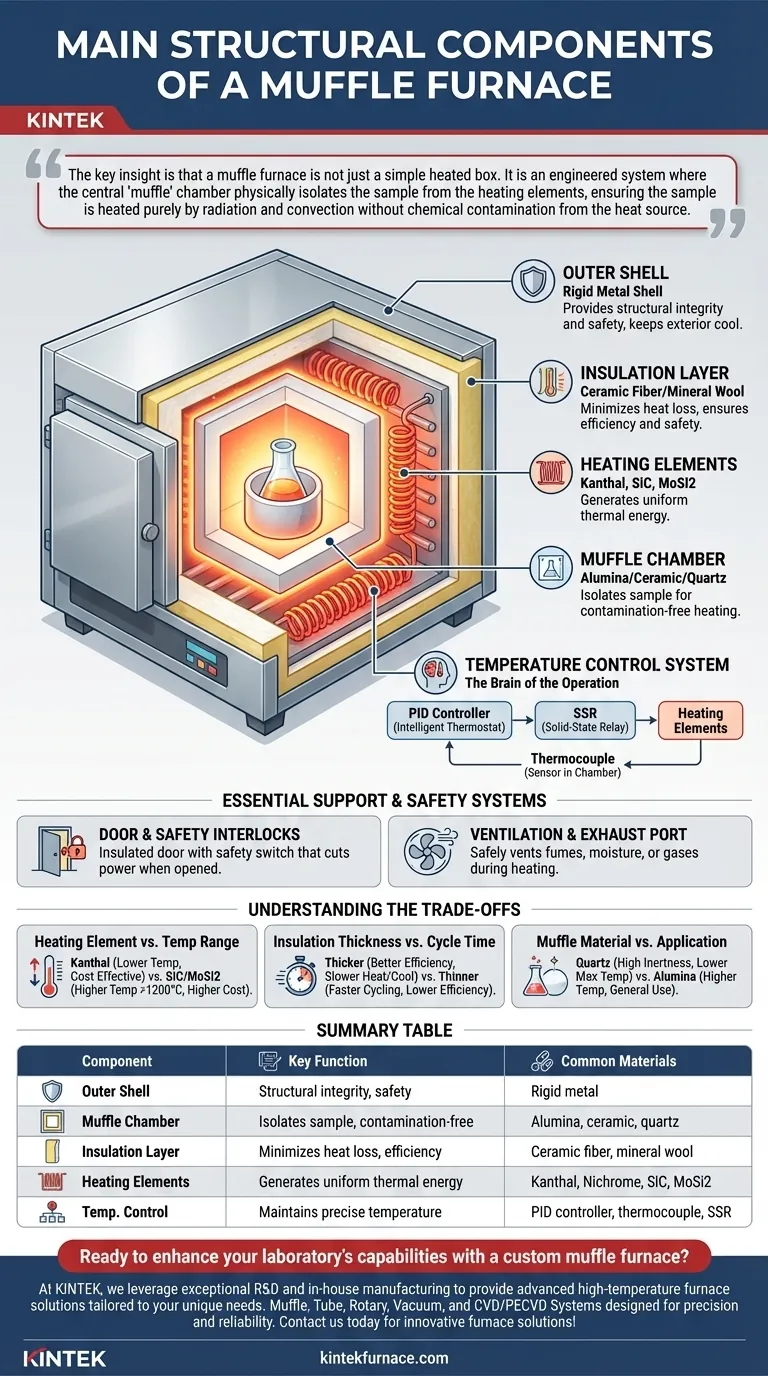
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven built around a system of five primary structural components. These are the insulated outer shell, the inner muffle chamber, the surrounding heating elements, a precise temperature control system, and integrated safety features. Each component works in concert to achieve the furnace's primary goal: delivering uniform, contamination-free heat to a sample.
The key insight is that a muffle furnace is not just a simple heated box. It is an engineered system where the central "muffle" chamber physically isolates the sample from the heating elements, ensuring the sample is heated purely by radiation and convection without chemical contamination from the heat source.
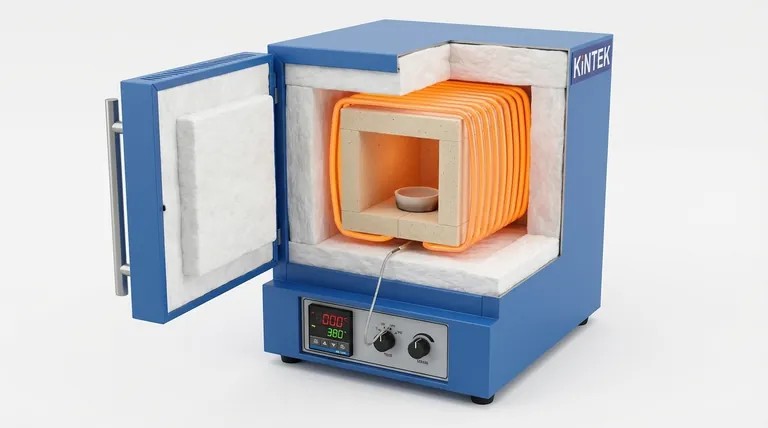

The Core Architecture: A System of Isolation and Control
Understanding a muffle furnace begins with its layered construction, which is designed to contain extreme heat, ensure uniformity, and protect the sample.
The Outer Shell
The outermost layer is a rigid metal shell. This component provides structural integrity and a protective housing for the internal components. It also serves as the first line of defense, keeping the exterior relatively cool and safe to touch.
The Muffle Chamber: The Heart of the Furnace
The defining component is the muffle, an inner chamber that holds the sample. It is constructed from a refractory material, such as high-purity alumina or ceramic, which can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading.
Its critical function is to create a clean, isolated environment. By separating the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, it prevents any potential chemical reactions or contamination.
The Insulation Layer
Between the outer shell and the muffle chamber lies a thick layer of insulation. Typically made from materials like ceramic fiber or mineral wool, this layer is essential for performance and safety.
Its primary job is to minimize heat loss, which allows the furnace to reach high temperatures efficiently and maintain them stably. This insulation also keeps the external casing from becoming dangerously hot.
The Heating System: Generating Uniform Temperature
The ability to generate and precisely manage intense heat is what makes the furnace a valuable tool. This is handled by a dedicated heating and control system.
Heating Elements: The Source of Thermal Energy
The heat itself is generated by heating elements. These are strategically placed around the outside of the muffle chamber to ensure even heat distribution.
Common element types include resistance wires like Kanthal or Nichrome for general use, with silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) used for furnaces requiring exceptionally high temperatures (above 1200°C).
The Temperature Control System: The Brain of the Operation
This system is responsible for executing heating protocols with high precision. It consists of three key parts working together.
- The Controller: Modern furnaces use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This is an intelligent digital thermostat that continuously adjusts power to prevent overshooting or undershooting the target temperature.
- The Sensor: A thermocouple is a sensor placed inside the chamber to provide real-time temperature feedback to the PID controller.
- The Power Relay: The controller sends signals to a Solid-State Relay (SSR), which precisely modulates the flow of electricity to the heating elements.
Essential Support and Safety Systems
Beyond heating and isolation, several components ensure reliable and safe operation.
The Door and Safety Interlocks
The furnace door is lined with the same insulation as the body to prevent heat from escaping the front. Critically, it includes a safety switch that automatically cuts power to the heating elements when the door is opened, protecting the user from extreme heat and thermal shock.
Ventilation and Exhaust Port
Many muffs and crucibles can release fumes, moisture, or gases during heating. An exhaust port, often located at the top or rear of the furnace, allows these byproducts to be safely vented away, sometimes connecting to an external ventilation system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or using a muffle furnace involves balancing component capabilities with your specific needs. The design of each component presents a trade-off.
Heating Element vs. Temperature Range
The type of heating element directly dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature. Kanthal elements are cost-effective but typically max out around 1200°C. For applications like sintering advanced ceramics, you need more robust MoSi2 elements that can exceed 1600°C but come at a higher cost.
Insulation Thickness vs. Cycle Time
Thicker, denser insulation provides better thermal efficiency and stability at high temperatures. However, it also means the furnace will take longer to heat up and cool down. Furnaces designed for rapid cycling may use less dense insulation, trading some efficiency for speed.
Muffle Material vs. Application
While most muffles are made of durable ceramics, specific applications may require different materials. For example, working with highly reactive chemicals might necessitate a furnace with a high-purity quartz muffle for its superior chemical inertness, even though it may have a lower maximum temperature than an alumina one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace means matching its components to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature ashing or sintering (>1200°C): Prioritize a furnace with silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements and high-density ceramic fiber insulation.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and trace element analysis: Ensure the muffle is made from a high-purity, inert material like alumina or quartz to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and precision: Invest in a furnace with a high-quality, auto-tuning PID controller and a durable, well-placed thermocouple.
- If your primary focus is working with materials that outgas: Confirm the furnace is equipped with a properly located exhaust port for safe ventilation.
By understanding how these core components function and interact, you can confidently select and operate the correct instrument for your work.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Provides structural integrity and safety | Rigid metal |
| Muffle Chamber | Isolates sample for contamination-free heating | Alumina, ceramic, quartz |
| Insulation Layer | Minimizes heat loss and ensures efficiency | Ceramic fiber, mineral wool |
| Heating Elements | Generates uniform thermal energy | Kanthal, Nichrome, SiC, MoSi2 |
| Temperature Control System | Maintains precise temperature via PID controller | PID controller, thermocouple, SSR |
| Safety Features | Ensures user protection and operational safety | Safety interlock, exhaust port |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a custom muffle furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all designed for precision and reliability. Whether you're focused on high-temperature sintering, sample purity, or process repeatability, our deep customization capabilities ensure your experimental requirements are met. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your work with innovative furnace solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















