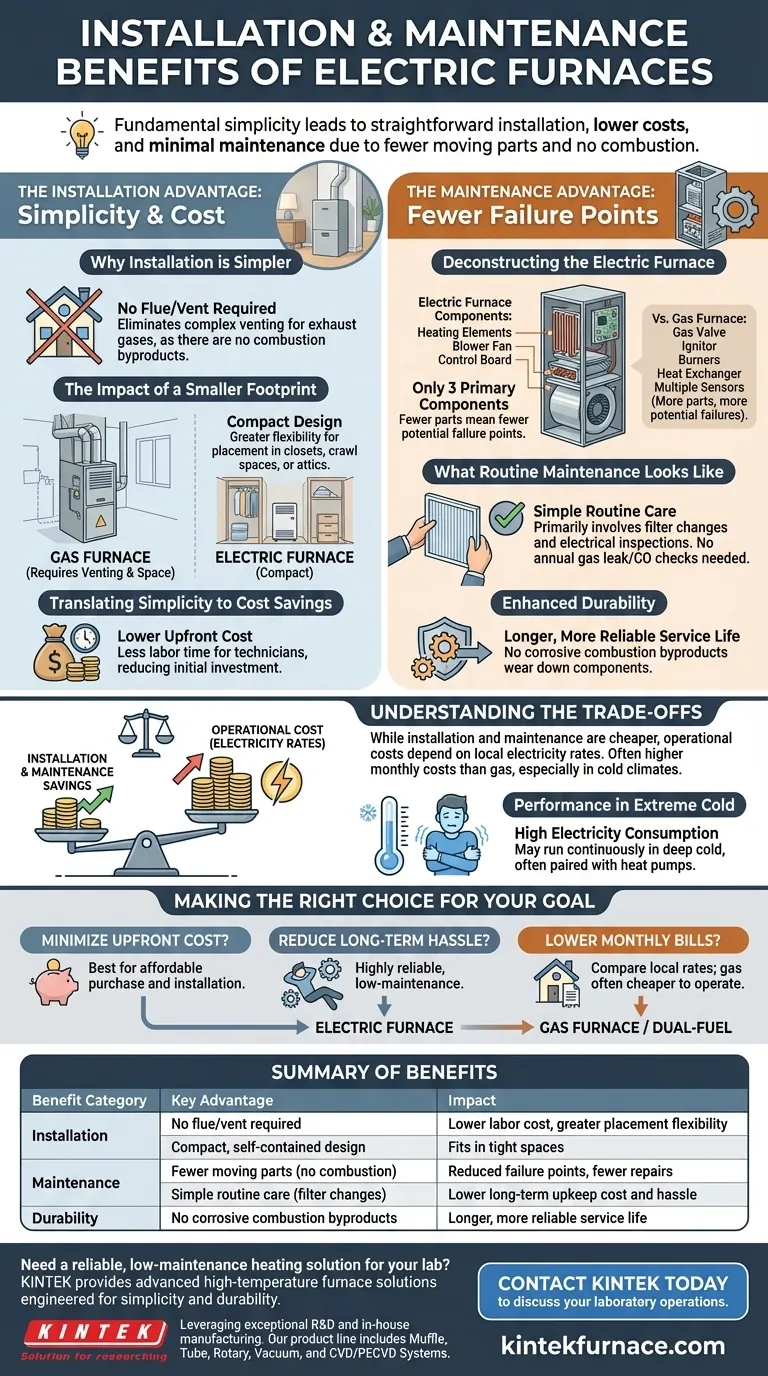
When evaluating heating systems, an electric furnace stands out for its fundamental simplicity. This translates directly into a more straightforward and often less expensive installation process, as well as significantly lower maintenance demands over the life of the unit due to its minimal number of moving parts and lack of combustion.
While the upfront benefits of simple installation and low maintenance are clear, the true value of an electric furnace depends on balancing these advantages against its operational costs, which are dictated by your local electricity rates.

The Installation Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
The primary appeal of an electric furnace often begins with its installation. Unlike fuel-burning alternatives, the process is streamlined, reducing both complexity and upfront investment.
Why Installation is Simpler
An electric furnace does not burn fuel, so it produces no combustion byproducts like carbon monoxide. This eliminates the need for a flue or vent pipe to exhaust gases outside your home.
This single factor dramatically simplifies installation, as there's no need to run complex venting through walls or the roof.
The Impact of a Smaller Footprint
Electric furnaces are generally more compact than their gas-powered counterparts. Their design is self-contained and does not require the extensive internal machinery needed for combustion.
This smaller size provides greater flexibility for placement, allowing them to be installed in closets, crawl spaces, or attics where a larger gas furnace might not fit.
Translating Simplicity to Cost Savings
A less complex installation requires less labor. Without the need for gas lines or specialized venting, the time an HVAC technician spends on the job is reduced, directly lowering your upfront cost.
The Maintenance Advantage: Fewer Failure Points
The design philosophy of an electric furnace is "less is more." This mechanical simplicity is the foundation of its reliability and low maintenance requirements.
Deconstructing the Electric Furnace
An electric furnace consists of three primary components: the heating elements (which function like the coils in a toaster), the blower fan that circulates air, and the control board that activates them.
In contrast, a gas furnace involves a gas valve, ignitor, burners, a heat exchanger, and multiple safety sensors. Each additional component represents a potential point of failure that an electric furnace simply does not have.
What Routine Maintenance Looks Like
For an electric furnace, routine maintenance is exceptionally straightforward. It primarily involves inspecting the electrical connections and, most importantly, regularly changing the air filter.
Keeping the blower motor and coils clean ensures the system runs efficiently, but it does not require the annual safety checks for gas leaks or carbon monoxide that are critical for fossil fuel systems.
Enhanced Durability
With fewer moving parts and no corrosive combustion byproducts wearing down components like a heat exchanger, electric furnaces tend to be highly durable. This inherent simplicity often contributes to a long and reliable service life with fewer unexpected repair bills.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While simple to install and maintain, an electric furnace is not the right choice for every situation. Its primary drawback lies not in its mechanics, but in its operational cost.
The Operational Cost Factor
The most significant trade-off is the cost of electricity. In most regions, natural gas is a cheaper energy source per unit of heat (BTU) than electricity.
While an electric furnace may be cheaper to install, it will almost certainly be more expensive to run per month than a high-efficiency gas furnace, especially in cold climates.
Performance in Extreme Cold
Electric furnaces produce a steady, consistent heat. However, during periods of deep and sustained cold, they must run almost continuously to maintain the desired temperature, leading to very high electricity consumption.
For this reason, they are often used in milder climates or paired with a more efficient heat pump in a dual-fuel system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace requires aligning the equipment's strengths with your specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront installation cost: An electric furnace is one of the most affordable heating systems to purchase and install.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term maintenance and hassle: The simple design with very few failure points makes the electric furnace a highly reliable and low-maintenance option.
- If your primary focus is lowering monthly energy bills: You must compare your local electricity and natural gas rates, as a gas furnace is frequently cheaper to operate in most areas.
By understanding both the upfront simplicity and the long-term operational costs, you can confidently determine if an electric furnace aligns with your financial and practical priorities.
Summary Table:
| Benefit Category | Key Advantage | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | No flue/vent required | Lower labor cost, greater placement flexibility |
| Installation | Compact, self-contained design | Fits in tight spaces like closets or attics |
| Maintenance | Fewer moving parts (no combustion) | Reduced failure points, fewer repairs |
| Maintenance | Simple routine care (filter changes) | Lower long-term upkeep cost and hassle |
| Durability | No corrosive combustion byproducts | Longer, more reliable service life |
Need a reliable, low-maintenance heating solution for your lab?
At KINTEK, we understand that your laboratory's efficiency depends on equipment that is both powerful and dependable. Just like the electric furnaces described here, our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions are engineered for simplicity and durability.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let us help you achieve your goals:
- Minimize upfront costs with efficient installation.
- Reduce long-term maintenance with robust, reliable designs.
- Customize a solution perfectly tailored to your specific application.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our furnace solutions can bring simplicity and reliability to your laboratory operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















