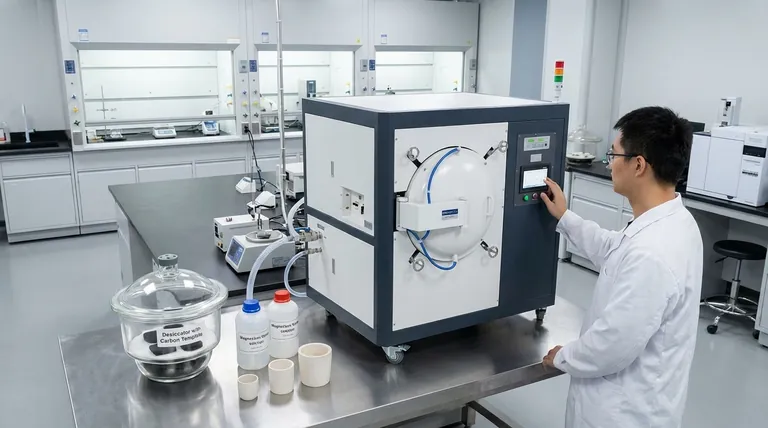
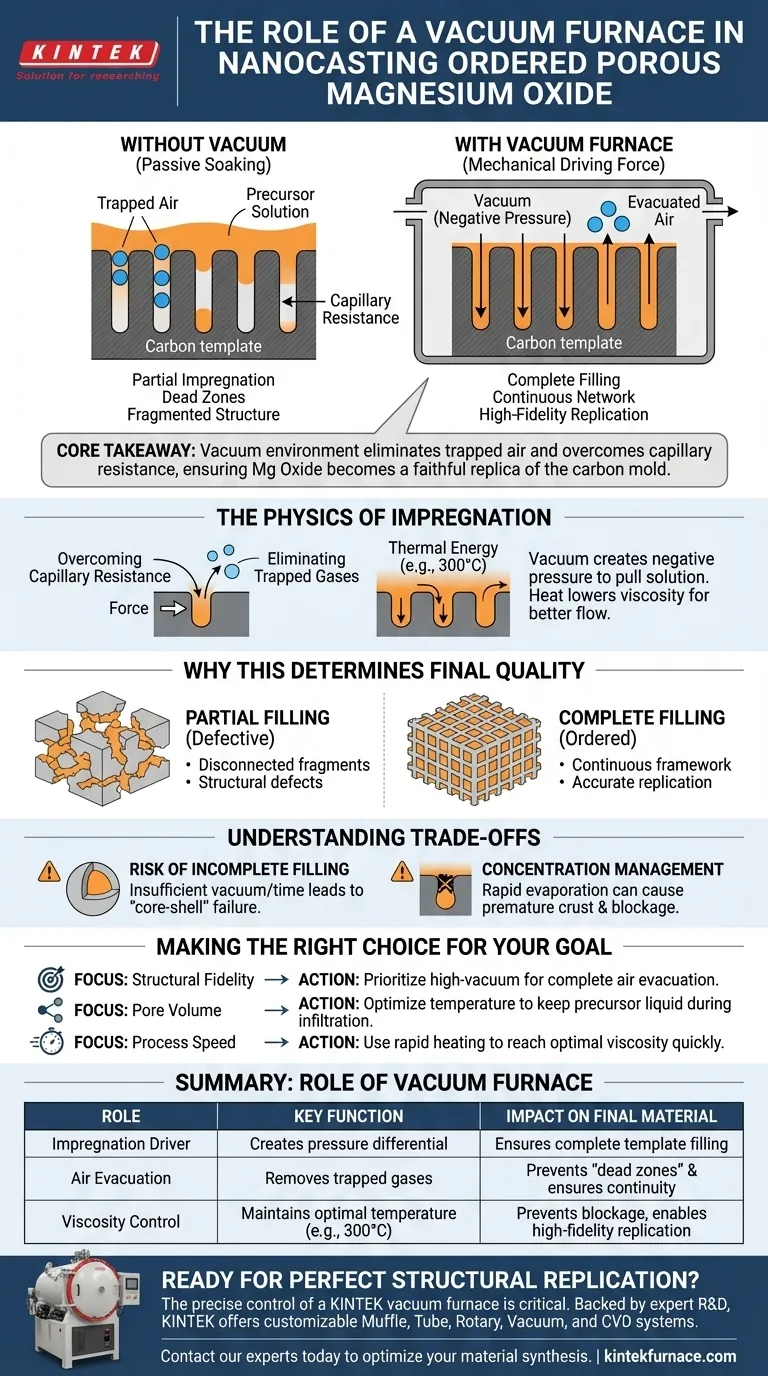
The primary function of a vacuum oven or furnace in the nanocasting of magnesium oxide is to act as a mechanical driving force during the impregnation stage. By creating a pressure differential, it forces the magnesium nitrate precursor solution to penetrate the microscopic voids of the carbon template, a task that passive soaking cannot accomplish effectively.
Core Takeaway Achieving a highly ordered structure relies entirely on how well the precursor fills the template. The vacuum environment eliminates trapped air and overcomes capillary resistance, ensuring the magnesium oxide becomes a faithful, structural replica of the carbon mold.

The Physics of Vacuum Impregnation
Overcoming Capillary Resistance
In nanocasting, the carbon template contains pores that are merely nanometers in diameter. At this scale, capillary resistance is a significant barrier.
Without external force, surface tension prevents the liquid precursor from entering these tiny spaces. The vacuum creates a negative pressure environment that physically pulls the solution into the deep internal structure of the carbon.
Eliminating Trapped Gases
The pores of a dry carbon template are naturally filled with air. If you simply pour a solution over the template, this air gets trapped, creating "dead zones" where the liquid cannot reach.
By operating under vacuum, you actively evacuate the air from within the pores. This removes the back-pressure that would otherwise repel the liquid, clearing the path for the magnesium nitrate to occupy 100% of the available volume.
The Role of Thermal Energy
The process often involves maintaining specific temperatures, such as 300°C, while under vacuum.
This elevated temperature lowers the viscosity of the precursor solution. When combined with the vacuum, this thermal energy increases the mobility of the ions, allowing them to flow more freely into the intricate pore network before solidification occurs.
Why This Determines Final Quality
Ensuring Structural Continuity
The goal of nanocasting is to create an "ordered" porous material. This order requires a continuous framework.
If the impregnation is partial, the resulting magnesium oxide will consist of disconnected fragments rather than a coherent structure. The vacuum ensures the precursor forms a continuous network inside the mold.
Accurate Template Replication
The final magnesium oxide is intended to be an inverse image of the carbon template.
Any void in the template that remains unfilled results in a defect in the final product. The vacuum furnace ensures high-fidelity replication, guaranteeing that the specific surface area and pore architecture of the magnesium oxide match the design of the carbon template.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Incomplete Filling
While vacuum helps, it is not a magic wand. If the vacuum pressure is insufficient, or if the time at temperature is too short, the center of the template particles may remain dry.
This leads to a "core-shell" failure where only the outer surface of the material is ordered, while the inside collapses during the template removal step.
Concentration Management
Using a vacuum at high temperatures (like 300°C) promotes rapid evaporation or decomposition components of the solution.
If the solvent evaporates too quickly before the pores are filled, the precursor may precipitate at the pore mouths, blocking them. This creates a crust that prevents further infiltration, ruining the internal structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your ordered porous magnesium oxide, tailor your approach to your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is Structural Fidelity: Prioritize a high-vacuum level to ensure every nanoscale void is evacuated of air before introducing the precursor.
- If your primary focus is Pore Volume: Ensure the temperature is optimized to keep the precursor strictly in the liquid phase during infiltration to prevent premature blockage.
- If your primary focus is Process Speed: Use a vacuum furnace with rapid heating capabilities to quickly reach the optimal viscosity point for the precursor.
The vacuum step is not merely a drying phase; it is the architect of your material's final internal structure.
Summary Table:
| Role of Vacuum Furnace | Key Function | Impact on Final Material |
|---|---|---|
| Impregnation Driver | Creates pressure differential to force precursor into nano-pores | Ensures complete filling of the carbon template |
| Air Evacuation | Removes trapped gases from template pores | Prevents "dead zones" and ensures structural continuity |
| Viscosity Control | Maintains optimal temperature (e.g., 300°C) for precursor flow | Prevents premature blockage and enables high-fidelity replication |
Ready to achieve perfect structural replication in your nanocasting process?
The precise control offered by a KINTEK vacuum furnace is critical for driving precursor infiltration and eliminating defects in ordered porous materials like magnesium oxide. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique nanocasting needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can optimize your material synthesis for superior structural fidelity and pore volume.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum oven for Fe-N-C precursor synthesis? Optimize Catalyst Structural Integrity
- What environmental controls does a vacuum diffusion furnace provide? Master High-Vacuum Heat Treatment
- Why is a high-temperature annealing furnace required for HP40Nb reformer tubes? Ensure Crack-Free Repair Welding
- How are vacuum furnaces used in lithium battery materials preparation? Achieve High Purity and Performance
- What other applications do vacuum furnaces have? Unlock Advanced Material Processing Across Industries
- What is the role of a Shell Preheating Furnace? Master C1023 Superalloy Fluidity and Precision
- What temperature range is used in vacuum brazing? Achieve Strong, Flux-Free Metal Joints
- Why is the use of a vacuum drying oven or a vacuum freeze dryer necessary? Preserve Carbon Nitride Nanosheet Integrity



















