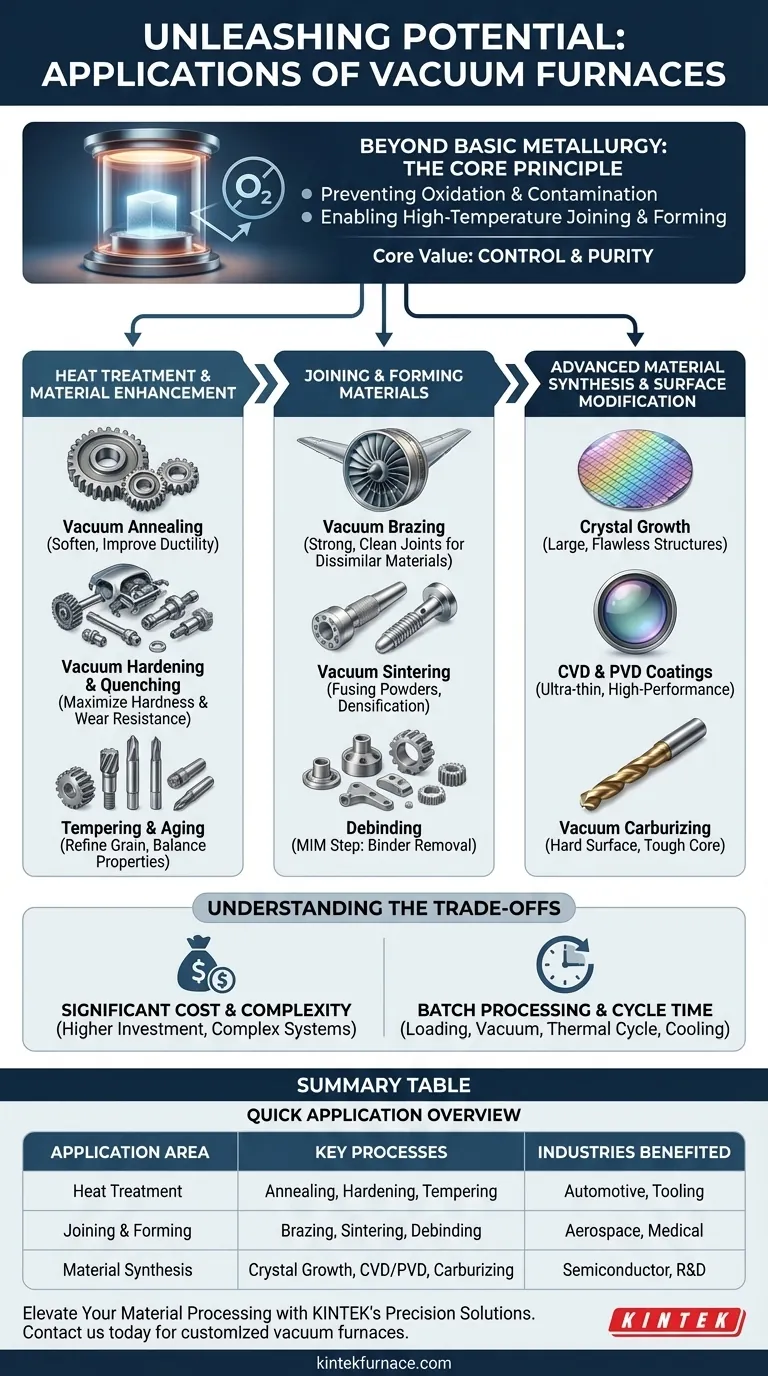
Beyond basic metallurgy, vacuum furnaces are indispensable tools across a vast spectrum of advanced industrial and scientific fields. Their applications range from creating cutting-edge electronics and medical implants to joining critical aerospace components and synthesizing next-generation composite materials. The furnace's ability to create a controlled, contaminant-free environment is the key to its versatility.
The core value of a vacuum furnace is not just heat, but control. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, it allows for thermal processes that are impossible in open air, enabling the creation of materials with superior purity, strength, and specific engineered properties.

The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
To understand the breadth of applications, you must first understand the fundamental problem a vacuum solves. At high temperatures, most materials react aggressively with the gases in our atmosphere, primarily oxygen.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The primary function of the vacuum is to create a chemically inert environment. This prevents oxidation, which can degrade a material's surface, compromise its structural integrity, and alter its electrical or mechanical properties.
This purity is essential for materials used in sensitive applications like electronics, medical devices, and aerospace, where even microscopic impurities can lead to catastrophic failure.
Enabling High-Temperature Joining and Forming
Processes like brazing (joining metals) and sintering (fusing powders into a solid) require pristine surfaces to form a strong bond. A vacuum removes atmospheric contaminants that would otherwise interfere with this metallurgical bonding.
This allows for the creation of complex, high-strength assemblies and dense, fully formed parts from powdered metals or ceramics.
Key Applications Across Industries
The principle of a controlled atmosphere unlocks a wide range of processes, each tailored to a specific outcome and industry.
Heat Treatment and Material Enhancement
This is the most traditional category of use, focused on altering the internal crystal structure of a material to improve its physical properties.
Key processes include:
- Vacuum Annealing: Softening metals to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility, making them easier to work with.
- Vacuum Hardening & Quenching: Rapidly cooling high-alloy steels in a controlled manner to achieve maximum hardness and wear resistance, crucial for the tool and automotive industries.
- Tempering and Aging: Low-temperature heat treatments that refine the material's grain structure to achieve a precise balance of hardness and toughness.
Joining and Forming Materials
These applications use the vacuum furnace to manufacture components or join them together.
Key processes include:
- Vacuum Brazing: Joining dissimilar materials (like ceramic-to-metal) using a filler metal that melts and flows in the vacuum. This creates incredibly strong, clean joints for components like aerospace turbine blades and electrical switchgear.
- Vacuum Sintering: Heating compacted powder materials (like tungsten carbide or ceramics) to bond the particles together, forming a dense, solid object. This is fundamental to producing cutting tools and medical implants.
- Debinding: A preliminary step for Metal Injection Molding (MIM), where the furnace is used to carefully burn off a polymer binder from a "green" part before the final sintering phase.
Advanced Material Synthesis and Surface Modification
This is where vacuum furnaces are used at the forefront of material science and high-technology manufacturing.
Key processes include:
- Crystal Growth: Creating large, single-crystal structures for the semiconductor and optics industries. The extreme purity of the vacuum environment is non-negotiable for producing flawless silicon wafers and optical crystals.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) & Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Applying ultra-thin, high-performance coatings to a substrate to enhance its hardness, wear resistance, or electrical properties.
- Vacuum Carburizing: A case-hardening process where carbon is diffused into the surface of steel at high temperatures to create a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a softer, tougher core.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, vacuum furnace technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Significant Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a substantial capital investment compared to atmospheric furnaces. They require complex vacuum pump systems, sophisticated controls, and robust chamber engineering to withstand extreme temperatures and pressure differentials.
Batch Processing and Cycle Time
Most vacuum furnace operations are batch processes, meaning parts must be loaded, the chamber sealed, a vacuum pulled, the thermal cycle run, and the chamber cooled before unloading. This can lead to longer overall cycle times compared to continuous, atmospheric belt furnaces.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your choice of process depends entirely on the material properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is joining complex parts with superior strength: Vacuum brazing is the definitive method for creating clean, flux-free, and exceptionally strong joints, especially with sensitive or dissimilar materials.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, pure components from powders: Vacuum sintering is essential for processing advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and parts made via Metal Injection Molding (MIM).
- If your primary focus is maximizing the hardness and fatigue life of alloys: Vacuum heat treatments like hardening and carburizing provide precise control over the material's final microstructure, free from the surface degradation seen in atmospheric processing.
- If your primary focus is research and development of novel materials: The furnace provides a pristine and controllable environment for synthesizing composites, growing crystals, and developing processes for additive manufacturing.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace is not just a heat source; it is a precision instrument for engineering materials at a fundamental level.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Industries Benefited |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Automotive, Tooling |
| Joining & Forming | Brazing, Sintering, Debinding | Aerospace, Medical |
| Material Synthesis | Crystal Growth, CVD/PVD, Carburizing | Semiconductor, R&D |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, electronics, or R&D, we can help you achieve superior results with clean, controlled environments. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can transform your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity



















