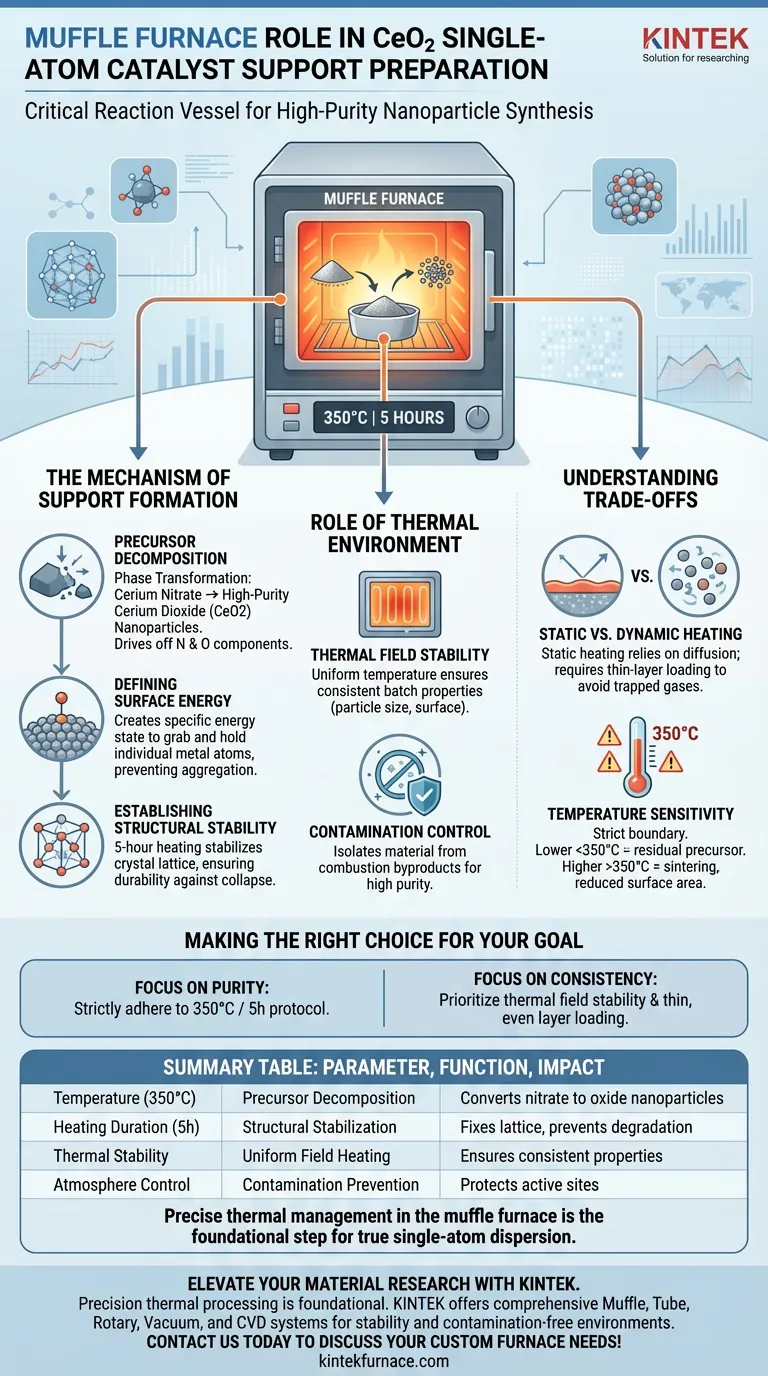
The muffle furnace serves as the critical reaction vessel for converting raw chemical precursors into a structured physical support. Specifically, in the preparation of cerium dioxide (CeO2) single-atom catalyst supports, it performs static heating of a cerium nitrate precursor at 350°C for 5 hours to ensure complete decomposition into high-purity nanoparticles.
The muffle furnace provides more than just heat; it defines the material's architecture. By executing a precise thermal program, it engineers the specific surface energy and structural stability necessary to anchor individual metal atoms, preventing them from aggregating into clusters during subsequent processing.

The Mechanism of Support Formation
Precursor Decomposition
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this context is phase transformation. The raw material, cerium nitrate, is a salt that must be fully converted into an oxide.
Through static heating at 350°C, the furnace drives off nitrogen and oxygen components. This ensures the full decomposition of the precursor, leaving behind only high-purity cerium dioxide nanoparticles.
Defining Surface Energy
For a "single-atom" catalyst to function, the support must have the ability to grab and hold individual metal atoms. This capability is determined during the calcination process.
The thermal treatment creates a physical substrate with specific surface energy. This energy state is what allows the support to effectively disperse metal atoms later, rather than allowing them to bond with each other.
Establishing Structural Stability
Durability is a key requirement for catalyst supports. The 5-hour heating duration is not arbitrary; it allows the crystal lattice of the cerium dioxide to stabilize.
This programmed thermal treatment ensures the nanoparticles achieve structural stability. Without this stable framework, the support could collapse or degrade under the stress of subsequent chemical reactions.
The Role of Thermal Environment
Thermal Field Stability
Consistency is vital for reproducible science. The muffle furnace provides excellent thermal field stability, meaning the temperature is uniform throughout the chamber.
This ensures that every part of the cerium nitrate batch receives the exact same energy input. The result is a consistent batch of catalyst supports where the particle size and surface properties are uniform.
Contamination Control
In single-atom catalysis, even trace impurities can ruin the performance of the active sites. The muffle furnace offers a contamination-free environment.
By isolating the material from combustion byproducts (unlike open-flame heating), it protects the purity of the cerium dioxide. This is essential for maintaining the integrity of the active centers that will be formed later.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Static vs. Dynamic Heating
The muffle furnace utilizes static heating, typically in static air. While this is excellent for stability and simplicity, it relies on diffusion for gas exchange.
If the precursor layer is too thick, decomposition gases may get trapped, leading to uneven structural properties. Unlike rotary tube furnaces that tumble particles for uniform exposure, a muffle furnace requires careful, thin-layer loading to ensure uniformity.
Temperature Sensitivity
The specific temperature profile (350°C) is a strict boundary. Deviating from this poses risks.
Lower temperatures may leave residual nitrate precursors, contaminating the support. Significantly higher temperatures (e.g., approaching the 800°C range used in other steps like atom trapping) could cause the cerium dioxide nanoparticles to sinter and grow, reducing the surface area available for anchoring single atoms.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your cerium dioxide supports, align your furnace protocols with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Support Purity: Adhere strictly to the 350°C protocol for 5 hours to ensure complete precursor decomposition without inducing sintering.
- If your primary focus is Batch Consistency: Prioritize the thermal field stability of the furnace and ensure the precursor is spread in a thin, even layer to mitigate the limitations of static heating.
Precise thermal management in the muffle furnace is the foundational step that dictates whether your final catalyst achieves true single-atom dispersion or fails due to aggregation.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Function | Impact on CeO2 Support |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (350°C) | Precursor Decomposition | Converts cerium nitrate into high-purity oxide nanoparticles. |
| Heating Duration (5h) | Structural Stabilization | Fixes the crystal lattice to prevent degradation during reactions. |
| Thermal Stability | Uniform Field Heating | Ensures consistent particle size and surface energy across the batch. |
| Atmosphere Control | Contamination Prevention | Protects active sites from impurities and combustion byproducts. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision thermal processing is the foundation of high-performance catalysis. At KINTEK, we understand that even a minor temperature deviation can compromise your catalyst's surface energy and structural integrity.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements. Whether you are performing delicate precursor decomposition or high-temperature atom trapping, our furnaces provide the thermal field stability and contamination-free environment essential for single-atom catalyst innovation.
Ready to optimize your synthesis? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Jinshu Tian, Yong Wang. NO Reduction with CO on Low‐loaded Platinum‐group Metals (Rh, Ru, Pd, Pt, and Ir) Atomically Dispersed on Ceria. DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202301227
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace required for sodium-ion cathode heat treatment? Engineering P2/P3 Crystal Phase Structures
- What are the primary uses of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What are the advantages of considering door opening options in a muffle furnace? Optimize Safety and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an oven? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing Purity
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it differ from a vacuum furnace? Choose the Right High-Temperature Solution
- How are muffle furnaces utilized in dental labs? Essential for Precision Dental Restorations
- How does an industrial electric box furnace maintain sample alignment? Ensure Precision in High-Throughput Calcination
- Why is a muffle furnace with precise temperature control required for space holder removal? Ensure Structural Integrity



















