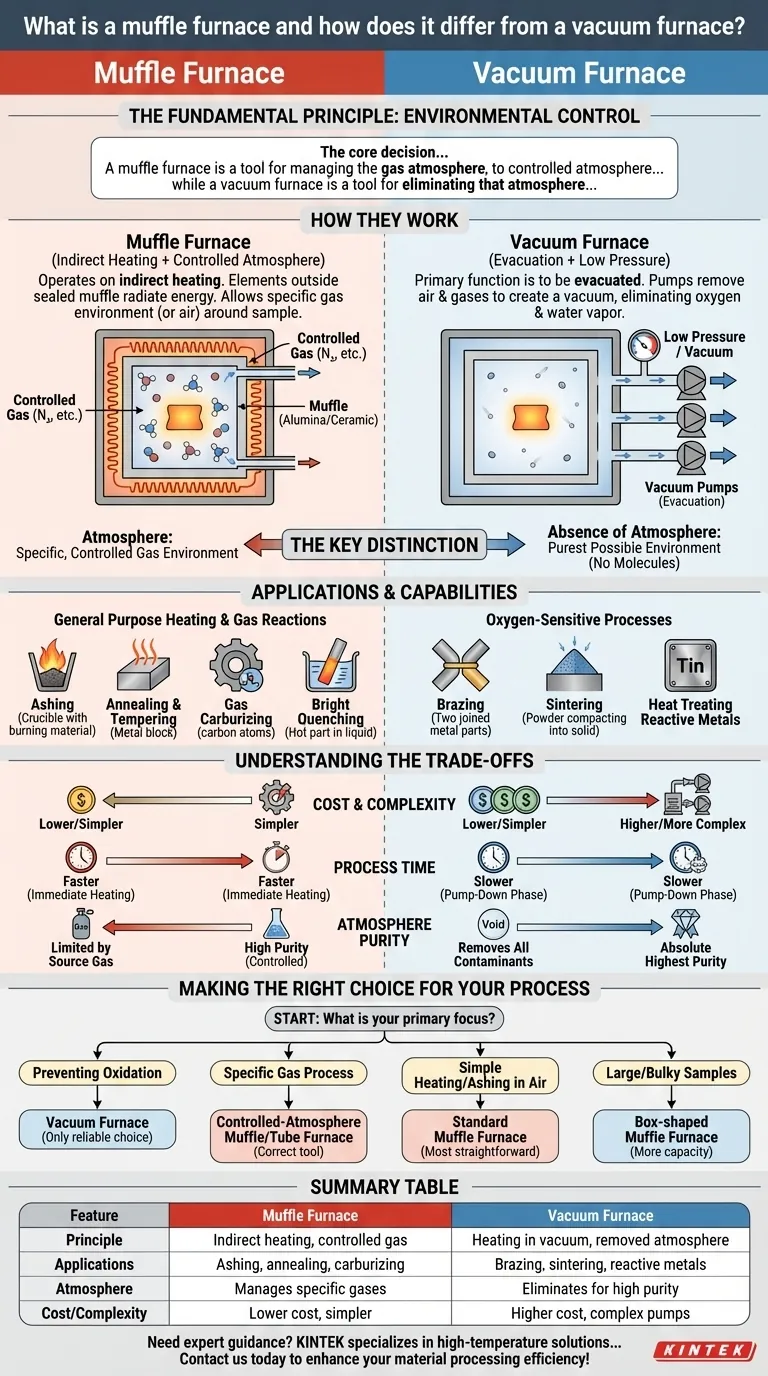
In high-temperature material processing, a muffle furnace is a chamber designed to isolate a sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any byproducts of combustion. It differs from a vacuum furnace primarily in its operating environment; a muffle furnace controls the atmosphere within its chamber, while a vacuum furnace works by removing the atmosphere entirely. The choice between them depends on what you need to protect your sample from: the heat source itself, or the gases in the air.
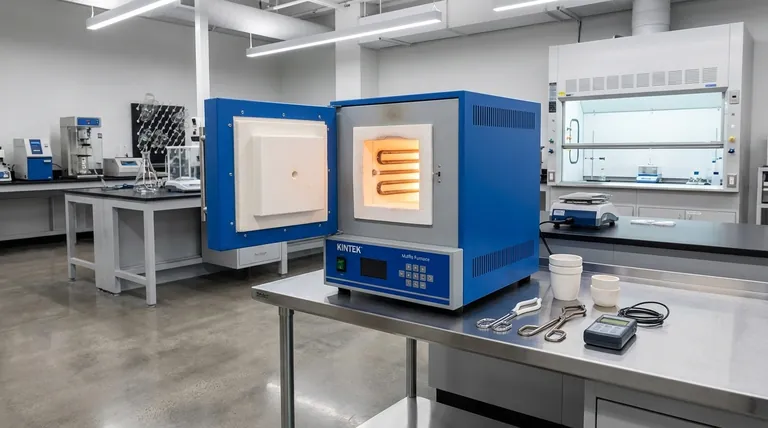
The core decision between a muffle furnace and a vacuum furnace is a question of environmental control. A muffle furnace is a tool for managing the gas atmosphere around a sample, while a vacuum furnace is a tool for eliminating that atmosphere to prevent reactions like oxidation.

The Fundamental Principle: What Are You Isolating?
To select the right furnace, you must first define what environmental factor poses the biggest risk to your process. Both furnace types are designed for isolation, but they isolate the sample from different things.
How a Muffle Furnace Works
A muffle furnace operates on the principle of indirect heating. The heating elements are located outside a sealed inner chamber, known as the "muffle."
This muffle, typically made of a high-temperature ceramic like alumina, heats up and radiates that energy evenly to the sample inside. Think of it as a perfectly uniform "oven within an oven." This design protects the sample from direct radiation and any contaminants from the electric elements.
Crucially, this allows an operator to fill the muffle chamber with a specific, controlled atmosphere—such as nitrogen for annealing or a carbon-rich gas for carburizing. It can also simply operate with air.
How a Vacuum Furnace Works
A vacuum furnace also uses an isolated, sealed chamber, but its primary function is to be evacuated by a series of pumps. This removes air and other gases to create a low-pressure, or vacuum, environment.
The goal is to eliminate atmospheric components, especially oxygen and water vapor, that can react with materials at high temperatures. By removing these reactive gases, the furnace prevents oxidation, discoloration, and contamination of sensitive materials.
The Key Distinction: Atmosphere vs. Absence of Atmosphere
The functional difference is simple but profound. A muffle furnace is used when you need to perform a heat treatment in a specific, controlled gas environment.
A vacuum furnace is used when the mere presence of any standard atmosphere, even an inert one, is detrimental to the material. It creates the purest possible environment by removing virtually all molecules.
Comparing Key Applications and Capabilities
The distinct operating principles of these furnaces make them suitable for very different tasks.
General Purpose Heating and Gas Reactions (Muffle Furnace)
Because they can operate with air or a specific gas, muffle furnaces are versatile. They are ideal for applications like:
- Ashing: Burning off organic material to determine inorganic content.
- Annealing & Tempering: Modifying material properties in a controlled gas.
- Gas Carburizing: Introducing carbon into a metal's surface.
- Bright Quenching: Cooling a material in a protective atmosphere to prevent surface oxidation.
Oxygen-Sensitive Processes (Vacuum Furnace)
Vacuum furnaces are essential for processes where any oxidation would lead to component failure or contamination. Common uses include:
- Brazing: Joining metals with a filler material that melts at a lower temperature.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials together with heat and pressure.
- Heat Treating reactive metals like titanium or certain superalloys.
A Note on Geometry: Tube vs. Muffle Chambers
The furnace chamber itself can have different shapes. Tube furnaces are cylindrical and best for small or continuous samples, while muffle furnaces are box-shaped, accommodating larger or bulkier items.
It's important to note that you can have a vacuum muffle furnace or a vacuum tube furnace. The term "muffle" or "tube" describes the chamber's shape, while "vacuum" describes its atmospheric capability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capability with complexity and cost.
Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are inherently more complex systems. They require sophisticated pumps, seals, and control systems to create and maintain a vacuum, making them significantly more expensive to purchase and maintain than most standard atmosphere muffle furnaces.
Process Time
A vacuum furnace requires a "pump-down" phase to evacuate the chamber before heating can begin. This can add considerable time to the overall process cycle compared to a muffle furnace that can start heating immediately.
Atmosphere Purity
While a controlled-atmosphere muffle furnace can provide a very pure environment, it is limited by the purity of the source gas. For the absolute highest level of purity, nothing surpasses a high-vacuum environment, which removes nearly all potential contaminants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided entirely by the chemical and physical requirements of your material at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of reactive materials: A vacuum furnace is the only reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is executing a process in a specific gas (e.g., nitrogen, argon): A controlled-atmosphere muffle or tube furnace is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is simple high-temperature heating or ashing in air: A standard, cost-effective muffle furnace is the most straightforward solution.
- If your primary focus is processing large, bulky samples: A box-shaped muffle furnace provides more internal capacity than a tube furnace, regardless of its atmospheric capability.
By understanding the core principle of environmental control, you can confidently select the precise furnace your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Indirect heating with controlled atmosphere (e.g., air, nitrogen) | Heating in a vacuum to remove atmosphere and prevent reactions |
| Key Applications | Ashing, annealing, gas carburizing, bright quenching | Brazing, sintering, heat treating reactive metals |
| Atmosphere Control | Manages specific gases within the chamber | Eliminates atmosphere entirely for high purity |
| Cost & Complexity | Generally lower cost and simpler operation | Higher cost due to pumps, seals, and maintenance |
| Process Time | Faster start-up with immediate heating | Slower due to pump-down phase before heating |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature solutions, offering Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your material processing efficiency and achieve precise results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















