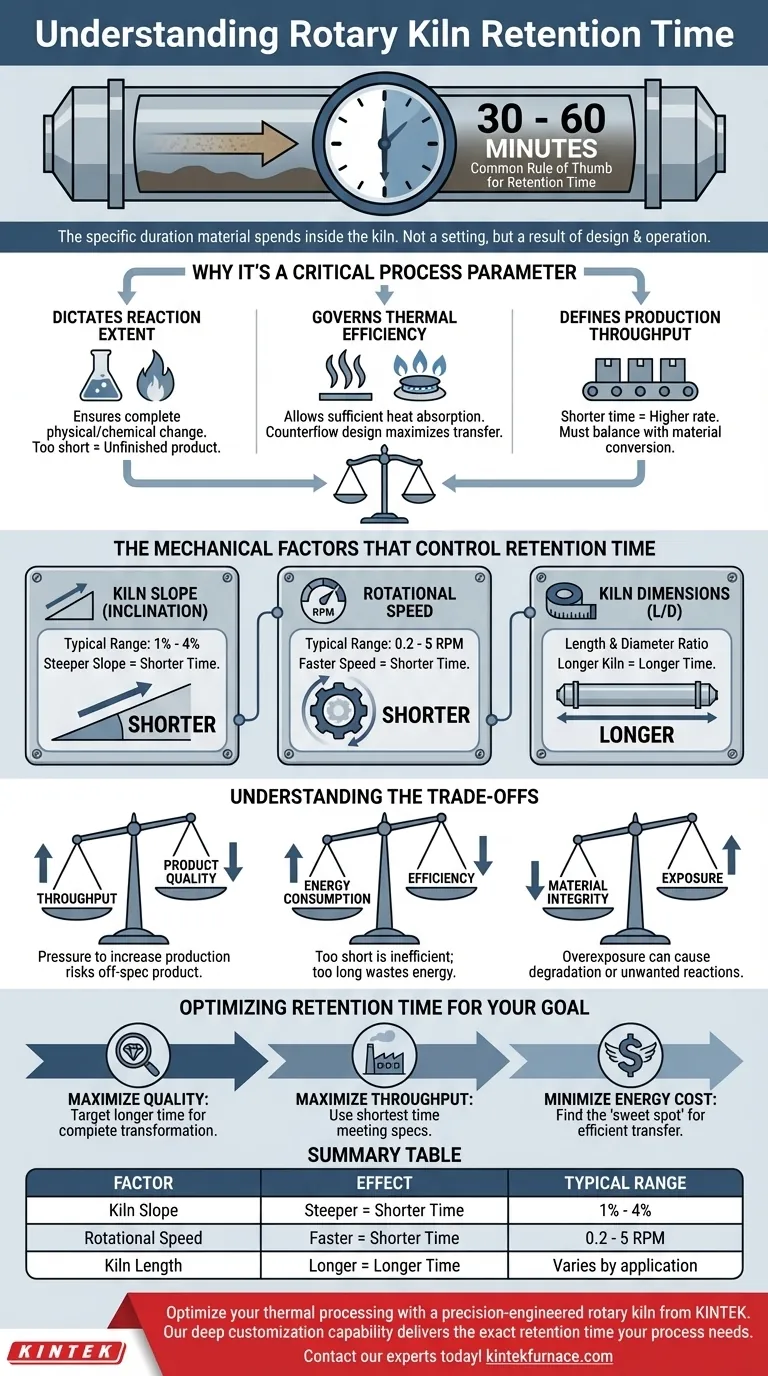
In a rotary kiln, retention time is the specific duration that a material spends inside the kiln being processed. While there is no single universal value, a common rule of thumb for many industrial applications is a retention time of 30 to 60 minutes. This duration is not arbitrary; it is a critical parameter carefully determined by the thermal and chemical requirements needed to transform the raw feed into a finished product.
Retention time is not an independent setting but a direct consequence of the kiln's mechanical design and operating parameters. Understanding the factors that control it is essential for optimizing both product quality and operational efficiency.
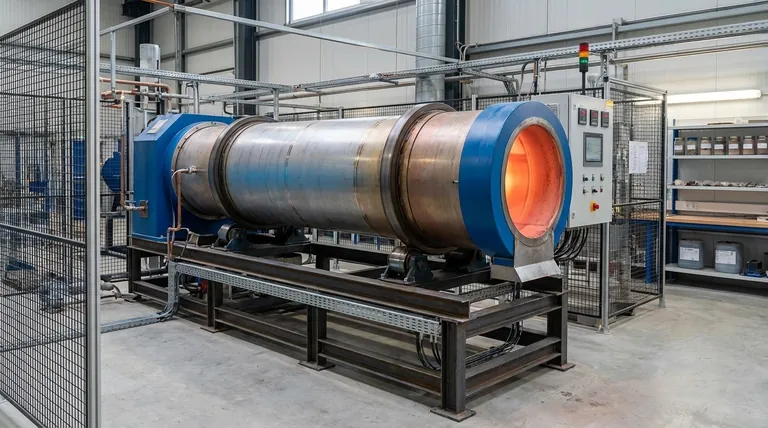

Why Retention Time is a Critical Process Parameter
Retention time, also called residence time, is one of the most important variables in kiln operation. It directly influences the final product characteristics, energy consumption, and overall plant throughput.
It Dictates the Extent of Reaction
The primary purpose of a kiln is to induce a physical or chemical change through heating. This transformation requires exposing the material to a specific temperature for a certain amount of time.
If the retention time is too short, the material may exit the kiln before the reaction is complete, resulting in a low-quality or unfinished product.
It Governs Thermal Efficiency
Heat transfer from the gas stream (generated by the burner) to the solid material is not instantaneous. A sufficient retention time ensures the material has enough exposure to absorb the necessary thermal energy.
This is often optimized with a counterflow design, where hot gases flow opposite to the material, maximizing the temperature difference and improving heat transfer efficiency over the material's entire journey.
It Defines Production Throughput
Retention time is inversely proportional to the kiln's production rate. A shorter retention time means material moves through the system faster, increasing the amount of product that can be processed per hour.
This creates a fundamental conflict between maximizing throughput and ensuring complete material conversion, which must be carefully balanced.
The Mechanical Factors That Control Retention Time
You cannot directly "set" the retention time. Instead, it is the outcome of several key mechanical and operational factors.
Kiln Slope (Inclination)
Rotary kilns are installed at a slight downward angle, typically between 1% and 4%. This inclination is the primary force that causes material to advance from the feed end to the discharge end.
A steeper slope results in faster material travel and therefore a shorter retention time.
Rotational Speed
The kiln shell rotates slowly on its axis, generally between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute (rpm). This rotation tumbles the material, exposing new surfaces to the hot gases and helping it move down the slope.
A faster rotational speed increases the rate of material advance, leading to a shorter retention time.
Kiln Dimensions (Length and Diameter)
The physical dimensions of the kiln shell establish the total travel path for the material. All other factors being equal, a longer kiln will naturally result in a longer retention time.
The ratio of the kiln's length to its diameter (L/D) is a fundamental design parameter that engineers use to achieve a target retention time for a specific process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing retention time is not about maximizing it; it's about finding the ideal balance for a specific operational goal. Making a change to improve one metric often comes at the expense of another.
Throughput vs. Product Quality
This is the most common trade-off. Operators are often pressured to increase production (shorter retention time), but this can risk incomplete reactions and off-spec product. Conversely, guaranteeing high quality with a long retention time may sacrifice valuable throughput.
Energy Consumption vs. Efficiency
A very short retention time can be inefficient, as unburned fuel and heat may exit the kiln before being fully transferred to the material. However, an excessively long retention time can also waste energy by heating the kiln structure and product for longer than necessary.
Material Integrity vs. Exposure
For some sensitive materials, too much time at high temperatures can be detrimental. It can lead to unwanted secondary reactions, melting, or physical degradation of the product. In these cases, retention time must be strictly limited.
Optimizing Retention Time for Your Goal
The "correct" retention time is entirely dependent on your primary objective. It is a key lever to pull when adjusting the kiln's performance.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product quality: Target a longer retention time to ensure all chemical and physical transformations are fully completed.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production throughput: Operate with the shortest possible retention time that still consistently meets minimum product quality specifications.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy cost: Find the operational sweet spot where retention time is just long enough for efficient heat transfer but no longer, avoiding unnecessary energy waste.
Ultimately, controlling retention time is about mastering the interplay between the kiln's mechanical design and the material's transformation requirements.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Retention Time | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Kiln Slope | Steeper slope = Shorter time | 1% - 4% inclination |
| Rotational Speed | Faster speed = Shorter time | 0.2 - 5 RPM |
| Kiln Length | Longer kiln = Longer time | Varies by application |
Optimize your thermal processing with a precision-engineered rotary kiln from KINTEK.
Achieving the perfect balance between product quality, throughput, and energy efficiency requires a kiln designed for your specific material and process requirements. KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, perfectly suited for demanding industrial applications.
Our strong deep customization capability allows us to tailor a rotary kiln's design—controlling critical factors like slope, speed, and L/D ratio—to deliver the exact retention time your process needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary kiln can enhance your operational performance and profitability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















