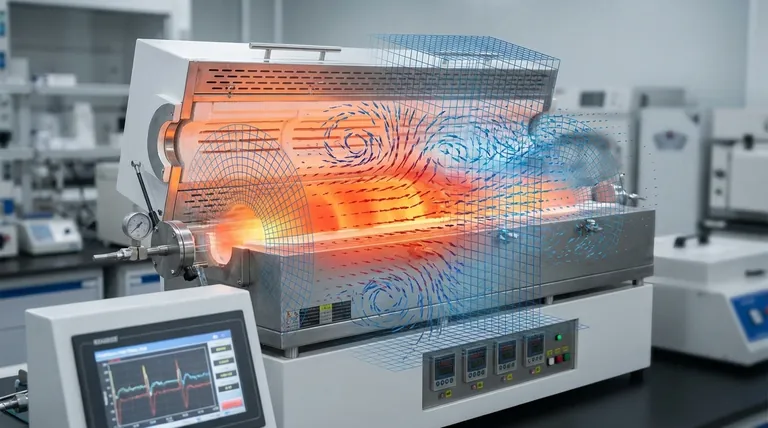
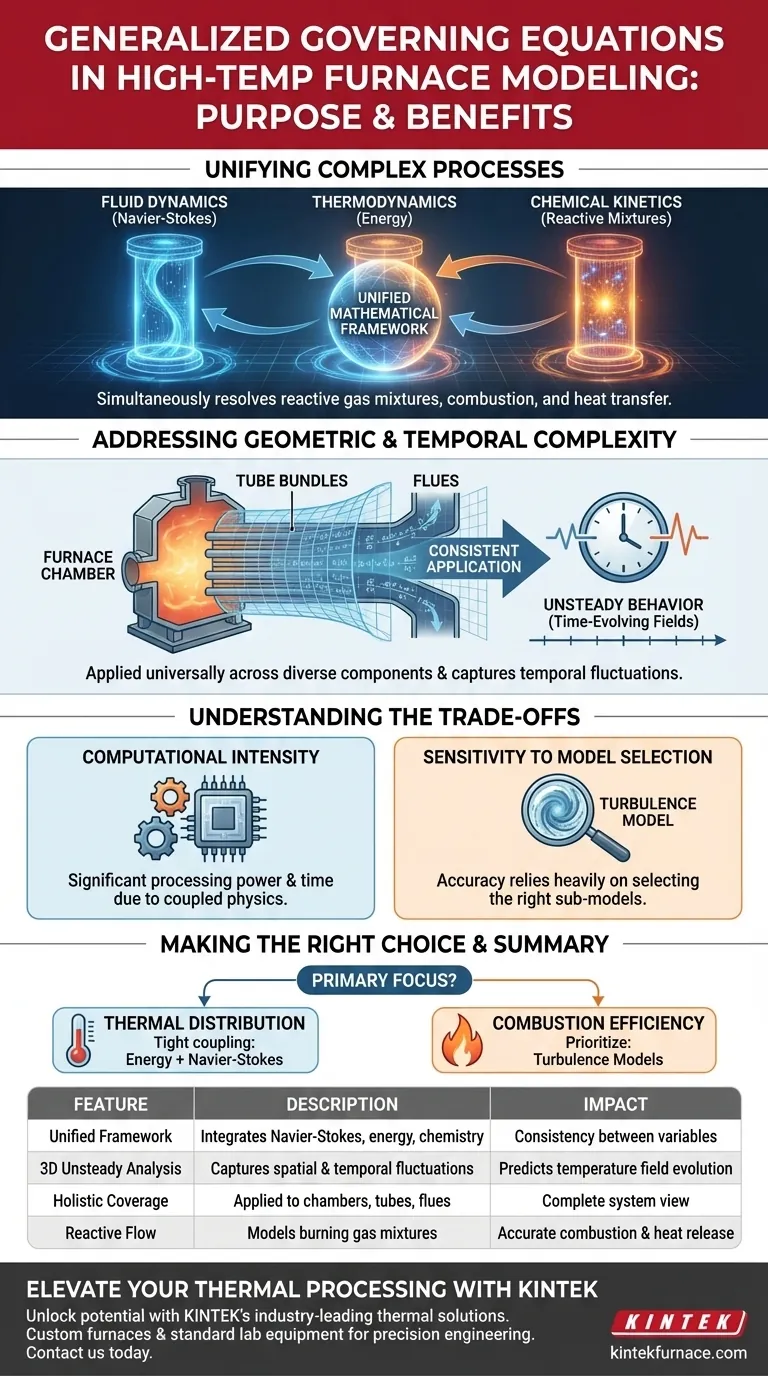
The primary purpose of using generalized governing equations is to establish a unified mathematical framework that simultaneously resolves fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and chemical kinetics. By integrating three-dimensional unsteady Navier-Stokes equations with energy equations and turbulence models, this approach allows for the accurate simulation of reactive gas mixtures as they flow, combust, and transfer heat within a furnace.
This modeling approach provides the necessary structural foundation for numerical analysis, ensuring that complex physical and chemical processes are calculated consistently across the furnace's chamber, tube bundles, and flues.
Unifying Complex Physical Processes
To accurately model a high-temperature furnace, you cannot treat airflow and heat transfer as separate, isolated events.
Integration of Distinct Physics
The generalized equations serve as a bridge. They combine the laws of motion (Navier-Stokes) with the laws of thermodynamics (energy equations) and statistical flow approximations (turbulence models).
This creates a single system where changes in one variable, such as velocity, immediately impact others, such as temperature distribution.
Handling Reactive Gas Mixtures
Inside a furnace, the fluid is not static; it is a chemically reacting mixture.
The governing equations are designed to describe how these reactive gases behave during combustion. This ensures the model captures the dynamic relationship between the flow of fuel and the release of heat energy.
Addressing Geometric and Temporal Complexity
Real-world furnaces possess intricate internal structures that disrupt simple flow patterns.
Modeling Across Diverse Components
The "generalization" of these equations allows them to be applied universally across different parts of the furnace.
Whether the gas is moving through the open furnace chamber, navigating dense tube bundles, or exiting through flues, the mathematical framework remains consistent. This provides a holistic view of the system rather than a piecemeal analysis.
Capturing Unsteady Behavior
Furnace operations are rarely perfectly steady; they involve fluctuations over time.
These equations specifically address three-dimensional unsteady conditions. This allows engineers to predict how flow and temperature fields evolve temporally, rather than just seeing a static snapshot.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While generalized governing equations provide high-fidelity simulations, they introduce specific challenges that must be managed.
Computational Intensity
Because these equations couple multiple complex physics (flow, heat, and turbulence) into a single framework, the computational cost is significant.
Solving these unsteady 3D equations requires substantial processing power and time compared to simplified, steady-state, or lower-dimensional models.
Sensitivity to Model Selection
The accuracy of the generalized framework relies heavily on the sub-models selected, particularly for turbulence.
If the turbulence model integrated into the governing equations does not match the specific flow regime of the furnace, the predictions for mixing and combustion efficiency may diverge from reality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Simulation
To leverage generalized governing equations effectively, align your modeling strategy with your specific engineering goals.
- If your primary focus is accurate thermal distribution: Ensure your energy equations are tightly coupled with the Navier-Stokes terms to capture how flow recirculation affects heat transfer in tube bundles.
- If your primary focus is combustion efficiency: Prioritize the accuracy of the turbulence models within the generalized equations, as these dictate how well reactive gas mixtures interact.
Ultimately, using generalized governing equations transforms disjointed physical data into a coherent, actionable digital twin of your furnace operations.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Impact on Furnace Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Unified Framework | Integrates Navier-Stokes, energy, and chemistry equations | Ensures consistency between flow, heat, and reaction variables |
| 3D Unsteady Analysis | Captures spatial and temporal fluctuations | Predicts how temperature fields evolve over time across complex geometries |
| Holistic Coverage | Applied to chambers, tube bundles, and flues | Provides a complete system view rather than isolated component analysis |
| Reactive Flow | Models behavior of burning gas mixtures | Accurate simulation of combustion efficiency and heat release |
Elevate Your Thermal Processing with Precision Engineering
Unlock the full potential of your high-temperature operations with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your specific research or industrial requirements.
Whether you need custom-engineered furnaces for complex 3D thermal profiles or standard lab equipment, KINTEK delivers the reliability and accuracy your work demands. Contact us today to discuss your unique needs and see how our customizable high-temperature systems can optimize your furnace performance.
Visual Guide
References
- O. I. Varfolomeeva, D. A. Khvorenkov. Development of a universal model for numerical analysis of firebox processes in heat-generating plants. DOI: 10.30724/1998-9903-2025-27-6-171-186
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the holding time in a high-temperature furnace affect 0W Fe-C-B-Cr-W alloys? Optimize Phase Dissolution
- How do aerospace industries benefit from high-temperature furnaces? Unlock Superior Strength and Durability
- How does the QIO algorithm improve temperature control precision in electric furnaces? Achieve Global Optimization
- Why is a laboratory oven required for drying samples at 80°C for MoO3/Ti-Felt? Ensure Electrode Structural Integrity
- What is the function of ball milling in Li-NASICON synthesis? Optimize Your Solid Electrolyte Performance
- How does a vacuum drying oven contribute to biodiesel moisture control? Ensure Fuel Quality & Stability
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for precursors on carbon paper? Maximize Material Performance
- How does the sintering process enhance conventional ceramics with Alumina? Boost Strength and Insulation



















