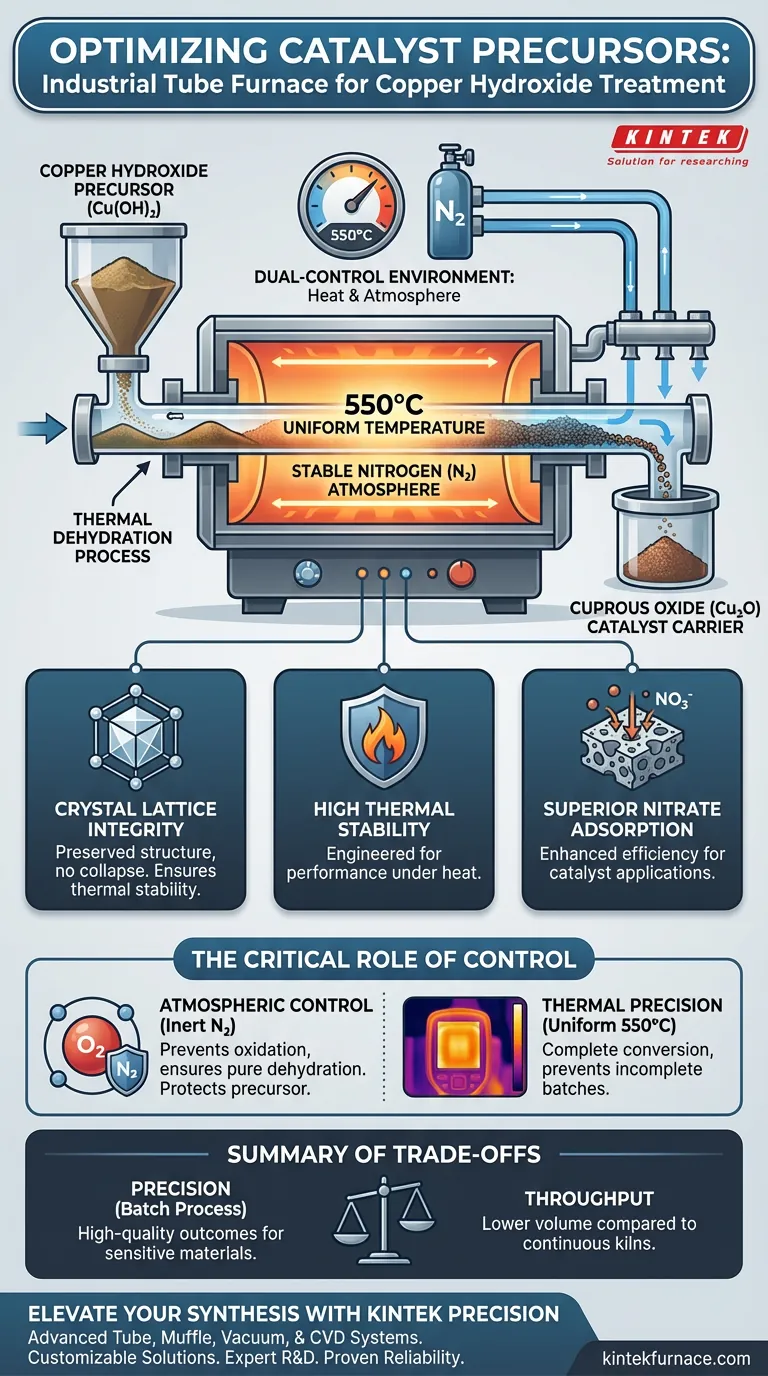
The primary purpose of an industrial-grade tube furnace in this context is to facilitate the precise thermal dehydration of copper hydroxide precursors into chemically stable cuprous oxide (Cu2O). By maintaining a consistent temperature of 550°C within a stable nitrogen atmosphere, the furnace ensures the material undergoes complete conversion while preserving its crystal lattice integrity.
Core Takeaway: The tube furnace provides a dual-control environment—regulating both heat and atmosphere—to transform copper hydroxide into cuprous oxide. This specific process is essential for creating a catalyst carrier with high thermal stability and superior nitrate adsorption capabilities.
The Critical Role of Atmospheric Control
Establishing an Inert Environment
The defining feature of the tube furnace for this application is its ability to maintain a stable nitrogen inert atmosphere.
Unlike open-air heating, which introduces oxygen that could unpredictably alter the oxidation state of the copper, a nitrogen environment protects the precursor.
Facilitating Pure Dehydration
The goal is to remove water molecules without degrading the material's fundamental chemistry.
The inert atmosphere ensures that the process remains a strict thermal decomposition (dehydration) rather than an oxidative reaction. This specificity is what allows the copper hydroxide to convert cleanly into cuprous oxide (Cu2O).
Thermal Precision and Material Conversion
Achieving Complete Dehydration
The furnace is operated at a specific target temperature, typically 550°C, to drive the chemical conversion.
At this thermal plateau, the copper hydroxide completely releases its water content. The industrial-grade nature of the furnace ensures that this temperature is uniform throughout the heating zone, preventing incomplete conversion in parts of the batch.
Preserving Crystal Lattice Integrity
Heat treatment is not just about changing chemical composition; it is about engineering the physical structure.
The controlled environment ensures the integrity of the crystal lattice structure is maintained during the transition from hydroxide to oxide. This structural preservation is directly responsible for the material's thermal stability.
Enhancing Adsorption Capabilities
The ultimate output of this process is a catalyst carrier designed for performance.
Because the lattice structure is preserved rather than collapsed or distorted, the final cuprous oxide exhibits superior nitrate adsorption capabilities. The furnace conditions are therefore directly linked to the final efficiency of the catalyst.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precision vs. Throughput
While industrial tube furnaces offer exceptional control over atmosphere and temperature, they often operate as batch or semi-continuous processes.
This ensures high-quality outcomes for sensitive materials like copper hydroxide, but it may have lower throughput compared to continuous rotary kilns used for less sensitive bulk materials.
Sensitivity to Parameters
The quality of the final cuprous oxide is heavily dependent on the stability of the nitrogen flow and temperature uniformity.
If the atmosphere is breached or the temperature fluctuates significantly from 550°C, the crystal lattice may deform, or the dehydration may be incomplete, drastically reducing the material's nitrate adsorption performance.
Optimizing Your Heat Treatment Strategy
When selecting equipment for precursor conversion, align your operational parameters with your desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is Adsorption Performance: Prioritize the stability of the nitrogen atmosphere to protect the crystal lattice structure from oxidative defects.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure the furnace can maintain a strict 550°C profile to guarantee complete dehydration of the hydroxide into cuprous oxide.
Precise environmental control is the difference between a generic oxide and a high-performance catalyst carrier.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Requirement | Role in Material Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temperature | 550°C | Ensures complete dehydration and chemical conversion. |
| Atmosphere | Stable Nitrogen (Inert) | Prevents oxidation and protects the Cu2O oxidation state. |
| Structural Goal | Lattice Integrity | Guarantees high thermal stability and adsorption performance. |
| Final Product | Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) | Optimized catalyst carrier for nitrate adsorption. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect crystal lattice integrity requires more than just heat—it requires total environmental control. KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal solutions, providing high-performance Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for sensitive chemical transformations like precursor dehydration.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our furnaces are engineered for unmatched temperature uniformity and atmospheric stability.
- Customizable Solutions: We adapt our systems to meet your specific nitrate adsorption or catalyst carrier requirements.
- Proven Reliability: Trusted by laboratories and industrial facilities for high-temp processing.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment strategy? Contact our technical experts today to find the ideal customizable furnace for your unique research and production needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Wanru Liao, Min Liu. Sustainable conversion of alkaline nitrate to ammonia at activities greater than 2 A cm−2. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45534-2
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- What materials are commonly used for furnace tube construction and why? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab's Needs
- How do split tube furnaces provide access to the chamber? Unlock Easy Sample Handling for Your Lab
- What is the primary role of a tubular furnace in industrial production? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Superior Materials
- What design features make horizontal furnaces versatile? Achieve High-Volume, Uniform Thermal Processing
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the preparation of highly porous carbon sheets from cellulose?
- Why is the first stage of sintering in a tube vacuum sintering furnace necessary? Master the Space-Holder Technique
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in STO thin film annealing? Unlock Neuromorphic Potential



















