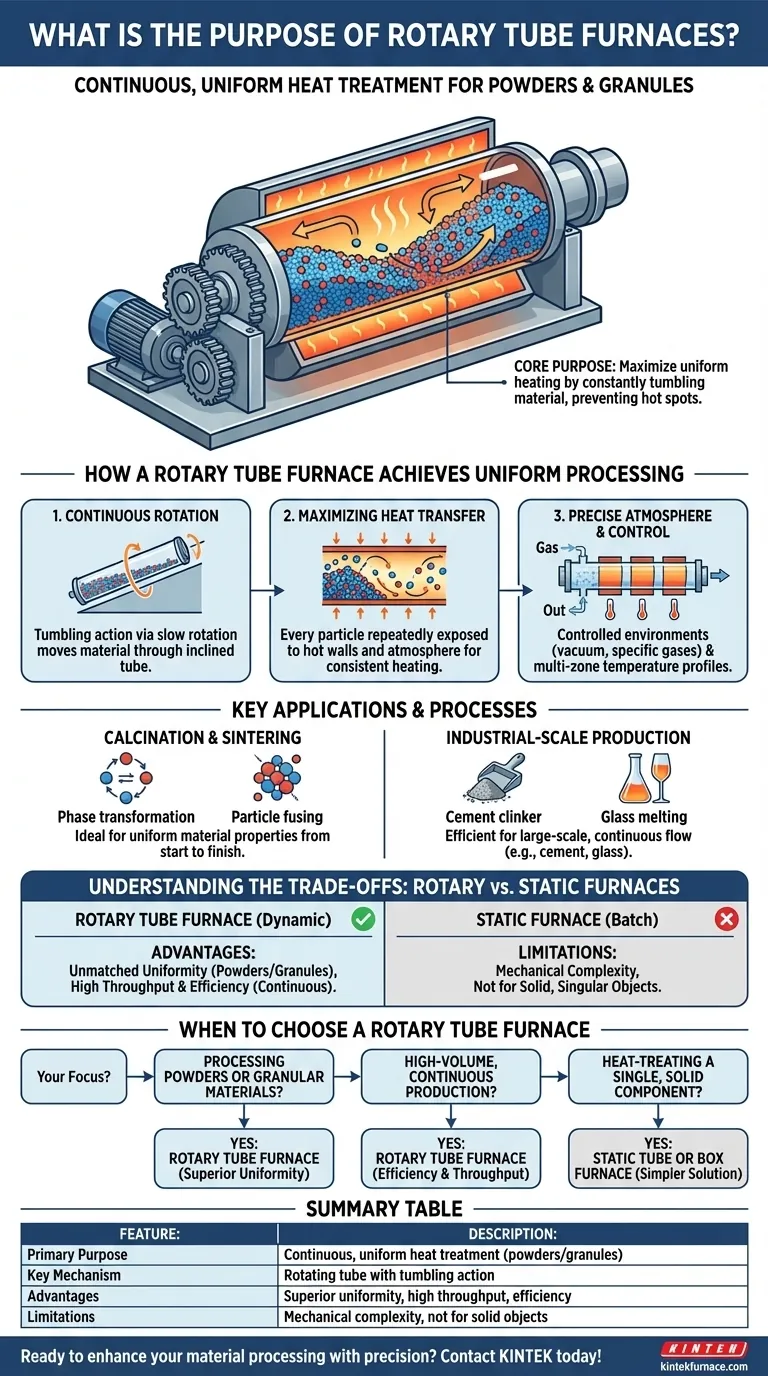
In essence, a rotary tube furnace is designed for the continuous heat treatment of materials, particularly powders and granules. Its primary purpose is to ensure exceptionally uniform heating by constantly tumbling the material inside a rotating, heated tube, which maximizes exposure to the desired temperature and atmospheric conditions.
The core challenge in heat-treating powders is preventing hot spots and ensuring every particle is processed identically. A rotary tube furnace solves this directly through its rotation, which provides a level of thermal uniformity and efficiency that static furnaces cannot easily match for these material types.
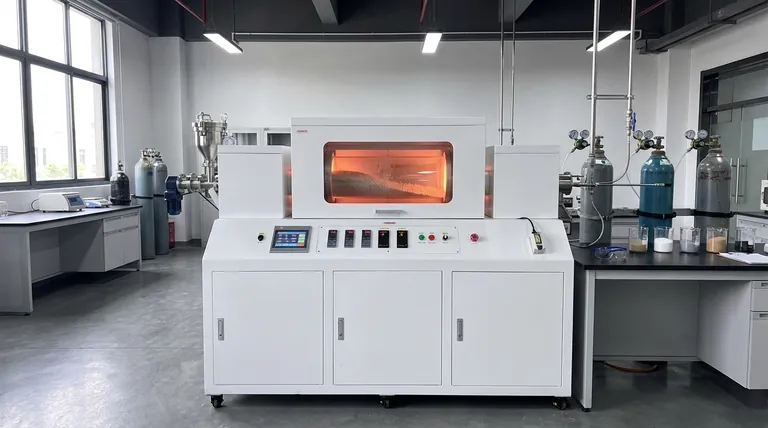

How a Rotary Tube Furnace Achieves Uniform Processing
A rotary tube furnace's effectiveness comes from its unique mechanical design, which combines movement with precise thermal and atmospheric control.
The Principle of Continuous Rotation
The furnace is built around a long, cylindrical tube, often set at a slight incline. This tube rotates slowly during operation.
As material is fed into the higher end, the combination of the incline and the rotation causes it to tumble and move continuously toward the lower end for collection.
Maximizing Heat Transfer
External heating elements provide the thermal energy. The constant tumbling motion is the critical feature.
This movement ensures that every particle of the material is repeatedly exposed to the hot inner wall of the tube and the controlled atmosphere within it. This prevents the outer layers of the material from insulating the core, guaranteeing uniform heat distribution throughout the entire batch.
Precise Atmosphere and Temperature Control
These systems allow for a highly controlled environment. Many are designed with multiple thermal zones along the length of the tube, enabling precise temperature profiles for complex processes.
They can also be filled with specific gases or operated under a vacuum, allowing for processes like oxidation (adding oxygen) or treatments in inert atmospheres to prevent unwanted reactions.
Key Applications and Processes
The unique capabilities of rotary tube furnaces make them ideal for a range of specific, high-temperature applications.
Calcination and Sintering
Calcination is a process that uses heat to cause phase transformations or remove volatile components from a material. Sintering uses heat to fuse particles together without melting them.
The uniform heating of a rotary furnace is perfect for these processes, ensuring consistent material properties from start to finish.
Industrial-Scale Production
In the building materials industry, rotary furnaces are workhorses for producing cement clinkers and burning gypsum. Their ability to handle a continuous flow of material makes them highly efficient for large-scale production.
They are also used in the glass industry for melting raw materials, where uniform temperature is critical for achieving a high-quality, homogenous final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rotary vs. Static Furnaces
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages in context is key to making the right choice.
Advantage: Unmatched Uniformity for Powders
For powders, granules, or small parts, a rotary furnace's tumbling action provides superior temperature uniformity compared to a static furnace, where material sits motionless and can suffer from uneven heating.
Advantage: High Throughput and Efficiency
The continuous nature of a rotary furnace makes it far more efficient for processing large volumes of material. It avoids the downtime of loading and unloading required by batch-based static furnaces, resulting in higher throughput and lower operating costs.
Limitation: Mechanical Complexity
The rotation mechanism, including the motor, seals, and drive system, adds mechanical complexity. This introduces more maintenance points and potential for wear and tear compared to the simpler design of a static box or tube furnace.
Limitation: Not Ideal for Solid, Singular Objects
These furnaces are designed for materials that can flow and tumble. They are entirely unsuitable for heat-treating a single, large, or dimensionally sensitive solid part that must remain stationary.
When to Choose a Rotary Tube Furnace
Your specific processing goal is the most important factor in selecting the right thermal equipment.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granular materials: The superior temperature uniformity offered by a rotary furnace makes it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A rotary furnace provides significant efficiency and throughput advantages over batch-based systems.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a single, solid component: A static tube furnace or a simple box furnace is the more appropriate and straightforward solution.
By understanding its unique rotational mechanism, you can confidently determine if this powerful tool is the right solution for your material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Continuous, uniform heat treatment of powders and granules |
| Key Mechanism | Rotating tube with tumbling action for even exposure |
| Main Applications | Calcination, sintering, cement production, glass melting |
| Advantages | Superior temperature uniformity, high throughput, efficiency |
| Limitations | Mechanical complexity, not suitable for solid objects |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Tube Furnaces, designed for uniform heating and high efficiency in powder and granule applications. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your lab's performance and throughput!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency



















