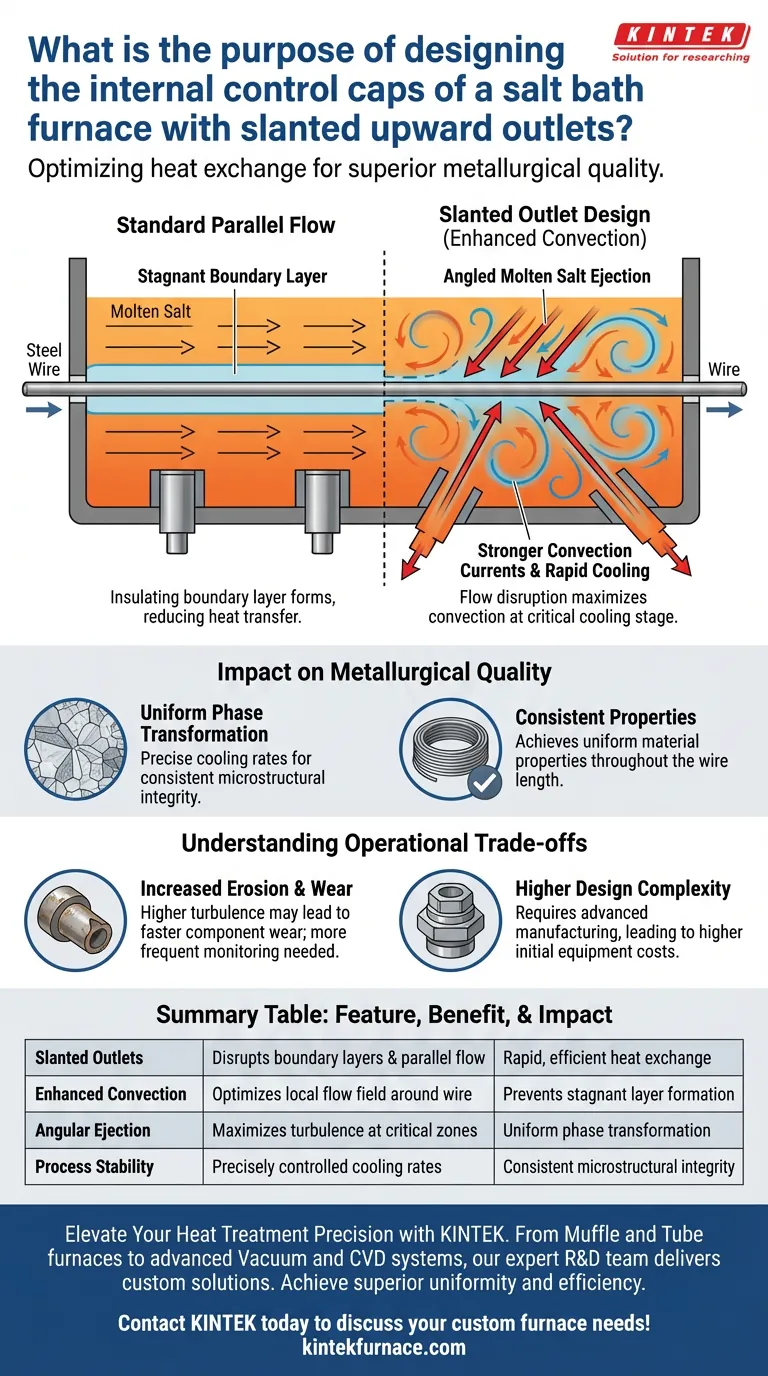
The specific geometry of the control cap outlets is designed to manipulate fluid dynamics for superior heat transfer. By slanting the outlets upward, the design forces molten salt to exit at an angle rather than traveling parallel to the moving steel wire. This intentional disruption creates stronger convection currents, significantly optimizing the local flow field around the wire.
By shifting the salt flow from a parallel stream to an angled ejection, this design maximizes convection during the critical early stages of cooling. The result is a rapid and uniform phase transformation within the steel wire.
Optimizing Heat Exchange Through Flow Control
Breaking the Parallel Flow
In standard linear processing, fluid moving parallel to a wire can create a boundary layer that insulates the material.
The slanted internal structure ensures the molten salt is ejected at an angle relative to the wire's travel direction.
Inducing Stronger Convection
This angular impact disrupts the flow field, preventing stagnant layers from forming around the steel.
The design induces stronger convection, which is the primary mechanism for transferring heat away from the wire.
Maximizing Efficiency at the Outlet
The area immediately exiting the control cap is the most vital zone for temperature control.
By optimizing the local flow field here, the system significantly increases heat exchange efficiency exactly where it is needed most.
Impact on Metallurgical Quality
Controlling Phase Transformation
Steel wire properties are defined during the phase transformation process.
The slanted design targets the critical initial stage of this transformation, where cooling rates must be precise.
Ensuring Uniformity
Rapid cooling is useless if it is uneven, as this causes internal stresses or structural defects.
The enhanced convection ensures the steel wire achieves uniform cooling effects, leading to consistent material properties throughout the wire length.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Erosion and Wear
While angled flow improves heat transfer, the increased turbulence and direct impact of the fluid can lead to higher mechanical wear.
Operators should monitor the control caps for erosion more frequently than in systems with purely laminar, parallel flow.
Design Complexity
Creating internal slanted channels requires more complex manufacturing and casting processes than standard straight-bore designs.
This often results in higher initial equipment costs, which must be weighed against the performance gains in product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
If you are evaluating furnace specifications or troubleshooting quality issues, consider how flow dynamics align with your goals:
- If your primary focus is microstructural integrity: Prioritize designs with slanted outlets to maximize convective turbulence and ensure the most uniform phase transformation possible.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Be aware that the high-velocity, angled flow that improves quality may inherently increase the wear rate of consumable components.
Mastering the angle of fluid impact is a precise mechanical adjustment that yields significant dividends in final steel quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Design Benefit | Metallurgical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Slanted Outlets | Disrupts boundary layers & parallel flow | Rapid, efficient heat exchange |
| Enhanced Convection | Optimizes local flow field around wire | Prevents stagnant layer formation |
| Angular Ejection | Maximizes turbulence at critical zones | Uniform phase transformation |
| Process Stability | Precisely controlled cooling rates | Consistent microstructural integrity |
Elevate Your Heat Treatment Precision with KINTEK
Don't let inefficient cooling compromise your material properties. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions, ranging from Muffle, Tube, and Rotary furnaces to advanced Vacuum and CVD systems. Whether you need specialized flow dynamics for steel wire processing or custom-engineered high-temperature lab equipment, our expert R&D and manufacturing teams are ready to deliver a system tailored to your unique requirements.
Achieve superior uniformity and efficiency—contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Jun Li, Jieyu Zhang. A Novel Design of a Molten Salt Bath Structure and Its Quenching Effect on Wire Transformation from Austenite to Sorbite. DOI: 10.3390/met14040483
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic principle of a sintering furnace? Transform Powder into Dense, Strong Components
- What function does high-purity argon gas serve in BPEA PVT preparation? Ensure High-Quality Crystal Growth
- What is the function of a planetary high-energy ball mill in Al2O3/TiC ceramics? Achieve Sub-Micron Precision Today
- What material is used in porcelain fused to metal restoration? A Guide to Alloys & Aesthetics
- How does the pre-oxidation process affect high-temperature alloys? Enhancing Surface Integrity for Steam Cracking
- What is the operating principle of a vacuum freeze-dryer in the fabrication of carbon aerogels? Master Sublimation
- How does a temperature-controlled heating chamber ensure AEMWE testing accuracy? Unlock Reliable Electrolyzer Data
- What are the advantages of a Vacuum Drying Oven for NiCo2O4 nanosheet composites? Protect Your Nanostructural Integrity



















