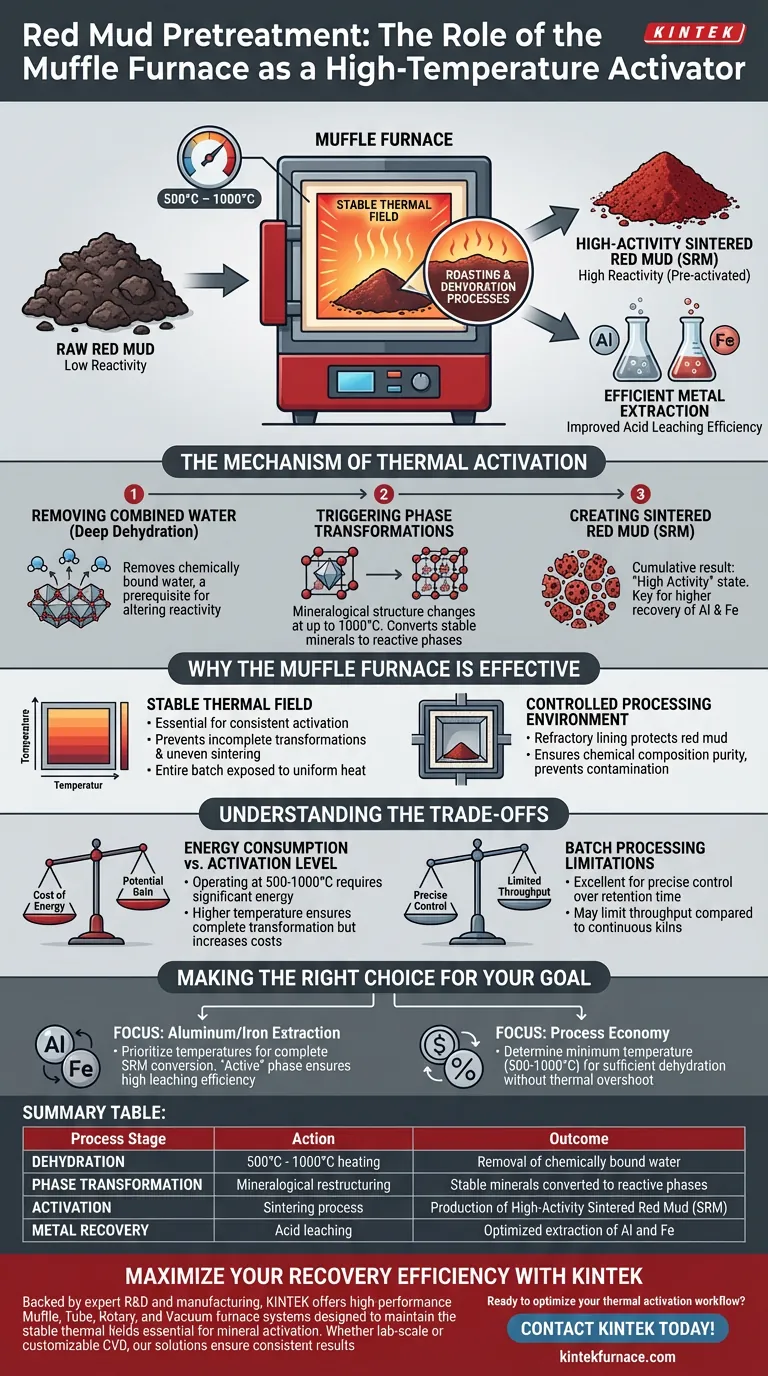
The primary role of a Muffle furnace in red mud pretreatment is to function as a high-temperature activator. By sustaining a stable thermal field between 500 °C and 1000 °C, the furnace executes critical roasting and dehydration processes. This thermal treatment transforms raw red mud into highly active sintered red mud (SRM), a necessary state for efficient metal extraction.
The Muffle furnace does not merely heat the material; it fundamentally alters its physicochemical properties by removing combined water and triggering mineral phase transformations. This creates a "pre-activated" material that significantly improves the extraction efficiency of aluminum and iron during subsequent acid leaching.
The Mechanism of Thermal Activation
Removing Combined Water
The first critical function of the Muffle furnace is deep dehydration.
While surface moisture is easily removed, red mud contains "combined water" chemically bound within its mineral structure.
The furnace's high-temperature environment effectively drives off this bound water, which is a prerequisite for altering the material's reactivity.
Triggering Phase Transformations
Once dehydration occurs, the furnace facilitates specific mineral phase transformations.
At temperatures up to 1000 °C, the mineralogical structure of the red mud changes.
These transformations convert stable, unreactive minerals into new phases that are more susceptible to chemical attack in later processing stages.
Creating Sintered Red Mud (SRM)
The cumulative result of roasting and phase transformation is the production of Sintered Red Mud (SRM).
SRM is distinct from the raw raw material due to its "high activity" state.
This enhanced activity is the key factor that allows for higher recovery rates of valuable metals like aluminum and iron when the material undergoes acid leaching.
Why the Muffle Furnace is Effective
Stable Thermal Field
The Muffle furnace provides a highly stable thermal environment, which is essential for consistent activation.
Fluctuations in temperature can lead to incomplete phase transformations or uneven sintering.
The design of the furnace ensures that the entire batch of red mud is exposed to the uniform heat required for the reaction to proceed simultaneously throughout the sample.
Controlled Processing Environment
While the primary reference highlights thermal stability, the isolated nature of a muffle furnace is also beneficial.
The refractory lining protects the red mud from direct contact with heating elements.
This ensures that the chemical composition of the SRM remains pure and is not contaminated by combustion byproducts or element materials during the sensitive roasting phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Energy Consumption vs. Activation Level
Operating at 500–1000 °C requires significant energy input.
You must balance the cost of energy against the potential gain in extraction efficiency.
Running the furnace at the higher end of this range (near 1000 °C) ensures complete phase transformation but increases operational costs substantially.
Batch Processing Limitations
Muffle furnaces are typically batch-processing units.
This setup is excellent for precise control over retention time and temperature profiles but may limit throughput compared to continuous rotary kilns.
For large-scale industrial applications, the transition from a lab-scale Muffle furnace to continuous equipment requires careful calibration to maintain the same "stable thermal field."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of your red mud pretreatment, align your furnace settings with your specific extraction targets.
- If your primary focus is Aluminum/Iron Extraction: Prioritize temperatures that ensure complete conversion to SRM, as the "active" phase is the only way to ensure high leaching efficiency.
- If your primary focus is Process Economy: Determine the minimum temperature threshold (within the 500–1000 °C range) that achieves sufficient dehydration without unnecessary thermal overshoot.
By precisely controlling the roasting environment, you turn a waste product into a valuable resource ready for efficient chemical processing.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | 500°C - 1000°C heating | Removal of chemically bound water |
| Phase Transformation | Mineralogical restructuring | Stable minerals converted to reactive phases |
| Activation | Sintering process | Production of High-Activity Sintered Red Mud (SRM) |
| Metal Recovery | Acid leaching | Optimized extraction of Al and Fe |
Maximize Your Recovery Efficiency with KINTEK
Transitioning red mud from waste to resource requires precision. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnace systems designed to maintain the stable thermal fields essential for mineral activation. Whether you need lab-scale testing or customizable CVD systems for unique material needs, our high-temp solutions ensure consistent results for your most demanding pretreatment processes.
Ready to optimize your thermal activation workflow? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhilei Zhen, Haotian Ma. A Novel Method of Synthesizing Polymeric Aluminum Ferric Sulfate Flocculant and Preparing Red Mud-Based Ceramsite. DOI: 10.3390/ma17061239
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What functions do drying ovens and sintering furnaces serve in Sol-Gel? Optimize Bioactive Coating Integrity
- Why is a high-precision muffle furnace required for TiCo1-xCrxSb? Achieve Perfect Phase Purity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in silver film transformation? Master Nanoparticle Self-Assembly with Precision
- What are the main components of a box type resistance furnace? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it differ from conventional furnaces? Discover the Key to Contamination-Free Heating
- How do muffle furnaces contribute to drug testing in pharmaceuticals? Ensure Purity and Compliance with Precision
- How does a high-temperature box-type resistance furnace facilitate LLTO sintering? Master Precise Thermal Control
- How is the muffle furnace packaged for shipping? Ensuring Safe Delivery for Your Lab Equipment



















