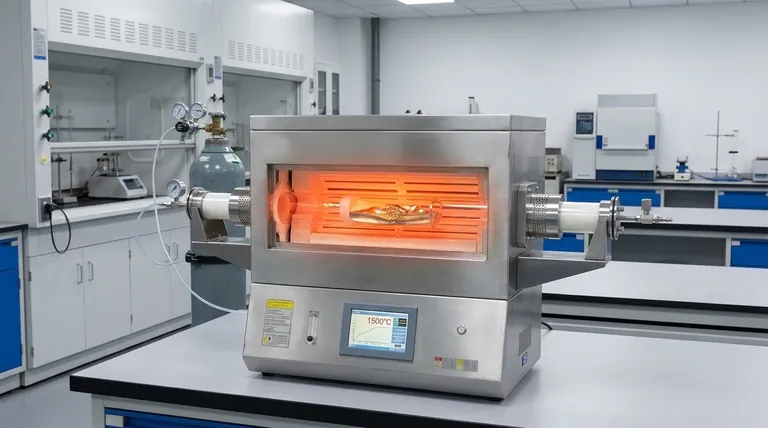
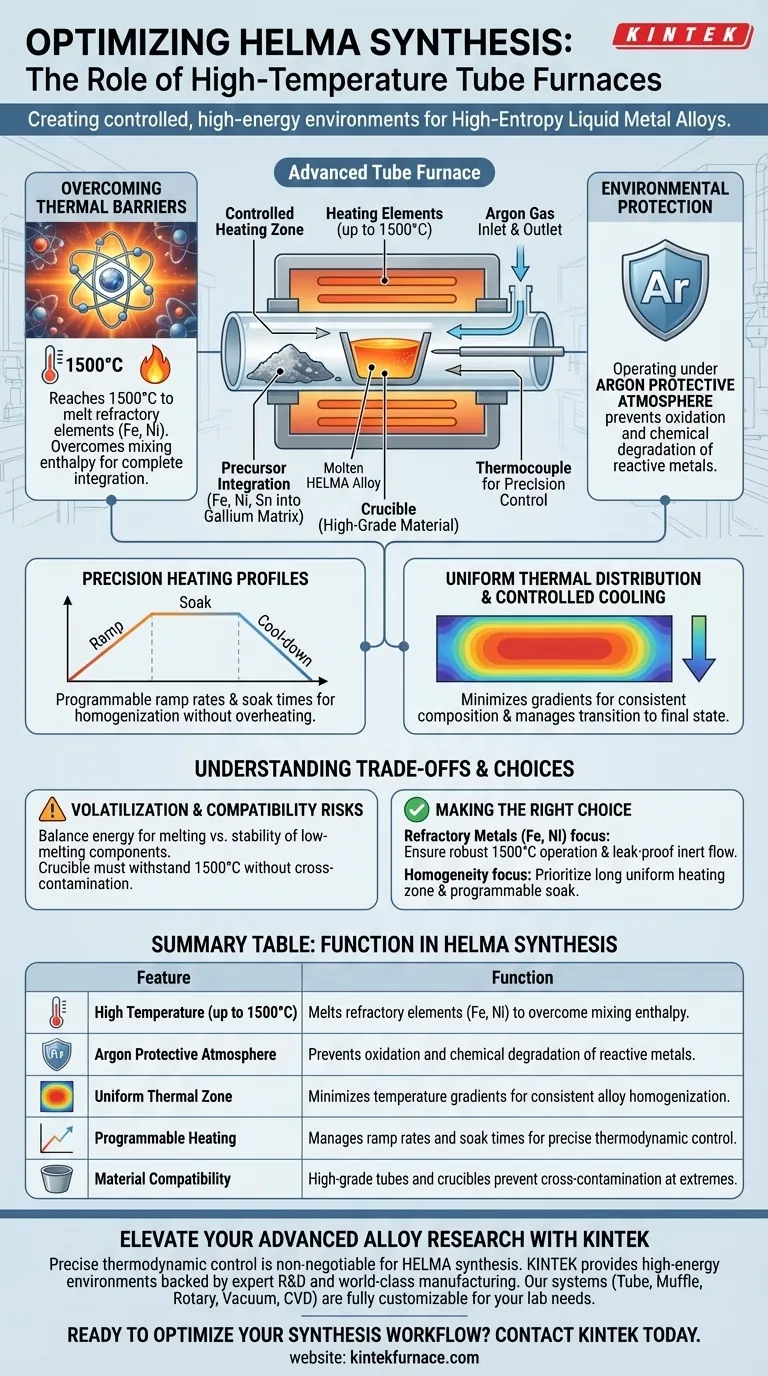
The primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in HELMA synthesis is to create a controlled, high-energy environment that forces high-melting-point precursors to alloy with a liquid matrix. By generating temperatures up to 1500°C under an argon protective atmosphere, the furnace melts refractory elements like iron and nickel, allowing them to dissolve completely into a gallium base.
The furnace provides the specific thermal energy required to overcome atomic mixing enthalpy. This intense heat drives the thermodynamic integration of solid metals into a liquid state, facilitating the fundamental alloying process.

The Mechanics of HELMA Synthesis
Overcoming Thermal Barriers
The synthesis of High-Entropy Liquid Metal Alloys (HELMA) requires combining elements with vastly different physical properties.
The furnace heats the metal precursors to approximately 1500°C to induce intense thermal motion.
This specific thermal threshold is critical for overcoming the mixing enthalpy between atoms, ensuring that high-melting-point elements—specifically iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), and tin (Sn)—fully melt and integrate into the gallium (Ga) matrix.
Environmental Protection
Melting reactive metals at such high temperatures introduces a significant risk of oxidation.
To mitigate this, the tube furnace operates under an argon protective atmosphere.
This inert environment shields the precursors during the heating phase, preventing chemical degradation and ensuring the purity of the final alloy.
Precision Heating Profiles
Successful alloying relies on more than just raw heat; it requires precise thermal management.
Tube furnaces utilize advanced temperature controllers to execute complex heating profiles, including specific ramp rates and soak times.
This programmability ensures that the material is held at the critical alloying temperature long enough for complete homogenization without overheating.
Why a Tube Furnace is Essential
Uniform Thermal Distribution
A core advantage of the tube furnace design is its ability to deliver consistent heat along the length of the processing tube.
This minimizes temperature gradients, which are detrimental to the synthesis process.
Uniform heating ensures that the entire batch reaches the necessary melting point simultaneously, preventing localized inconsistencies in the alloy's composition.
Controlled Cooling
The synthesis process often requires specific cooling regimens to stabilize the material structure.
Tube furnaces allow for controlled cooling rates after the soak period.
This capability is essential for managing the transition from the high-temperature synthesis state to the final room-temperature liquid state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Volatilization Risks
While 1500°C is necessary to melt iron and nickel, it pushes other elements near their boiling points.
There is a risk that lower-melting-point components (like the Gallium matrix) could volatilize if the pressure and atmosphere are not strictly managed.
Balancing the energy required for refractory elements against the stability of the liquid matrix is a critical challenge.
Material Compatibility
The extreme operating temperatures place significant stress on containment materials.
The crucible and tube materials must be able to withstand 1500°C without reacting with the HELMA melt.
Incorrect material selection can lead to cross-contamination, where the vessel creates impurities in the alloy, compromising the experiment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve successful HELMA synthesis, you must align your equipment capabilities with the thermodynamic needs of your specific alloy composition.
- If your primary focus is alloying refractory metals (Fe, Ni): Ensure your furnace is rated for continuous operation at 1500°C and supports a robust, leak-proof inert gas flow to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is alloy homogeneity: Prioritize a furnace with a long uniform heating zone and programmable soak times to ensure complete dissolution of all precursors.
Ultimately, the high-temperature tube furnace serves as the thermodynamic engine that forces disparate solid and liquid elements into a unified, high-entropy state.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in HELMA Synthesis |
|---|---|
| High Temperature (up to 1500°C) | Melts refractory elements (Fe, Ni) to overcome mixing enthalpy. |
| Argon Protective Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and chemical degradation of reactive metals. |
| Uniform Thermal Zone | Minimizes temperature gradients for consistent alloy homogenization. |
| Programmable Heating | Manages ramp rates and soak times for precise thermodynamic control. |
| Material Compatibility | High-grade tubes and crucibles prevent cross-contamination at extremes. |
Elevate Your Advanced Alloy Research with KINTEK
Precise thermodynamic control is non-negotiable for the successful synthesis of High-Entropy Liquid Metal Alloys (HELMA). KINTEK provides the high-energy environments needed to drive complex alloying processes, backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing.
Our range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems are engineered for performance up to 1500°C and beyond, ensuring uniform heating and inert atmosphere protection for your most sensitive precursors. Whether you are alloying refractory metals or developing custom materials, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs.
Ready to optimize your synthesis workflow? Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace solution for your research.
Visual Guide
References
- Sahar Nazari, Rouhollah Jalili. Configuring a Liquid State High‐Entropy Metal Alloy Electrocatalyst. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202504087
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How is sealing and atmosphere control achieved in a tube furnace? Master Precise Gas Environments for Your Lab
- What core environmental conditions does an industrial high-temperature tube furnace provide for Ta4AlC3 synthesis?
- What are the different designs of High Temperature Tube Furnaces? Choose the Right Design for Your Lab
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise Atmospheric Control for Material Processing
- What is a tube furnace and what are its primary uses? Essential for Controlled High-Temperature Processes
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in Silicon/Hard Carbon synthesis? Master Battery Anode Production
- What role does an atmosphere-controlled vacuum tube furnace play in sintering? Mastering Porous Stainless Steel
- What are the benefits of independent temperature control in a three-zone furnace? Enhance Precision and Uniformity



















