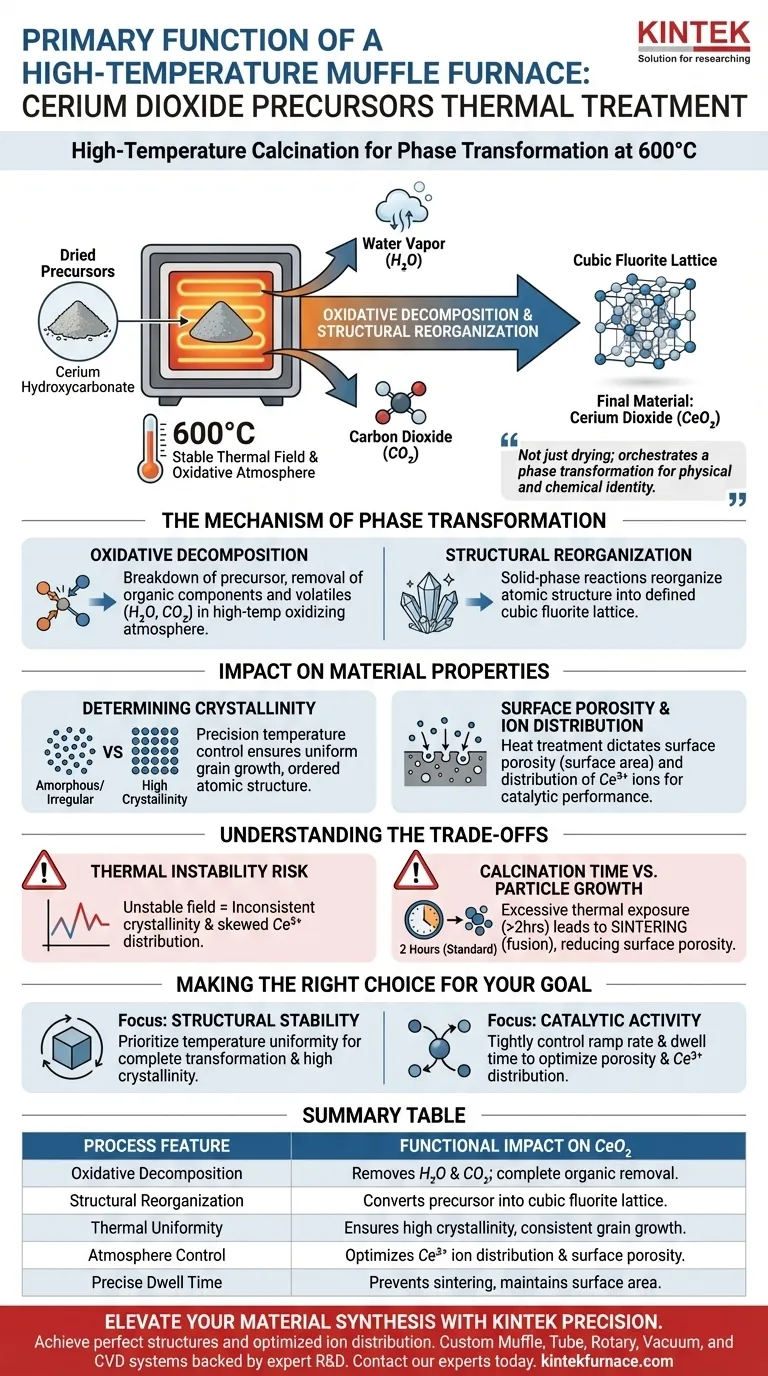
The primary function of a high-temperature muffle furnace during this stage is to execute high-temperature calcination, typically at 600°C, to convert dried precursors into the final material. Specifically, the furnace provides a stable thermal field that drives the oxidative decomposition of cerium hydroxycarbonate. This releases volatile byproducts—specifically water vapor and carbon dioxide—to transform the intermediate powder into cerium dioxide ($CeO_2$).
The muffle furnace does not merely dry the material; it orchestrates a phase transformation. It provides the precise thermal control required to reorganize the precursor's atomic structure into a stable cubic fluorite lattice, determining the material's final physical and chemical identity.

The Mechanism of Phase Transformation
Oxidative Decomposition
The core operation performed by the furnace is the breakdown of cerium hydroxycarbonate precursors.
By sustaining a high-temperature oxidizing atmosphere (air), the furnace ensures the complete removal of organic components and volatile impurities. As the material heats, it chemically acts to release water vapor ($H_2O$) and carbon dioxide ($CO_2$).
Structural Reorganization
Once the volatile components are expelled, the remaining solid undergoes a significant structural shift.
The thermal energy provided by the muffle furnace facilitates solid-phase reactions. This reorganizes the material from a precursor state into a defined cubic fluorite structure. This specific crystal lattice is the defining characteristic of stable, high-quality cerium dioxide.
Impact on Material Properties
Determining Crystallinity
The precision of the furnace's temperature control is the single most important factor regarding the structural integrity of the output.
A stable thermal field ensures uniform grain growth. This leads to high crystallinity, meaning the atomic structure is ordered and consistent throughout the powder, rather than amorphous or irregular.
Surface Porosity and Ion Distribution
The furnace parameters directly dictate the surface characteristics of the final $CeO_2$ product.
The heat treatment protocol establishes the surface porosity, which is critical for applications requiring high surface area. Furthermore, it controls the distribution of $Ce^{3+}$ ions. The presence and arrangement of these ions are often the key to the material's catalytic performance and oxygen storage capacity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Instability
While the muffle furnace is essential for synthesis, its effectiveness relies entirely on thermal precision.
If the thermal field within the furnace is unstable or fluctuates, it will result in inconsistent crystallinity. More critically, inaccurate temperatures can skew the $Ce^{3+}$ ion distribution, rendering the material less effective for its intended application.
Calcinaton Time vs. Particle Growth
There is a delicate balance between ensuring complete decomposition and preventing excessive particle growth.
Standard protocols often call for a duration of 2 hours at 600°C. Exceeding this thermal exposure can lead to sintering, where particles fuse together, reducing the desirable surface porosity that the furnace was meant to create.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your cerium dioxide, align your furnace protocols with your specific end-goal requirements:
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Prioritize temperature uniformity to ensure a complete transformation into the cubic fluorite phase with high crystallinity.
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Activity: Tightly control the ramp rate and dwell time to optimize surface porosity and maximize the specific distribution of $Ce^{3+}$ ions.
The muffle furnace is the tool that bridges the gap between a raw chemical mixture and a functional, engineered material.
Summary Table:
| Process Feature | Functional Impact on Cerium Dioxide ($CeO_2$) |
|---|---|
| Oxidative Decomposition | Removes $H_2O$ and $CO_2$; ensures complete organic component removal. |
| Structural Reorganization | Converts precursor into a stable cubic fluorite crystal lattice. |
| Thermal Uniformity | Ensures high crystallinity and consistent grain growth across the material. |
| Atmosphere Control | Optimizes $Ce^{3+}$ ion distribution and critical surface porosity. |
| Precise Dwell Time | Prevents particle sintering to maintain high catalytic surface area. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieve the perfect cubic fluorite structure and optimized $Ce^{3+}$ distribution for your cerium dioxide research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific calcination and thermal treatment needs. Don't let thermal instability compromise your crystallinity—leverage our advanced heating technology to ensure uniform grain growth every time.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Contact our furnace experts today to find the ideal thermal solution for your unique requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Xingzi Wang, Juanyu Yang. Controlled Synthesis of Triangular Submicron-Sized CeO2 and Its Polishing Performance. DOI: 10.3390/ma17092001
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory box muffle furnace in the compositional analysis of finger millet popcorn?
- What maintenance practices are recommended for muffle furnaces? Ensure Longevity and Precision in Your Lab
- What is the maximum temperature of the muffle furnace? It's a critical design choice.
- What is one of the primary functions of a muffle furnace in material analysis? Discover Its Role in Precise Ash Content Determination
- How does a high-performance sintering furnace influence KNN-based ceramics? Master Microstructure & Precision
- What personal protective equipment (PPE) is recommended for benchtop furnace use? Ensure Lab Safety with Proper Gear
- How should the temperature controller be set up before using the muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Accurate Heating
- How is the temperature controlled in a muffle furnace? Master Precise Heating for Your Lab



















