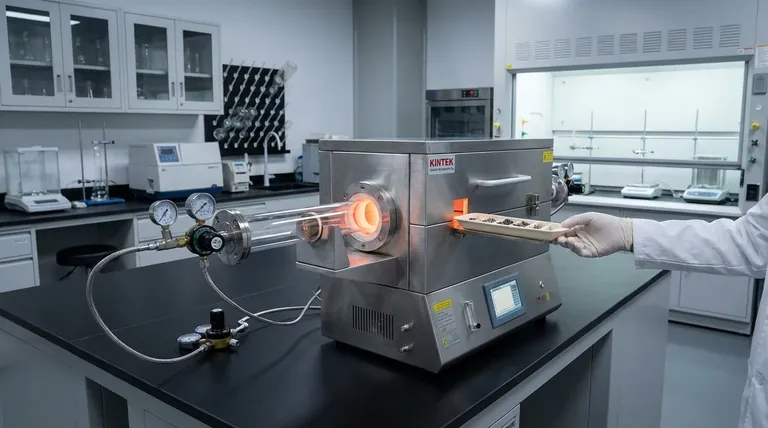
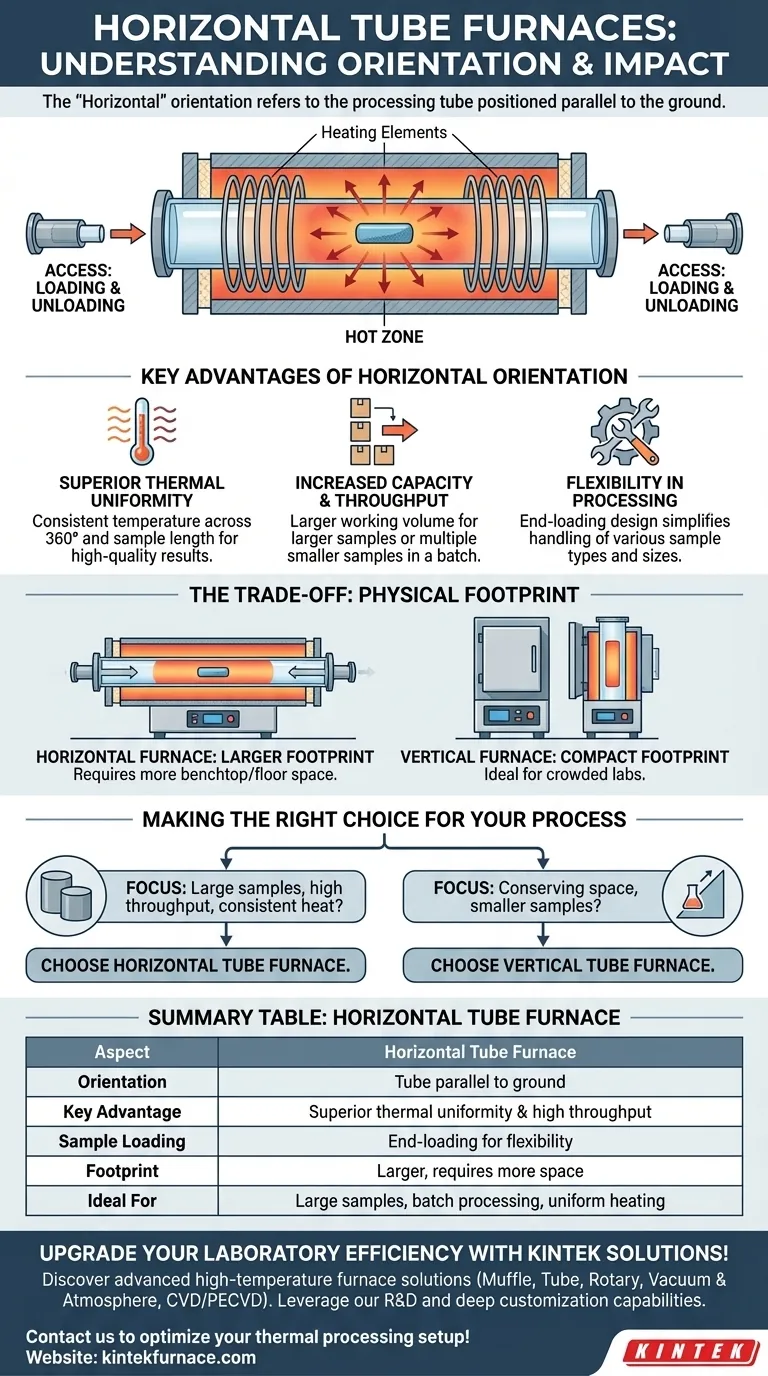
In a horizontal tube furnace, the term 'horizontal' refers to the orientation of the processing tube or chamber. This means the cylindrical chamber, where the material is heated, is positioned parallel to the ground, with access points for loading and unloading samples located at either end.
The choice of a horizontal furnace is not merely about orientation; it is a strategic decision that prioritizes high-volume throughput and exceptional temperature uniformity across a large area, often at the expense of a larger physical footprint.

The Fundamental Design of a Horizontal Furnace
The horizontal orientation directly influences how the furnace operates, how samples are handled, and the results you can achieve. It is the most common design for many thermal processing applications.
Defining the Orientation
A horizontal tube furnace features a heating chamber that is oriented horizontally. The sample or material is placed on a holder or boat and inserted into this tube from one of the ends.
How Heat Is Applied
Heating elements, typically made of high-resistance wire or other materials like silicon carbide, surround the exterior of the processing tube. This design creates a central "hot zone" with highly consistent and stable temperatures.
The goal is to transfer heat radially, subjecting the sample to a uniform temperature across its entire 360° axis, which is a key strength of this design.
Access and Sample Loading
Because the tube is horizontal, samples are loaded and unloaded from the ends. These ends are typically sealed with plugs or flanges, which can be configured for vacuum or to allow a controlled flow of inert or reactive gas during the process.
Key Advantages of the Horizontal Orientation
This design offers several distinct operational benefits that make it the preferred choice for specific applications.
Superior Thermal Uniformity
The primary advantage is outstanding heat distribution along the sample's length. This thermal uniformity ensures that every part of the sample experiences the same thermal conditions, leading to consistent, repeatable, and high-quality results.
Increased Capacity and Throughput
Horizontal furnaces inherently offer a larger working volume. This allows for the processing of larger individual samples or, more commonly, multiple smaller samples in a single batch. This makes them ideal for both batch and continuous production environments.
Flexibility in Processing
The straightforward end-loading design provides significant flexibility. It simplifies the loading and unloading of various sample types and sizes, making the furnace adaptable to changing research or production needs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single design is perfect for every situation. The horizontal orientation comes with one significant consideration that must be weighed against its benefits.
The Primary Drawback: Physical Footprint
The main trade-off for a horizontal tube furnace is its size. Due to its horizontal length, it occupies significantly more benchtop or floor space compared to its vertical counterpart.
Vertical furnaces, which orient the tube perpendicular to the ground, have a much more compact footprint. This makes them a better fit for crowded laboratories or facilities where space is at a premium. The decision often comes down to balancing available space against required processing volume.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific application and laboratory constraints will determine the ideal furnace orientation.
- If your primary focus is large samples, high throughput, or achieving the most consistent heat distribution: A horizontal tube furnace is almost always the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is conserving lab space and you are working with smaller samples: A vertical tube furnace may be a more practical solution.
By understanding the implications of the furnace's orientation, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific thermal processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Horizontal Tube Furnace |
|---|---|
| Orientation | Tube parallel to ground |
| Key Advantage | Superior thermal uniformity and high throughput |
| Sample Loading | End-loading for flexibility |
| Footprint | Larger, requires more space |
| Ideal For | Large samples, batch processing, uniform heating |
Upgrade Your Laboratory Efficiency with KINTEK Solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether you need high-throughput horizontal furnaces for superior thermal uniformity or space-saving vertical options, we deliver tailored solutions to enhance your research and production outcomes. Don't let equipment limitations hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing setup!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















