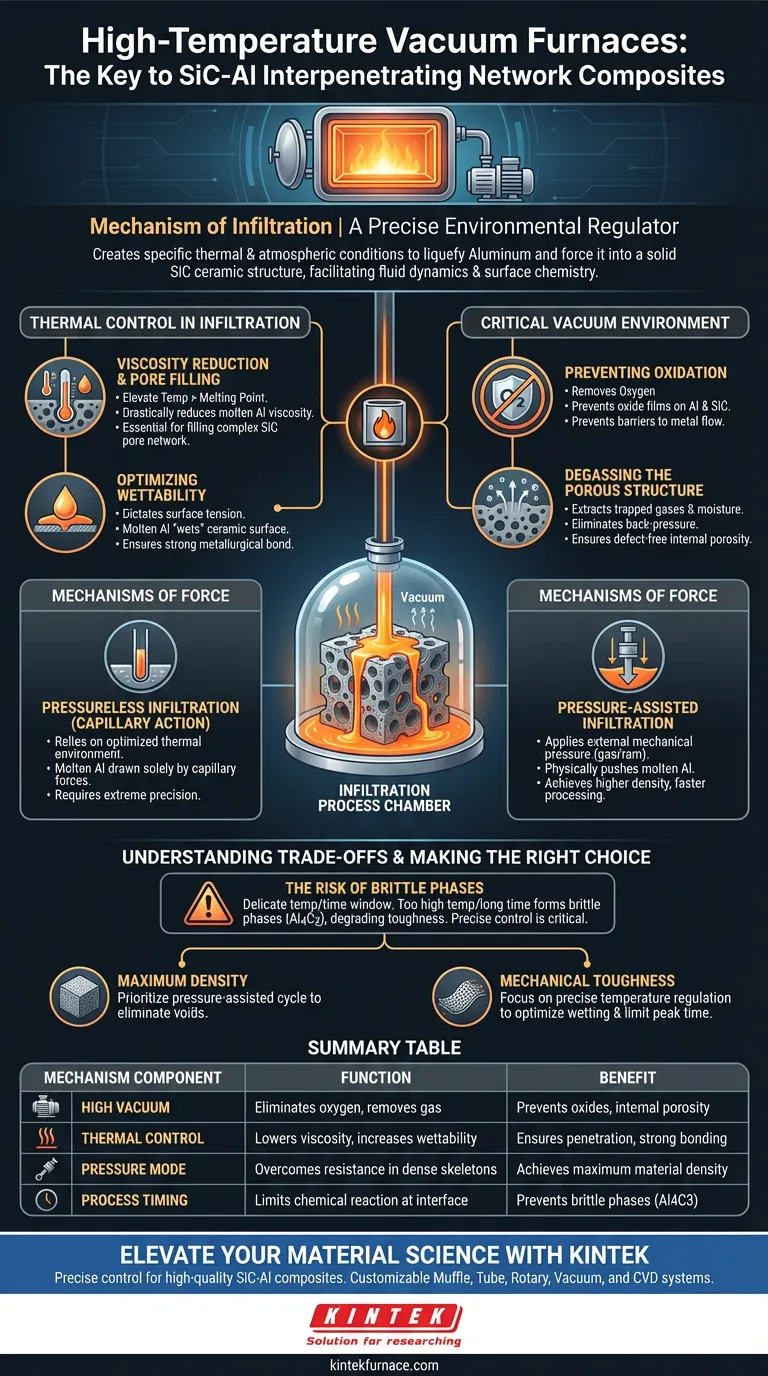
A high-temperature vacuum furnace acts as a precise environmental regulator, creating the specific thermal and atmospheric conditions necessary to liquefy aluminum and force it into a solid ceramic structure. It functions not merely as a heating element, but as a facilitator of fluid dynamics and surface chemistry.
The furnace functions by creating a high-purity vacuum that prevents aluminum oxidation while maintaining precise temperatures to lower the molten metal's viscosity. This combination allows liquid aluminum to penetrate the microscopic pores of the silicon carbide skeleton—driven by either capillary action or applied pressure—resulting in a fully dense, defect-free composite.

The Role of Thermal Control in Infiltration
Viscosity Reduction and Pore Filling
The primary mechanical function of the furnace is to elevate the temperature above the melting point of the aluminum alloy.
By maintaining specific high temperatures, the furnace drastically reduces the viscosity of the molten metal.
This increased fluidity is essential for the aluminum to navigate and fill the complex, micrometer-scale pore network of the rigid silicon carbide (SiC) skeleton.
Optimizing Wettability
Temperature control dictates the surface tension at the ceramic-metal interface.
The furnace must reach a thermal threshold where the molten aluminum effectively "wets" the ceramic surface rather than beading up on it.
Proper wettability ensures a strong metallurgical bond between the two distinct materials, which is the defining factor for the composite's structural integrity.
The Critical Function of the Vacuum Environment
Preventing Oxidation
Aluminum is highly reactive and forms oxide layers almost instantly in the presence of oxygen.
The vacuum environment removes oxygen from the chamber, preventing the formation of oxide films on the molten aluminum and the ceramic skeleton.
Without this vacuum protection, oxide barriers would block the flow of metal into the ceramic pores and severely weaken the final interface bonding.
Degassing the Porous Structure
The SiC skeleton contains trapped gases and adsorbed moisture within its pores.
The vacuum mechanism actively extracts these gases before and during the heating process.
Removing this trapped gas eliminates back-pressure that would otherwise resist the entry of the molten metal, ensuring the final material is free of internal porosity defects.
Mechanisms of Force: Pressure vs. Pressureless
Pressureless Infiltration (Capillary Action)
In this mode, the furnace relies entirely on the optimized thermal environment.
Once the vacuum prevents oxidation and the temperature maximizes wettability, the molten aluminum is drawn into the SiC skeleton solely by capillary forces.
This requires extremely precise temperature control to maximize the natural attraction between the liquid metal and the solid ceramic.
Pressure-Assisted Infiltration
For denser skeletons or more complex geometries, the furnace system applies external mechanical pressure (often using gas pressure or a ram).
This external force physically pushes the molten aluminum into the pores, overcoming the resistance that capillary action alone cannot handle.
This method typically achieves higher density and faster processing times but requires more robust equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Brittle Phases
There is a delicate window of operation regarding temperature and time.
If the furnace temperature is too high or the processing time too long, the aluminum may react chemically with the silicon carbide to form brittle phases (such as Aluminum Carbide, Al4C3).
These reaction products degrade the material's toughness; therefore, the furnace's ability to hold a stable, precise temperature is critical to preventing "over-cooking" the interface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve the best results with SiC-Al composites, align your processing parameters with your specific performance requirements:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Density: Prioritize a pressure-assisted cycle to forcibly eliminate all internal voids and overcome the resistance of fine-pore skeletons.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Toughness: Focus on precise temperature regulation to optimize wetting while strictly limiting the time at peak temperature to prevent the formation of brittle reaction phases.
The success of the infiltration process relies on the furnace's ability to balance fluidity with chemical stability in a contaminant-free vacuum.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism Component | Function in Infiltration | Benefit to Final Composite |
|---|---|---|
| High Vacuum | Eliminates oxygen and removes trapped gases | Prevents oxide films and internal porosity |
| Thermal Control | Lowers aluminum viscosity and increases wettability | Ensures full pore penetration and strong bonding |
| Pressure Mode | Overcomes resistance in dense ceramic skeletons | Achieves maximum material density |
| Process Timing | Limits chemical reaction at the interface | Prevents formation of brittle phases (Al4C3) |
Elevate Your Material Science with KINTEK
Precise control over thermodynamics and fluid dynamics is essential for producing high-quality SiC-Al interpenetrating network composites. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique infiltration needs.
Whether you require pressure-assisted cycles for maximum density or precise vacuum control for superior wettability, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the stability and purity your research demands.
Ready to optimize your composite production? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Arash Kariminejad, Mart Viljus. Effect of thermal shock treatment parameters on the efficiency of WC-Co cermet recycling. DOI: 10.1063/5.0189330
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does laboratory vacuum impregnation equipment facilitate precursor infiltration in PIP? Maximize SiC Composite Density
- How does an inert gas circulation system work in a vacuum furnace? Achieve Rapid, Controlled Cooling for Your Materials
- Why is a vacuum degassing system required for BET testing? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Surface Area Analysis
- Why is long-duration temperature stability in a sintering furnace essential for Bi-2223? Master Phase Purity
- What is the temperature of a vacuum furnace brazing? Optimize Your Joint Strength and Cleanliness
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum brazing furnace over other metal joining processes? Achieve Clean, Strong, and Distortion-Free Metal Joints
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum furnace play in sintering magnesium composites? Key Success Factors
- What is Age Hardening in vacuum heat treating? Unlock Peak Metal Performance with Precision



















