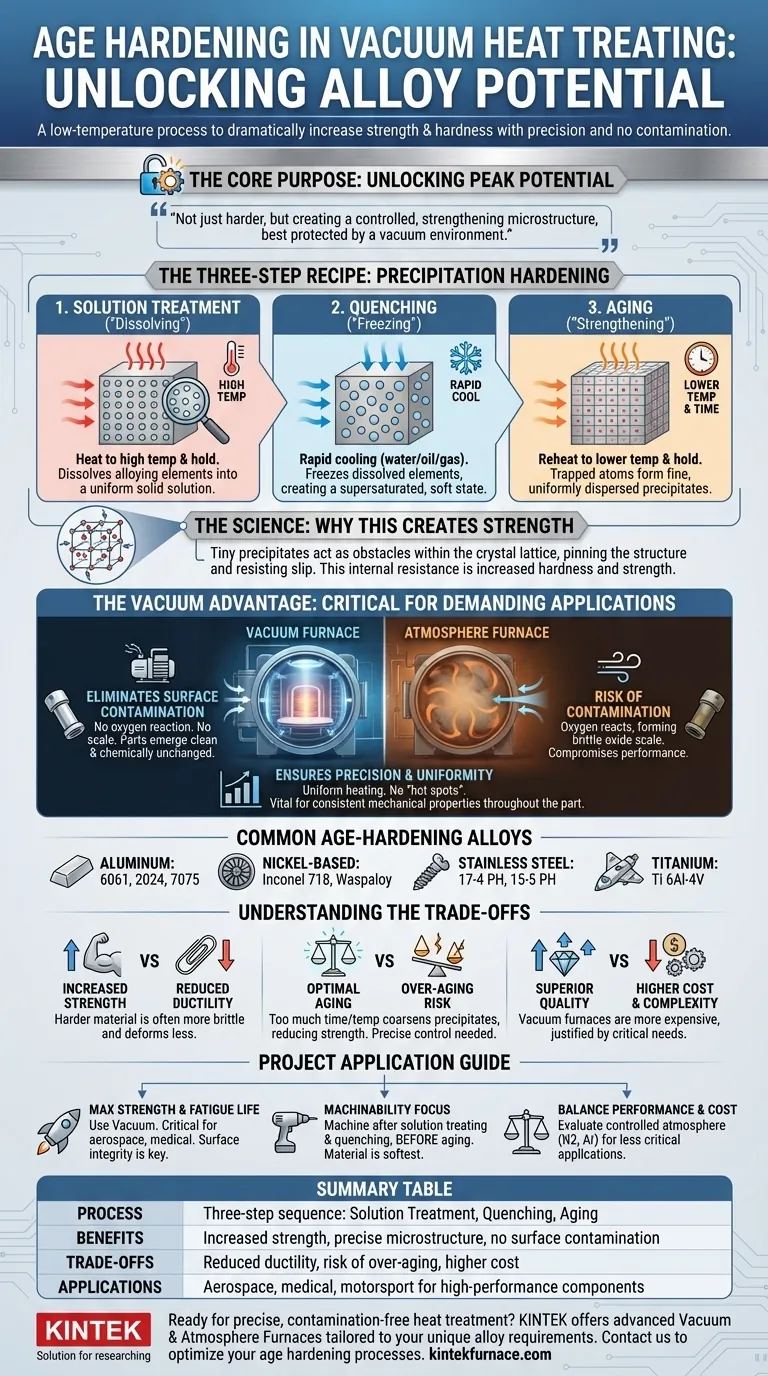
At its core, age hardening is a low-temperature heat treatment process used to dramatically increase the strength and hardness of certain metal alloys. Performing this process in a vacuum furnace ensures that the strengthening occurs with extreme precision and without any surface contamination, which is critical for high-performance components.
The true purpose of age hardening is not just to make a metal harder, but to unlock an alloy's peak potential performance. It achieves this by creating a highly controlled, strengthening microstructure within the metal, a result best protected and guaranteed by a vacuum environment.

The Science of Age Hardening
Age hardening is more accurately known as precipitation hardening. The name comes from the controlled formation of microscopic particles, or precipitates, within the metal's crystal structure. These precipitates are the source of the added strength.
The Three-Step Recipe
The process is not a single heating step but a carefully controlled three-part sequence. The final "aging" step is what gives the process its name, but it is ineffective without the first two.
1. Solution Treatment (The "Dissolving" Phase) The alloy is first heated to a high temperature and held there. This dissolves the key alloying elements into the base metal, much like sugar dissolving in hot water, creating a uniform solid solution.
2. Quenching (The "Freezing" Phase) Next, the material is rapidly cooled, typically in water, oil, or inert gas. This sudden temperature drop freezes the dissolved elements in place, creating a supersaturated and unstable state. At this stage, the metal is relatively soft.
3. Aging (The "Strengthening" Phase) Finally, the alloy is reheated to a much lower temperature and held for a specific amount of time. This is the age hardening step. This gentle heating gives the trapped atoms just enough energy to move and form extremely fine, uniformly dispersed precipitates.
Why This Creates Strength
These tiny precipitates act as obstacles within the metal's crystal lattice. They effectively pin the atomic structure in place, making it much more difficult for the atomic planes to slip past one another under stress. This internal resistance to "slip" is what we measure as increased hardness and strength.
Why Use a Vacuum? The Critical Advantage
Combining age hardening with a vacuum furnace is not always necessary, but for demanding applications, it is the only way to guarantee results. The vacuum environment provides two decisive benefits.
Eliminating Surface Contamination
Even at the low temperatures of aging, many high-performance alloys can react with oxygen and other elements in the air. This forms a thin, brittle oxide layer (scale) on the surface that can compromise performance and fatigue life. A vacuum removes the air, ensuring the part emerges clean and chemically unchanged.
Ensuring Precision and Uniformity
Vacuum furnaces provide exceptionally uniform heating. There are no "hot spots" caused by convection currents found in air furnaces. This precise temperature control, along with controlled cooling rates, is vital for achieving the exact desired precipitate size and distribution throughout the entire part, ensuring consistent mechanical properties.
Common Age-Hardening Alloys
This process is not for all metals. It is specific to alloys designed for it, including:
- Aluminum Alloys: 6061, 2024, 7075
- Nickel-Based Superalloys: Inconel 718, Waspaloy
- Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steels: 17-4 PH, 15-5 PH
- Titanium Alloys: Ti 6Al-4V (benefits from a specific aging cycle)
Understanding the Trade-offs
Age hardening offers immense benefits but requires acknowledging its inherent compromises.
Reduced Ductility
The primary trade-off for increased strength is a decrease in ductility. A harder material is often more brittle and will stretch or deform less before it fractures.
The Risk of Over-aging
The aging process is a balancing act. If the temperature is too high or the time is too long, the fine precipitates will coarsen and grow too large. This condition, called over-aging, actually reduces the material's strength, sometimes below its initial, pre-hardened state. This highlights the need for precise process control.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and expensive to operate than standard atmosphere furnaces. The decision to use a vacuum must be justified by the need for superior surface finish and perfectly uniform material properties.
Applying This to Your Project
When specifying an age-hardening process, your end goal should dictate the approach.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue life: Age hardening is essential, and a vacuum process is critical for any component where surface integrity cannot be compromised (e.g., aerospace, medical, or motorsport parts).
- If your primary focus is machinability: Perform the bulk of machining operations after solution treating and quenching but before age hardening. The material is in its softest, most machinable state at that point.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and cost: For less critical applications, evaluate if a controlled atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) can provide sufficient protection, as it may be more cost-effective than a full vacuum.
By understanding the principles of precipitation hardening, you can transform a standard alloy into a high-performance material tailored precisely to your engineering needs.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Three-step sequence: Solution Treatment, Quenching, Aging |
| Benefits | Increased strength and hardness, precise microstructure control, no surface contamination |
| Common Alloys | Aluminum (e.g., 6061), Nickel-based (e.g., Inconel 718), Stainless steels (e.g., 17-4 PH) |
| Trade-offs | Reduced ductility, risk of over-aging, higher cost and complexity |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical, motorsport for high-performance components |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise, contamination-free heat treatment? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for alloys like aluminum, nickel superalloys, and stainless steels. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your age hardening processes and boost performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















