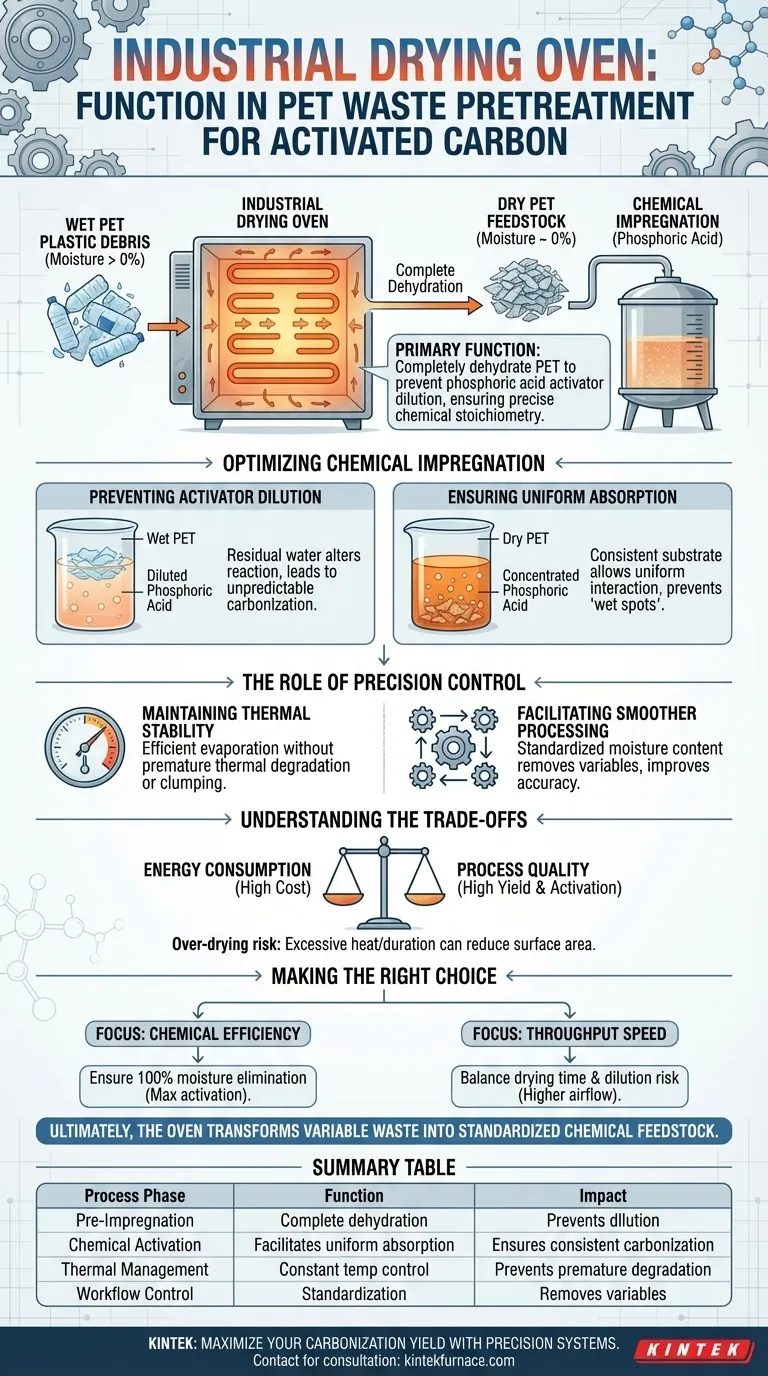
The primary function of an industrial drying oven in this context is to completely dehydrate cleaned PET plastic debris prior to the chemical impregnation stage. By removing all residual moisture, the oven ensures that the raw material does not dilute the phosphoric acid activators, preserving the specific chemical concentrations required for effective carbonization.
Moisture control is the foundation of chemical consistency. The industrial drying oven eliminates variable water content from the washing process, ensuring that the activation agents interact with the plastic at the precise stoichiometry intended.

Optimizing the Chemical Impregnation Stage
Preventing Activator Dilution
The most critical role of the drying oven is protecting the integrity of the chemical activators.
If wet PET debris is introduced to the impregnation stage, residual water immediately dilutes the concentration of phosphoric acid.
This dilution alters the chemical reaction, leading to unpredictable carbonization results and lower-quality activated carbon.
Ensuring Uniform Absorption
Thorough drying creates a consistent substrate for the chemicals to penetrate.
When the PET waste is completely dry, it allows for a more uniform interaction with the impregnation solution.
This prevents "wet spots" that could repel the acid, ensuring that the entire batch of material is activated evenly.
The Role of Precision Control
Maintaining Thermal Stability
While the primary goal is dehydration, the quality of the oven's temperature control is equally vital.
A precision constant temperature environment ensures that water is evaporated efficiently without thermally degrading the plastic prematurely.
Stable thermal conditions prevent local overheating, which could alter the physical structure of the PET before the chemical reaction begins.
Facilitating Smoother Processing
Industrial ovens are designed to provide a controlled environment that supports the overall workflow.
By standardizing the moisture content of the feedstock, the oven removes a major variable from the production line.
This allows operators to predict reaction times and chemical requirements with much higher accuracy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Energy Consumption vs. Process Quality
The primary trade-off in using industrial drying ovens is the energy cost relative to the improvement in yield.
Running high-capacity ovens increases the operational expenditure of the recycling process significantly.
However, skipping or shortening this step risks wasting expensive chemical activators and producing a sub-par final product, often making the energy cost a necessary investment.
The Risk of Over-Drying
While removing moisture is essential, excessive heat or duration can introduce new problems.
If the PET is subjected to temperatures too high for too long, the plastic may begin to soften or clump before impregnation.
This physical change can reduce the surface area available for chemical activation, negating the benefits of drying.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your PET-to-carbon production line, align your drying parameters with your specific quality targets.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Efficiency: Ensure the oven eliminates 100% of moisture to prevent phosphoric acid waste and ensure maximum activation potential.
- If your primary focus is Throughput Speed: Balance drying times against the risk of dilution; consider higher airflow ovens to accelerate evaporation without raising temperatures to dangerous levels.
Ultimately, the industrial drying oven transforms variable plastic waste into a standardized chemical feedstock, making high-quality carbonization possible.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Function of Drying Oven | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Impregnation | Complete dehydration of PET debris | Prevents dilution of phosphoric acid activators |
| Chemical Activation | Facilitates uniform acid absorption | Ensures consistent carbonization and pore structure |
| Thermal Management | Constant temperature control | Prevents premature degradation or clumping of plastic |
| Workflow Control | Standardization of feedstock | Removes moisture variables for predictable reaction cycles |
Maximize Your Carbonization Yield with KINTEK
Don’t let residual moisture compromise your chemical activation process. KINTEK provides high-precision Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous thermal demands of PET waste pretreatment and activated carbon production.
Backed by our expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer fully customizable laboratory and industrial high-temperature furnaces tailored to your unique stoichiometry and throughput needs. Ensure chemical consistency and prevent activator waste with our industry-leading heating solutions.
Ready to optimize your recycling process? Contact KINTEK today for a custom consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- Lai Thi Hoan, Duong Duc La. Sustainable Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Media by Activated Carbon Valorized from Polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) Plastic Waste. DOI: 10.3390/su17020548
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision furnace required for carbon aerogel activation? Achieve Optimal Pore Development & Control
- What is the significance of using different sizes of steel working ampoules? Precision vs. Efficiency in Lab Research
- What is the use of dental ceramic? Achieve Lifelike, Durable, and Biocompatible Restorations
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum drying oven in the post-treatment of Pd/BPC catalysts? Optimize Performance.
- What role does a PID controller play in the calcination process of eggshells? Precision Control for Pure Calcium Oxide
- What role does a high-performance thermostatic oven play in determining the moisture content of sugar beet by-products?
- What are the advantages of using magnetron sputtering equipment compared to MBE? Scalable 2D Transistor Solutions
- How does calcination temperature affect CuO grain growth? Optimize Nanoporous Film Morphology and Crystallinity















