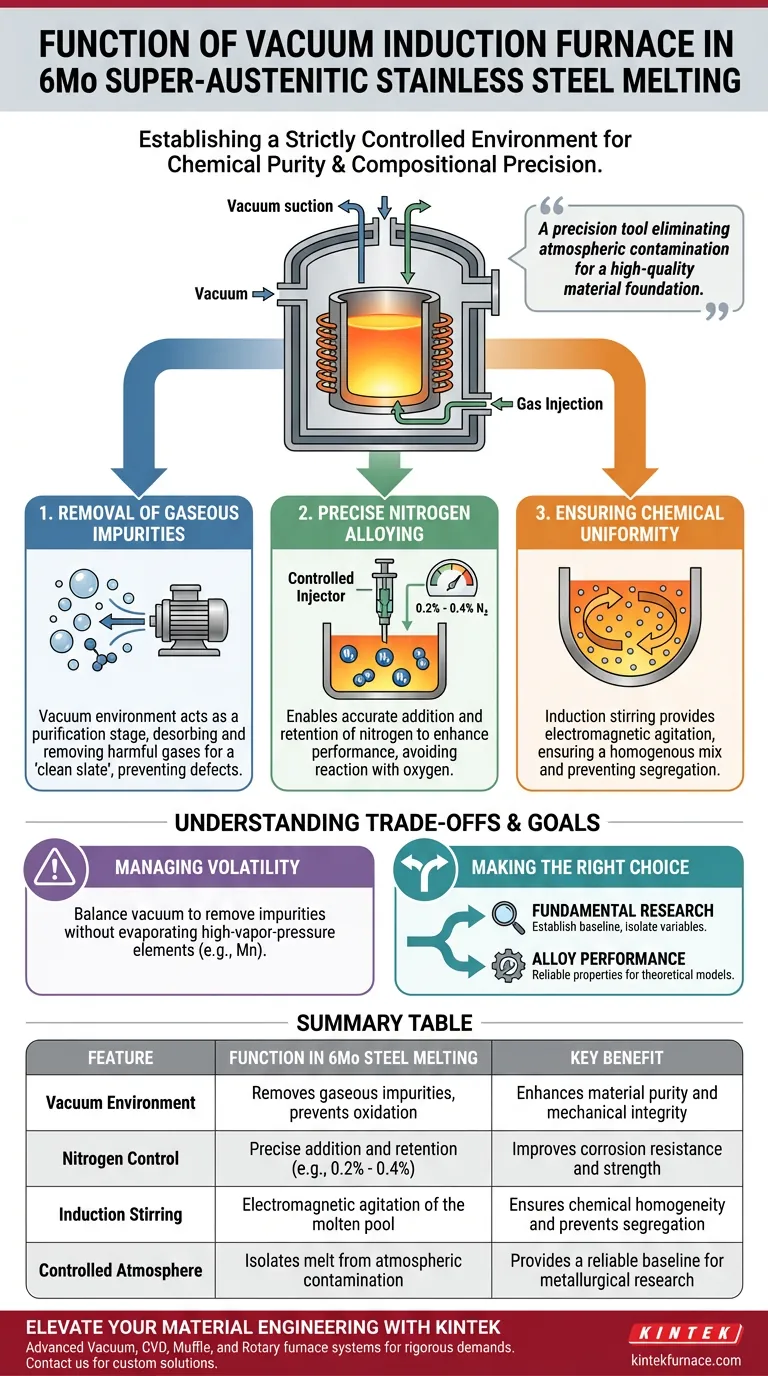
The primary function of a vacuum induction furnace in the melting of 6Mo super-austenitic stainless steel is to establish a strictly controlled environment that guarantees chemical purity and compositional precision. By isolating the melt from the atmosphere, the furnace effectively removes harmful gaseous impurities while simultaneously allowing for the accurate addition and retention of critical alloying elements like nitrogen.
The vacuum induction furnace acts as a precision tool that eliminates atmospheric contamination and ensures chemical uniformity, creating the high-quality material foundation necessary for reliable microstructural research and performance.
Establishing a High-Quality Material Foundation
The production of 6Mo super-austenitic stainless steel requires more than just high temperatures; it demands rigorous control over the alloy's chemistry. The vacuum induction furnace addresses this deep need through three specific mechanisms.
Removal of Gaseous Impurities
The furnace operates under a vacuum, which serves as a purification stage. This environment promotes the desorption and removal of unwanted gaseous impurities that are inherent in raw materials or that could be introduced during melting.
By stripping away these contaminants, the furnace establishes a "clean slate" for the alloy. This reduction in impurities is critical for preventing defects that could compromise the mechanical properties of the final steel.
Precise Nitrogen Alloying
Unlike standard melting processes where nitrogen might be considered an impurity to be removed, 6Mo steel often requires nitrogen as a deliberate alloying addition to enhance performance.
The vacuum induction furnace allows metallurgists to introduce nitrogen with extreme precision. The primary reference highlights the ability to control nitrogen additions at specific levels, such as 0.2% and 0.4%. The controlled environment ensures this nitrogen is retained within the molten matrix rather than reacting with oxygen or escaping uncontrolled.
Ensuring Chemical Uniformity
Achieving a homogenous mix of elements is vital for super-austenitic stainless steels, which contain high levels of molybdenum and other heavy alloying agents.
The furnace ensures chemical composition uniformity throughout the ingot. While the primary function is protection from the atmosphere, the induction mechanism inherently provides electromagnetic stirring. This keeps the molten pool agitated, ensuring that elements like nitrogen and molybdenum are evenly distributed, preventing segregation that would skew research results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum induction melting (VIM) is essential for high-purity alloys, it introduces specific operational constraints that must be managed.
Volatility of Alloying Elements
The same vacuum that removes unwanted gases can effectively lower the boiling point of desirable elements.
While the furnace is designed to prevent oxidative loss, operators must be vigilant regarding elements with high vapor pressures, such as manganese. The process requires balancing the vacuum level to remove impurities without inadvertently evaporating active alloying components before they bond with the steel matrix.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The utility of a vacuum induction furnace depends heavily on the specific requirements of your metallurgical project.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: The furnace is non-negotiable for establishing a baseline, as it allows for the isolation of specific variables (like 0.2% vs. 0.4% Nitrogen) without interference from impurities.
- If your primary focus is alloy performance: The equipment provides the necessary chemical homogeneity to ensure that mechanical properties tested in the lab translate reliably to theoretical models.
Use the vacuum induction furnace not just to melt metal, but to engineer its microstructure from the liquid state up.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in 6Mo Steel Melting | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Removes gaseous impurities and prevents oxidation | Enhances material purity and mechanical integrity |
| Nitrogen Control | Precise addition and retention (e.g., 0.2% - 0.4%) | Improves corrosion resistance and strength |
| Induction Stirring | Electromagnetic agitation of the molten pool | Ensures chemical homogeneity and prevents segregation |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Isolates melt from atmospheric contamination | Provides a reliable baseline for metallurgical research |
Elevate Your Material Engineering with KINTEK
Precision in the melting process is the foundation of high-performance alloys. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers advanced Vacuum, CVD, Muffle, and Rotary furnace systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of super-austenitic stainless steel production.
Whether you require exact nitrogen control for 6Mo steel or a customizable high-temperature solution for specialized research, our systems provide the chemical uniformity and atmospheric control you need.
Ready to refine your laboratory's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs and see how our expertise can drive your innovation.
Visual Guide
References
- Haiyu Tian, Peide Han. Effect of Nitrogen on the Corrosion Resistance of 6Mo Super Austenitic Stainless Steel. DOI: 10.3390/met14040391
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What additional features might advanced induction heater circuits incorporate? Enhance Precision, Efficiency, and Safety
- How does a vacuum environment help in metal purification? Achieve High Purity and Enhanced Properties
- What is the function of a Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace? Essential Precision for Steel Research
- What is a resonant tank circuit and how is it used in the described induction heater? Boost Efficiency with Energy Oscillation
- How does a vacuum induction furnace system physically enhance the deoxidation capability of carbon during steelmaking?
- What are the advantages of using a Vacuum Induction Melting furnace for Cr-Si alloys? Superior Uniformity & Purity
- What are the benefits of using induction furnaces for copper melting? Boost Quality, Efficiency & Safety
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace preferred for AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys? Achieve Peak Purity.



















