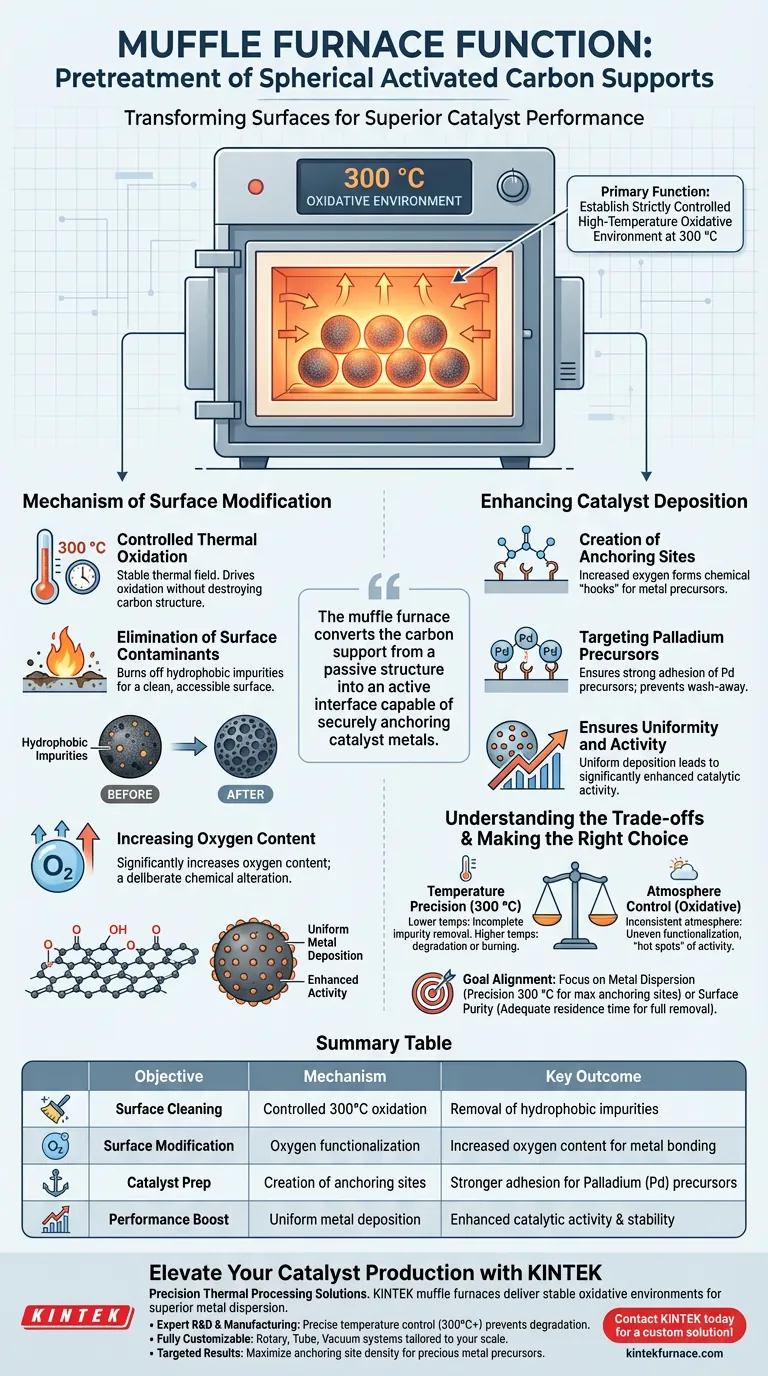
In the pretreatment of spherical activated carbon supports, the primary function of a muffle furnace is to establish a strictly controlled high-temperature oxidative environment. Specifically, by heating the supports to 300 °C, the furnace effectively strips away hydrophobic impurities and chemically modifies the surface to prepare it for metal loading.
The muffle furnace does more than simply clean the material; it fundamentally alters the surface chemistry of the carbon support, converting it from a passive structure into an active interface capable of securely anchoring catalyst metals.

The Mechanism of Surface Modification
Controlled Thermal Oxidation
The muffle furnace provides a stable thermal field at 300 °C. This specific temperature is critical because it is high enough to drive oxidation reactions but controlled enough to prevent the destruction of the carbon support itself.
Elimination of Surface Contaminants
Raw activated carbon supports often carry hydrophobic impurities on their surface. These impurities repel the solutions used in subsequent processing steps. The muffle furnace burns off these contaminants, ensuring the surface is clean and accessible.
Increasing Oxygen Content
The heat treatment significantly increases the oxygen content on the carbon surface. This chemical alteration is not a side effect but a deliberate goal of the pretreatment, changing how the carbon interacts with other chemicals.
Enhancing Catalyst Deposition
Creation of Anchoring Sites
The increased oxygen content results in the formation of specific anchoring sites. These sites act as chemical "hooks" that are essential for holding onto metal precursors during the catalyst manufacturing process.
Targeting Palladium Precursors
This pretreatment is particularly effective for preparing supports for palladium (Pd) catalysts. The anchoring sites created by the furnace ensure that palladium precursors adhere strongly to the support rather than washing away or agglomerating.
Ensuring Uniformity and Activity
By providing a clean surface with abundant anchoring sites, the muffle furnace ensures the uniform deposition of the metal. This even distribution directly translates to significantly enhanced catalytic activity in the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Precision is Vital
While the muffle furnace is effective, deviation from the optimal temperature (300 °C) can be detrimental. Lower temperatures may fail to fully remove hydrophobic impurities, while significantly higher temperatures could degrade the pore structure or burn off the carbon entirely.
Atmosphere Control
The process relies on an oxidative environment. If the furnace atmosphere is not consistent, the oxygen functionalization of the surface will be uneven, leading to "hot spots" of catalytic activity rather than the desired uniform distribution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your pretreatment process, align your furnace parameters with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Metal Dispersion: Prioritize the precise maintenance of the 300 °C setpoint to maximize the density of oxygen anchoring sites without damaging the support.
- If your primary focus is Surface Purity: Ensure adequate residence time in the furnace to fully mineralize and remove all hydrophobic organic impurities before introducing precursors.
The muffle furnace is the critical bridge between a raw carbon support and a high-performance catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Mechanism | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Cleaning | Controlled 300°C oxidation | Removal of hydrophobic impurities |
| Surface Modification | Oxygen functionalization | Increased oxygen content for metal bonding |
| Catalyst Prep | Creation of anchoring sites | Stronger adhesion for Palladium (Pd) precursors |
| Performance Boost | Uniform metal deposition | Enhanced catalytic activity & stability |
Elevate Your Catalyst Production with Precision Thermal Processing
Uniform surface modification is critical for high-performance activated carbon supports. KINTEK provides industry-leading muffle and specialized high-temperature furnace systems designed to deliver the stable oxidative environments required for superior metal dispersion.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our systems ensure the precise temperature control (300°C+) needed to prevent carbon degradation.
- Fully Customizable: Whether you require Rotary, Tube, or Vacuum systems, we tailor our solutions to your specific lab or production scale.
- Targeted Results: Backed by expertise in CVD and high-temp processing, we help you achieve maximum anchoring site density for your precious metal precursors.
Ready to optimize your pretreatment workflow? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Sarah L. Boyall, Thomas W. Chamberlain. Palladium nanoparticle deposition on spherical carbon supports for heterogeneous catalysis in continuous flow. DOI: 10.1039/d3cy01718d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What maintenance procedures are recommended for muffle furnaces? Ensure Accuracy and Safety in Your Lab
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles supported on Bamboo Biochar (Au-NPs/BC)?
- What are common high-temperature applications of muffle furnaces in laboratories? Unlock Precision in Material Testing and Synthesis
- What are the key disadvantages of a muffle furnace? Slow cycles, high energy use, and maintenance challenges
- What is the role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in solid-state synthesis? Master CaMnO3 Perovskite Production
- Which industries commonly use muffle furnaces? Essential for Clean High-Temp Processing
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it relate to laboratory furnaces? Discover Its Key Benefits for Your Lab
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.



















