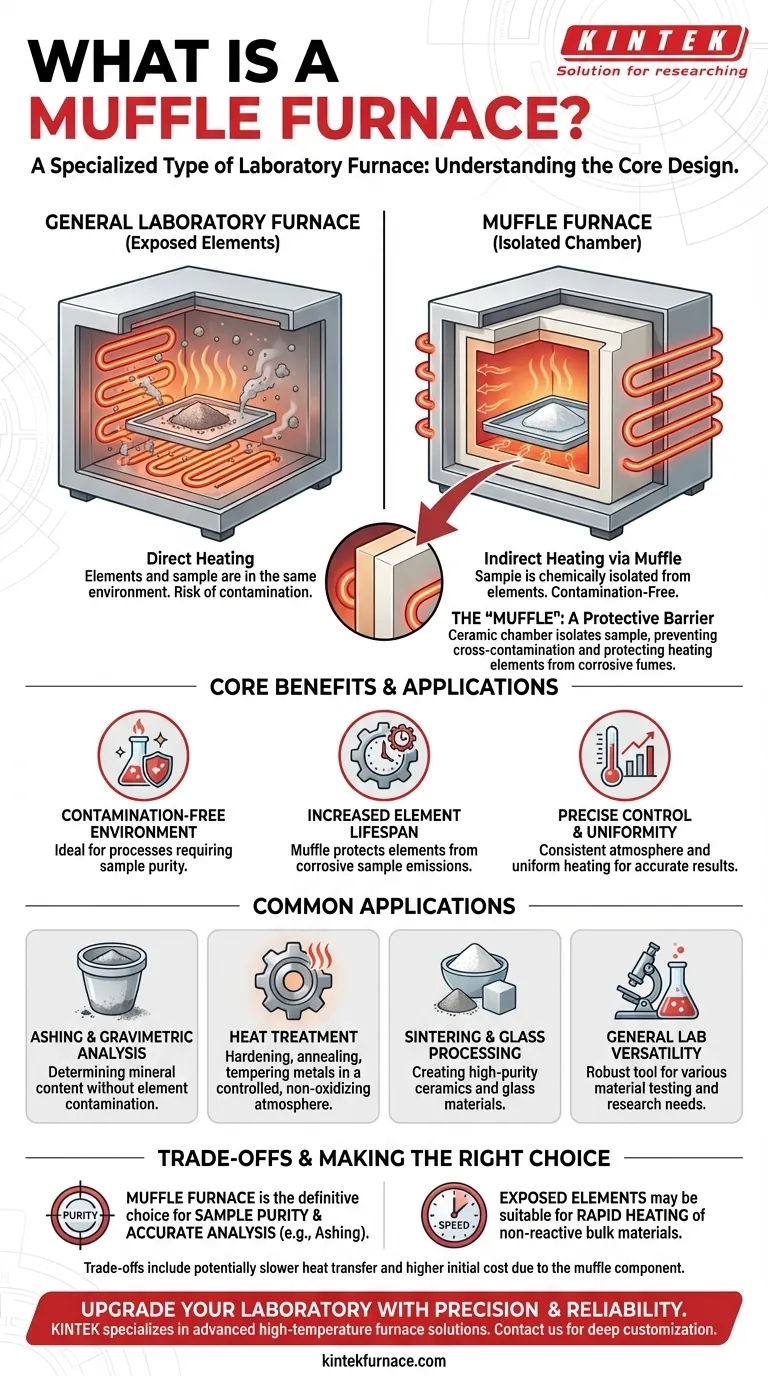
In short, a muffle furnace is a specific type of laboratory furnace. While "laboratory furnace" is a general term for any high-temperature heating device used in a lab, a muffle furnace is distinguished by its core design: an internal chamber (the "muffle") that isolates the material being heated from the actual heating elements. This separation is the key to its function and primary applications.
A muffle furnace's defining characteristic is its use of a "muffle" — a protective barrier that prevents contamination between the heating elements and the sample. This design makes it the standard choice for processes where sample purity and a controlled atmosphere are non-negotiable.

The Defining Principle: The 'Muffle' Itself
The term "muffle" is what separates this furnace from other designs. Understanding this single component explains nearly all of its benefits and applications.
What is a Muffle?
A muffle is essentially a high-temperature, enclosed chamber, often made of ceramic, that sits inside the furnace. The heating elements wrap around the outside of this muffle.
This means that the sample placed inside the furnace is never in direct contact with the electric heating elements. Heat radiates through the muffle walls to uniformly heat the sample within.
The Core Benefit: A Contamination-Free Environment
The primary advantage of this design is the creation of a chemically isolated heating environment.
As materials are heated to high temperatures, they can release vapors and fumes. Likewise, heating elements themselves can degrade and release microscopic particles. The muffle acts as a physical barrier, preventing cross-contamination.
The Consequence: Increased Element Lifespan
This isolation is a two-way street. Just as the sample is protected from the elements, the heating elements are protected from any corrosive fumes emitted by the sample.
This significantly increases the operational lifespan of the heating elements, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Common Applications Driven by the Muffle Design
The contamination-free, high-temperature environment makes a muffle furnace indispensable for specific, sensitive procedures in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing involves burning off organic substances to determine the non-combustible mineral content of a sample.
Because the final weight of the ash is the critical measurement, any contamination from the furnace's heating elements would invalidate the results. The muffle furnace ensures that only the sample's true ash content remains.
Heat Treatment of Materials
Processes like hardening, annealing, and tempering metals require precise temperature control and a consistent atmosphere to achieve the desired material properties.
The muffle provides a uniform heating chamber and prevents unwanted chemical reactions (like oxidation) on the material's surface, which could occur with direct heating.
Sintering and Glass Processing
Creating ceramics or melting glass requires high temperatures without introducing impurities. The isolated chamber of a muffle furnace is ideal for sintering ceramic powders or creating high-purity glass products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the muffle design has inherent characteristics that create trade-offs compared to furnaces with exposed heating elements.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
Because heat must be transferred through the muffle's walls, the process is one of indirect heating.
While modern muffle furnaces are engineered to be highly efficient and heat up quickly, a furnace with direct, exposed elements may sometimes reach its target temperature faster.
Maintenance and Cost
The muffle itself is a specialized component made of durable, high-temperature materials. It adds a layer of complexity to the furnace's construction.
This can sometimes translate to a higher initial purchase price and, in the event of damage to the muffle, a more involved repair compared to simply replacing an exposed heating element.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the sensitivity and requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and accurate analysis: The muffle furnace is the definitive and often only choice, especially for ashing or trace element work.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating non-reactive bulk materials: A simpler furnace with exposed elements might be a more cost-effective and slightly faster alternative.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab versatility: A muffle furnace is a robust workhorse, providing the control and cleanliness needed for a wide range of material testing and heat-treatment applications.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is an investment in process control and analytical integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Design | Internal chamber (muffle) isolates samples from heating elements to prevent contamination. |
| Key Benefit | Provides a contamination-free environment, protecting sample purity and extending element lifespan. |
| Common Applications | Ashing, gravimetric analysis, heat treatment (e.g., hardening), sintering, and glass processing. |
| Trade-offs | Slightly slower heat transfer and potentially higher initial cost compared to exposed-element furnaces. |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision and reliability! KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring contamination-free heating and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















