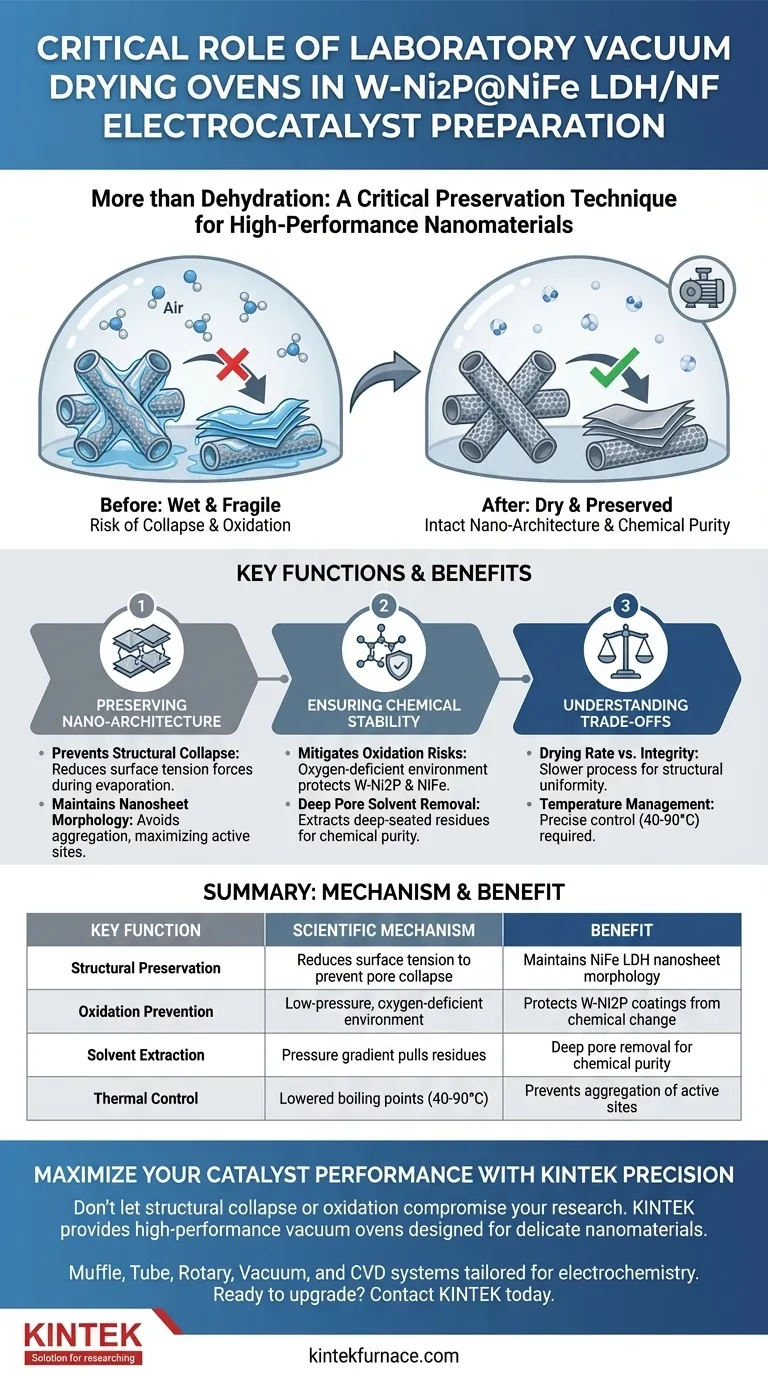
The primary function of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in the preparation of W-Ni2P@NiFe LDH/NF electrocatalysts is to remove solvent residues after the cleaning phase without damaging the material's delicate structure. By creating a low-pressure environment, the oven lowers the boiling point of solvents, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures. This process is essential for preventing the oxidation and structural collapse that typically occur when these specific nanomaterials are exposed to high heat under atmospheric pressure.
Core Insight: Vacuum drying is not merely a dehydration step; it is a critical preservation technique. Its low-pressure, low-temperature mechanism ensures the W-Ni2P coatings and NiFe LDH nanosheets retain their microscopic morphology and chemical stability, which are directly responsible for the catalyst's final electrochemical performance.

Preserving Nano-Architecture
The preparation of W-Ni2P@NiFe LDH/NF involves intricate nano-architectures that are highly sensitive to processing conditions. The vacuum drying oven addresses two main physical risks.
Preventing Structural Collapse
Under standard atmospheric drying, the surface tension of evaporating solvents can exert significant force on pore structures. This often leads to the collapse of fragile hollow structures or nanosheets. The vacuum environment facilitates evaporation with reduced surface tension forces, keeping the 3D structure intact.
Maintaining Nanosheet Morphology
The specific NiFe LDH nanosheets rely on a high surface area to function effectively as electrocatalysts. Vacuum drying prevents these sheets from aggregating or densifying. This ensures the material remains porous, maximizing the exposure of active sites.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
Beyond physical structure, the chemical composition of the catalyst must remain unaltered during the drying phase.
Mitigating Oxidation Risks
W-Ni2P coatings and NiFe components are susceptible to oxidation, particularly if exposed to oxygen at the high temperatures required for standard oven drying. The vacuum oven removes air from the chamber, creating an oxygen-deficient environment. This allows for thorough drying without chemically altering the metallic or phosphide components.
Deep Pore Solvent Removal
Solvents trapped deep within the internal pores of the catalyst can lead to side reactions or electrolyte decomposition later in the application. The pressure gradient in a vacuum oven effectively extracts these deep-seated residues. This ensures the final powder is chemically pure and ready for accurate electrochemical evaluation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum drying is superior for quality, it introduces specific operational constraints that must be managed.
Drying Rate vs. Integrity
Vacuum drying generally has a lower drying rate compared to rapid convective drying methods. While it mitigates deep penetration of binders and salts, the process is slower. You trade processing speed for the assurance of structural uniformity and an "eggshell" distribution that is not too deep nor too shallow.
Temperature Management
Although the vacuum allows for lower temperatures (often between 40°C and 90°C), precise control is still required. If the temperature is set too low, solvent removal may be incomplete; if set too high, even in a vacuum, thermal stress could affect the binder or surface functional groups.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of a vacuum drying oven is a strategic choice dependent on the sensitivity of your material and your performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize vacuum drying to prevent the collapse of hollow tubes and nanosheets, ensuring maximum surface area.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Use vacuum drying to eliminate oxidation risks and ensure deep solvent extraction from internal pores.
Ultimately, for high-performance W-Ni2P@NiFe LDH/NF electrocatalysts, vacuum drying is not optional but a requisite step to translate synthesis chemistry into functional stability.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Benefit for Electrocatalyst | Scientific Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Preservation | Maintains NiFe LDH nanosheet morphology | Reduces surface tension to prevent pore collapse |
| Oxidation Prevention | Protects W-Ni2P coatings from chemical change | Low-pressure, oxygen-deficient environment |
| Solvent Extraction | Deep pore removal for chemical purity | Pressure gradient pulls residues from internal structures |
| Thermal Control | Prevents aggregation of active sites | Lowered boiling points allow drying at 40°C-90°C |
Maximize Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK Precision
Don't let structural collapse or oxidation compromise your research. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory vacuum ovens designed to protect delicate nanomaterials like W-Ni2P and NiFe LDH nanosheets.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the most demanding electrochemistry applications. Whether you are scaling up synthesis or refining catalyst purity, our customizable high-temp furnaces ensure the structural integrity your project requires.
Ready to upgrade your lab's drying capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yu Gao, Xiaoteng Liu. In situ growth of three-dimensional walnut-like nanostructures of W-Ni2P@NiFe LDH/NF as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for water decomposition. DOI: 10.1007/s42114-024-01176-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of vacuum brazing? Understanding the trade-offs for your application
- What temperature range can most vacuum furnace systems operate within? Discover the Capabilities for Your Process
- What processes are performed in a high-temperature vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in Material Processing
- What are some common types of vacuum furnaces? Explore Their Uses and Benefits
- How does a rapid heating system affect Mg-Ti6Al4V composites? Unlock Superior Microstructure and Strength
- How does a pulsed DC power source in an ion nitriding furnace influence quality? Boost Efficiency & Precision Control
- What role does a high-vacuum heat treatment furnace play in the preparation of a GdEuZrO/YSZ double-layer coating system?
- How are vacuum sintering furnaces categorized based on temperature ranges? Find the Right Furnace for Your Materials



















