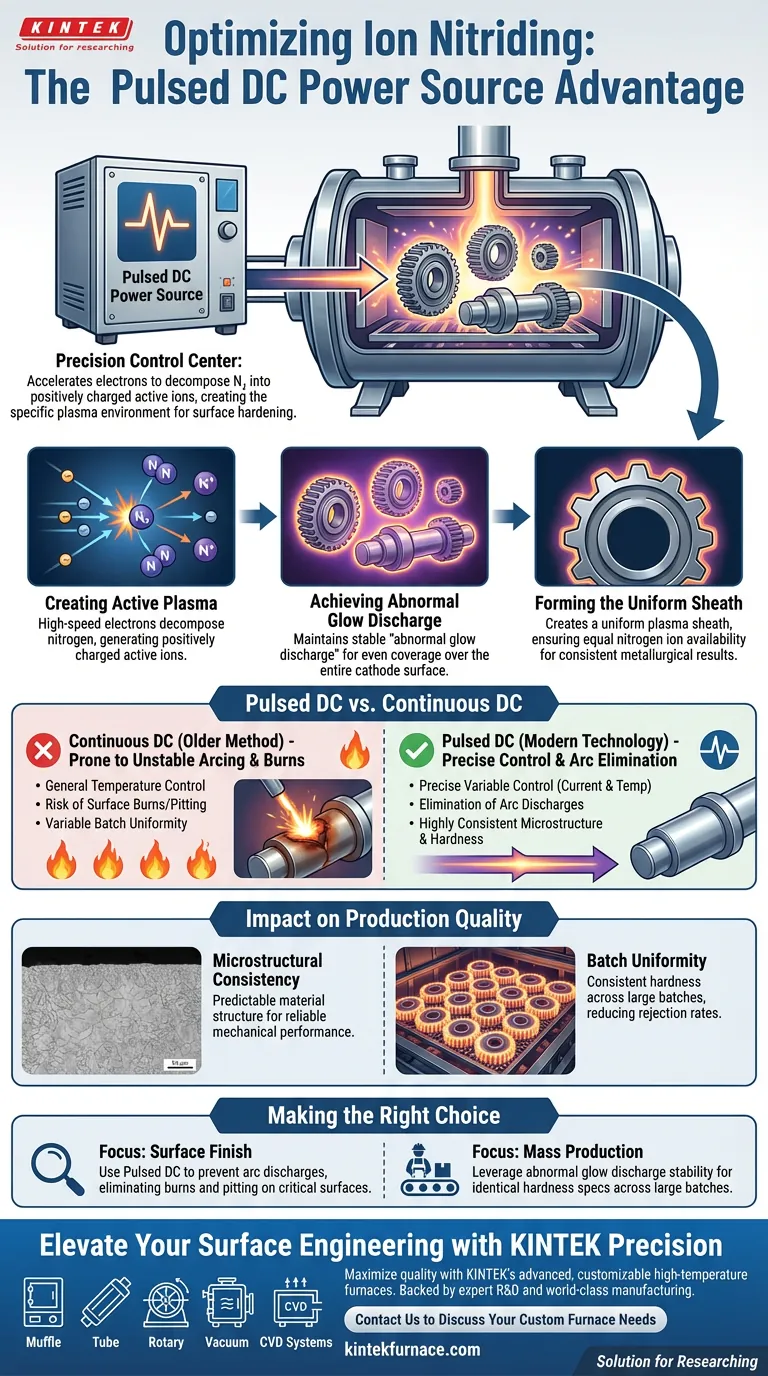
The pulsed DC power source acts as the precision control center for modern ion nitriding, fundamentally improving process stability and part quality. By accelerating electrons to decompose nitrogen gas into positively charged active ions, it creates the specific plasma environment necessary for surface hardening. Unlike continuous DC sources, pulsed power allows for distinct modulation of current density and temperature, resulting in a defect-free surface and uniform material properties.
The core value of a pulsed DC source lies in its ability to maintain a stable "abnormal glow discharge." This stability prevents destructive electrical arcs and ensures that every part in a batch receives a uniform plasma sheath, guaranteeing consistent hardness and microstructure.
How the Mechanism Works
Creating the Active Plasma
The process begins when the pulsed DC source accelerates electrons within the furnace.
These high-speed electrons collide with nitrogen gas, decomposing it. This reaction generates the positively charged active ions required to diffuse nitrogen into the surface of the workpiece.
Achieving "Abnormal Glow Discharge"
For effective nitriding, the plasma must exist in a specific state.
The pulsed power source maintains a stable condition known as "abnormal glow discharge." This state is critical because it ensures the discharge covers the entire surface area of the cathode (the workpiece) evenly.
Forming the Uniform Sheath
The stability provided by the pulsed source creates a uniform plasma sheath that wraps around the workpiece.
This sheath ensures that nitrogen ions are available equally at all points on the part's geometry. This uniformity is the foundation for consistent metallurgical results.
Advantages Over Continuous DC
Precise Variable Control
Pulsed DC technology offers significantly higher precision than older continuous DC methods.
Operators can exert fine control over current density. This direct regulation allows for tighter management of the overall process temperature, preventing overheating or under-heating specific zones.
Elimination of Arc Discharges
One of the most significant risks in ion nitriding is the formation of electrical arcs.
Arcs can cause immediate and irreparable surface burns on the workpiece. The pulsed nature of the power source detects and suppresses the conditions that lead to arcing, protecting high-value parts from damage.
The Impact on Production Quality
Microstructural Consistency
Because the plasma sheath is uniform and the temperature is controlled, the resulting material structure is predictable.
The process ensures a highly consistent microstructure within the nitrided layer. This translates to predictable mechanical performance of the finished part.
Batch Uniformity
Consistency extends beyond a single part to the entire production load.
The pulsed DC source ensures that hardness is uniform across large batches of parts. This reduces rejection rates and ensures that every part in the furnace meets the same quality specifications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
While pulsed DC is generally superior, understanding its specific strengths helps in application planning.
- If your primary focus is Surface Finish: Rely on pulsed DC to prevent arc discharges, which eliminates the risk of surface burns and pitting on critical sealing surfaces or polished parts.
- If your primary focus is Mass Production: Leverage the stability of the abnormal glow discharge to ensure that hardness specs are met identically across large batches, reducing quality control overhead.
Ultimately, the pulsed DC source transforms ion nitriding from a brute-force heat treatment into a precision engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Continuous DC Source | Pulsed DC Power Source |
|---|---|---|
| Discharge Stability | Prone to unstable arcing | Stable abnormal glow discharge |
| Temperature Control | General/Broad | High precision via current density modulation |
| Surface Quality | Risk of burns/pitting from arcs | Defect-free, smooth surface finish |
| Batch Uniformity | Variable results | Highly consistent microstructure & hardness |
| Process Safety | Higher risk of part damage | Built-in arc suppression & protection |
Elevate Your Surface Engineering with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the quality and consistency of your heat treatment with KINTEK’s advanced solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical requirements. Whether you are aiming for defect-free surface finishes or uniform batch hardening, our high-temperature systems provide the stability and control your research or production demands.
Ready to optimize your lab's efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- André Paulo Tschiptschin. PROCESSOS SOB VÁCUO USADOS PARA TRATAMENTOS TÉRMICOS E DE SUPERFÍCIE DE AÇOS E LIGAS ESPECIAIS. DOI: 10.17563/rbav.v43i1.1262
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Precision Solution Treatment for 17-4PH Steel
- What are the key components of a vacuum sintering furnace? Essential Parts for Precision Material Processing
- What are the environmental advantages of vacuum-environment furnaces for coking? Learn how to eliminate leakage.
- Why is a laboratory high-temperature furnace required for superalloys? Expert Super-Solvus Heat Treatment Guide
- What are the key features of vacuum performance customization? Achieve Precise Control for Your Lab Processes
- What role do laboratory arc furnaces and tungsten electrodes play in TiCo1-xCrxSb synthesis? Expert Material Analysis
- Why is precise heating slope control in a vacuum heat treatment furnace critical for niobium oxide experiments?
- What are the steps involved in the vacuum furnace process? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Cleaner, Stronger Parts



















