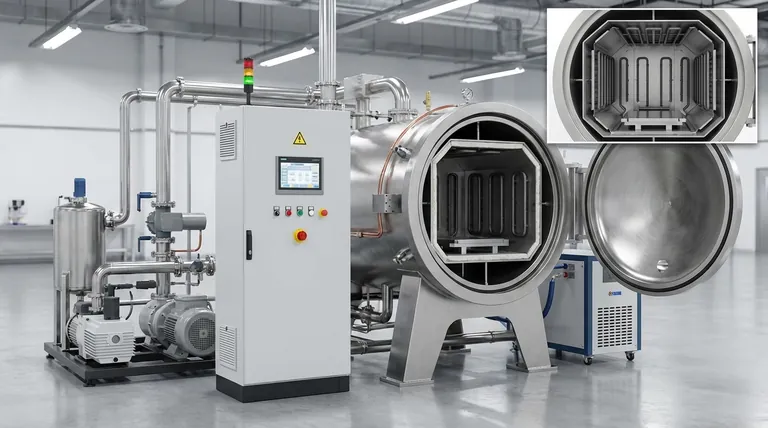
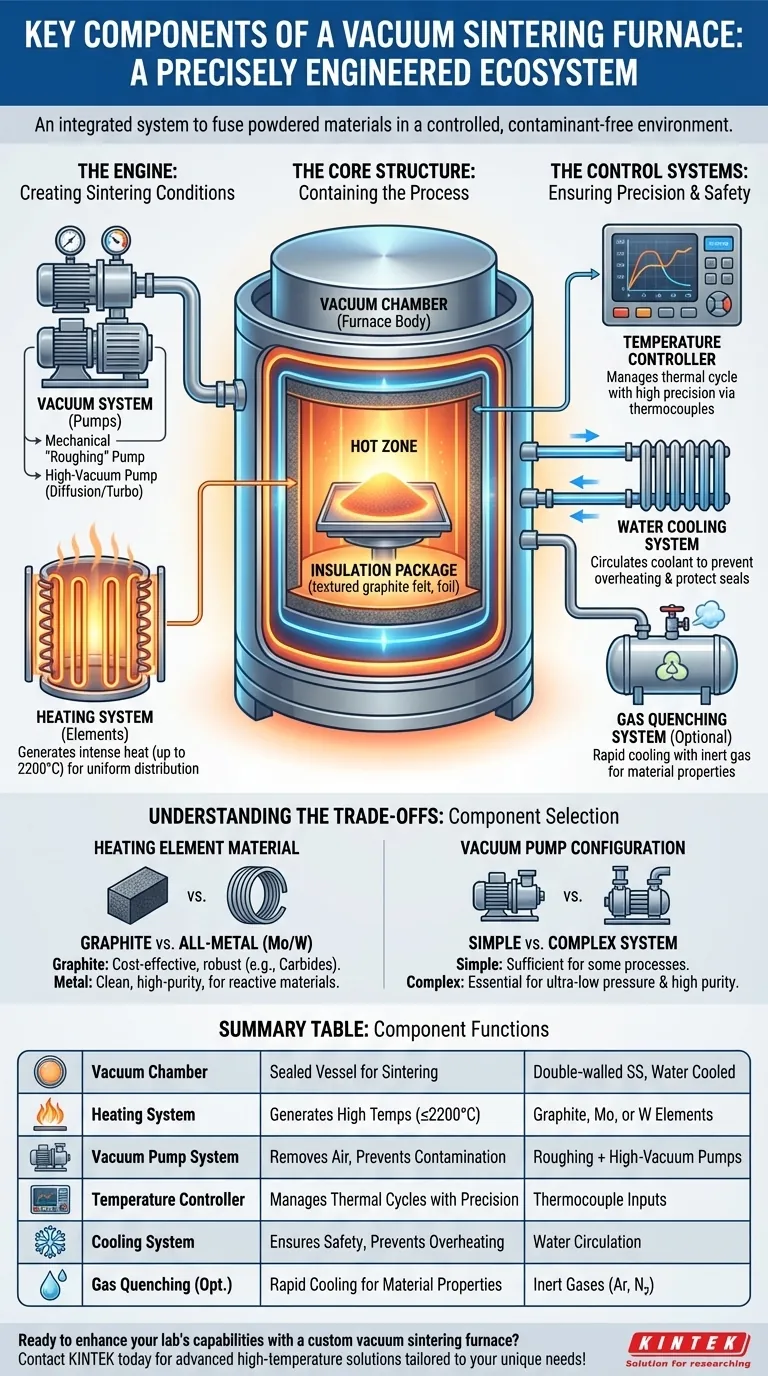
At its core, a vacuum sintering furnace is an integrated system designed for one purpose: to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass under tightly controlled conditions. The key components that make this possible are the vacuum chamber, heating system, vacuum pump system, temperature controller, and a robust cooling system. These elements work in concert to create an environment free of atmospheric contaminants and capable of reaching extreme temperatures.
A vacuum furnace is not merely a collection of parts, but a precisely engineered ecosystem. Understanding how each component contributes to controlling the internal atmosphere, temperature, and pressure is the key to mastering the sintering process and achieving desired material properties.

The Core Structure: Containing the Process
The physical body of the furnace provides the sealed environment necessary for the entire operation. It must withstand immense thermal and pressure differentials.
The Vacuum Chamber (Furnace Body)
This is the sealed vessel where the sintering takes place. It is typically a double-walled, cylindrical structure made from high-strength stainless steel.
The double-wall design creates a water jacket, allowing coolant to circulate and prevent the outer shell from overheating, which is critical for safety and maintaining the vacuum seals.
The Insulation Package
Lining the inside of the chamber, the insulation package is essential for thermal efficiency. It minimizes heat loss and helps ensure temperature uniformity within the "hot zone."
Common insulation materials include multi-layer graphite felt, flexible graphite paper, and sometimes ceramic fiber or metallic foils (like molybdenum) for specific applications.
The Engine: Creating the Sintering Conditions
These systems actively create the extreme temperature and vacuum required to transform powdered metal or ceramic into a dense, solid part.
The Heating System
This system is responsible for generating the intense heat needed for sintering, with some furnaces capable of reaching over 2200°C (3992°F).
Heating elements are strategically placed within the hot zone for uniform heat distribution. They are typically made from materials like graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten, chosen based on the required temperature and chemical compatibility with the material being processed.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum system removes air and other gases from the chamber, creating a contamination-free environment. This prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions that would compromise the material's final properties.
This system usually consists of a combination of pumps, such as a mechanical "roughing" pump to remove the bulk of the air and a high-vacuum pump (like a diffusion or turbomolecular pump) to achieve the required low pressure.
The Control Systems: Ensuring Precision and Safety
Control systems are the brain of the furnace, orchestrating the complex interplay of temperature, pressure, and time to ensure a repeatable and successful process.
The Temperature Controller
This system manages the entire thermal cycle with high precision. It controls the heating rate, the "soak" time at peak temperature, and the cooling rate.
Using inputs from thermocouples placed inside the furnace, the controller adjusts power to the heating elements, ensuring the process profile specified by the operator is followed exactly.
The Water Cooling System
This is a critical safety and operational component. It circulates water through the furnace's double-walled shell, the door, and power feed-throughs to keep them at a safe operating temperature.
A reliable cooling system is non-negotiable; failure can lead to damaged vacuum seals, burnt-out electrodes, and catastrophic failure of the furnace body.
The Gas Quenching System (Optional)
For applications requiring rapid cooling, a gas quenching system is included. It quickly floods the chamber with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
This rapid cooling can be used to "lock in" a specific metallurgical phase or grain structure, giving the operator additional control over the final material hardness and strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Component Selection and Impact
The choice of components is not arbitrary; it dictates the furnace's capabilities, cost, and the types of materials it can process. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial.
Heating Element Material: Graphite vs. Metal
Choosing between graphite and all-metal (molybdenum or tungsten) hot zones is a primary decision. Graphite is more cost-effective and robust for many applications, like sintering tungsten carbides.
However, graphite can introduce carbon into the atmosphere, which is unacceptable for certain reactive or high-purity materials. In these cases, a more expensive all-metal hot zone is required to ensure a clean, carbon-free environment.
Vacuum Pump Configuration
The type and combination of vacuum pumps determine the ultimate vacuum level and the time it takes to reach it. A simple mechanical pump might be sufficient for some processes.
For high-purity or reactive materials, a more complex system with diffusion or turbo pumps is necessary to achieve the very low pressures needed to remove trace amounts of oxygen and moisture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal furnace configuration depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, reactive materials (e.g., medical alloys, titanium): You require an all-metal hot zone (molybdenum/tungsten) and a high-performance vacuum system to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production (e.g., cemented carbides): A graphite-based heating system is typically the most durable and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is controlling material hardness and microstructure: A furnace equipped with a fast gas quenching system is essential for achieving the desired metallurgical properties.
Ultimately, each component is a critical link in a chain that determines the success and repeatability of your sintering process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials/Features |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed vessel for sintering | Double-walled stainless steel with water cooling |
| Heating System | Generates high temperatures (up to 2200°C) | Graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten elements |
| Vacuum Pump System | Removes air for contamination-free environment | Mechanical roughing pump, high-vacuum pump |
| Temperature Controller | Manages thermal cycles with precision | Uses thermocouples for accurate control |
| Cooling System | Ensures safety and prevents overheating | Water cooling for chamber and components |
| Gas Quenching (Optional) | Rapid cooling for material properties | Inert gases like argon or nitrogen |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a custom vacuum sintering furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your sintering processes and deliver superior results for materials like medical alloys, titanium, and cemented carbides!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement



















